Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disorder affecting millions of Americans with societal costs estimated in the billions. With the expansion in the number of biologic drugs available, the cost of care has continued to increase. Socioeconomic factors have been shown to affect the likelihood of immunosuppressive therapy prescribed in RA. The purpose of this study was to examine the association between medication prescribed and socioeconomic factors including gender, race, and median household income.
Methods: This was a retrospective, single center, hospital-affiliated outpatient cohort study. A systematic review of the electronic medical record yielded over 4000 patient’s records. These records were reviewed and of these, 116 patients who met the ACR/EULAR (2010) classification criteria for RA were randomly selected. General demographic information including age, gender and zip code, as well as serological testing was obtained through chart review. Supplemental socioeconomic information for each zip code in Southwest Virginia was obtained from the United States Government Census website. The data was analyzed by Kruskal-Wallis Test, Mann-Whitney U Test using SAS9.3.
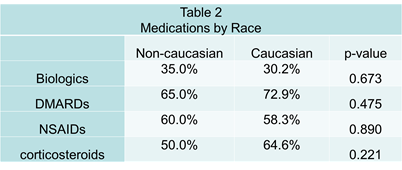
Results: Table 1 outlines the frequency of medication prescribed in the cohort. Among the 116 patients, there was no relationship between socioeconomic factors and medication prescribed. There was no statistical relationship between gender and medication prescribed including NSAIDs (p=0.153), corticosteroids (p=0.172), DMARDs (p=0.26) and biological drugs (p=0.350).There was no statistical relationship between race and medications including NSAIDs (p=0.890), corticosteroids (p=0.221), DMARDs (p=0.475) and biological drugs (p=0.673). There was no statistical relationship between median household income and medication prescribed including NSAIDs (p=0.071), corticosteroids (p=0.296), DMARDs (p=0.228) and biological drugs (p=0.046)
Conclusion: There was no relationship between socioeconomic factors and the medications prescribed in our RA cohort. This may be the result of standardization of RA treatment, and the adoption of “treat to target” ethos in RA. The limitations of this study include the small sample size and its restriction to a single center.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bankole A. The Relationship Between Socioeconomic Factors and Dmards Use in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-relationship-between-socioeconomic-factors-and-dmards-use-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-relationship-between-socioeconomic-factors-and-dmards-use-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/