Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Fatigue is a substantial problem in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) that needs to be considered in the core set of domains. This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between fatigue and disease activity levels as determined by various scales in patients with PsA.
Methods: A total of 1134 patients (726 females, 408 males) diagnosed with PsA according to the CASPAR criteria were included (Turkish League Against Rheumatism (TLAR) Network multi-center study). Demographic features and clinical conditions of the patients were recorded. The following parameters were assessed: Maastricht Ankylosing Spondylitis Enthesis Score (MASES), Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI), VAS fatigue (0-10 points: 0 – < 2 absent or mild, 2 – < 5 moderate, and 5 – 10 severe fatigue), Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HAD), Fibromyalgia Rapid Screening Tool (FIRST). Disease activity was evaluated using the scores of DAS28, DAPSA, BASDAI, minimal disease activity (MDA), and very low disease activity (VLDA). The Spearman correlation coefficient was used for correlations. The Mann-Whitney U and chi-squared tests were used for between-group comparisons. A P value of less than 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
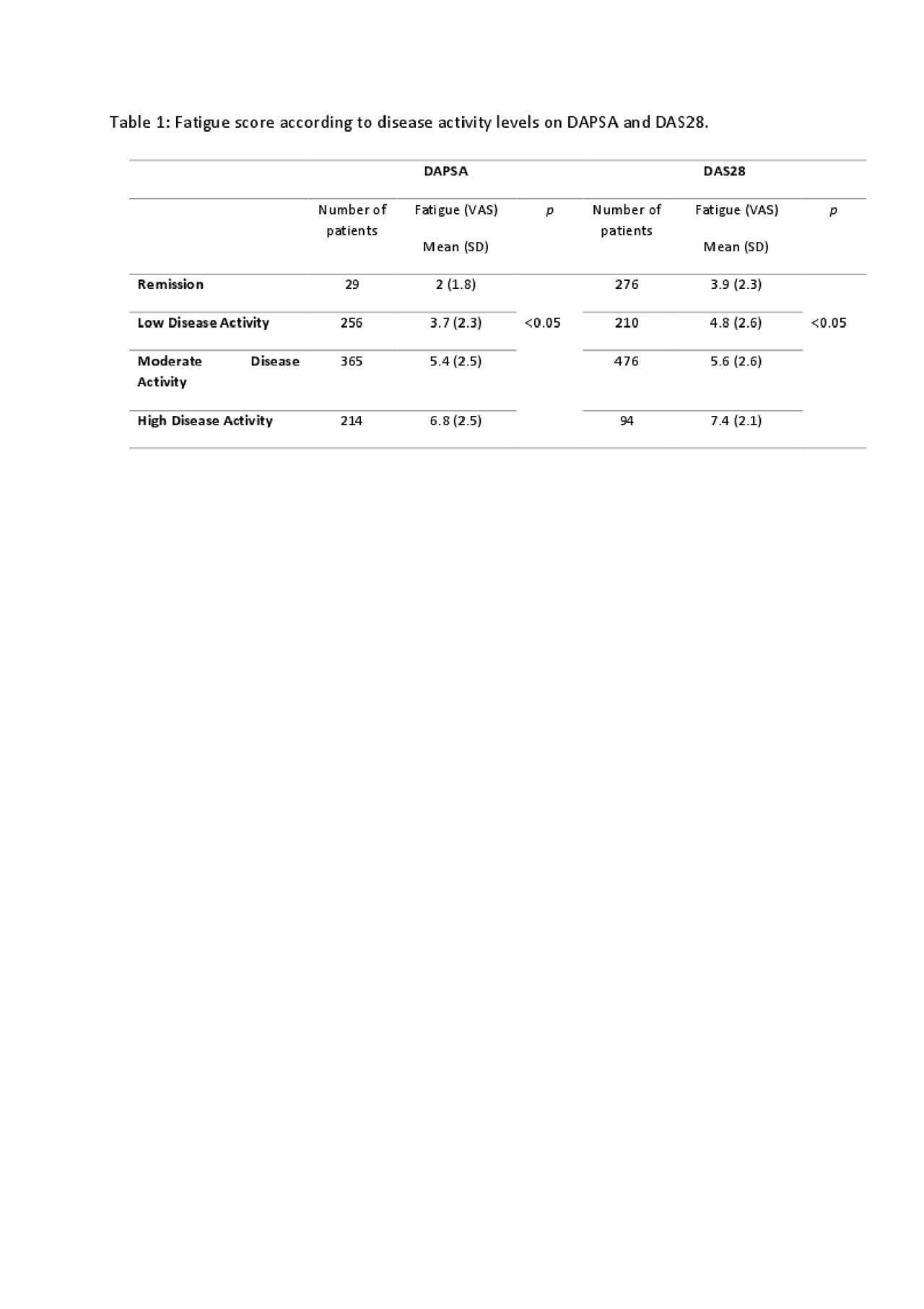
Results: The mean age of the patients was 46.9 (SD:12.1) years, and the median disease duration was four years (range 0-44 years). The mean fatigue score was 4.9 (SD:2.8), being absent or mild, moderate, and severe fatigue in 14.8%, 24.9%, and 60% of the patients, respectively. The mean of women’s fatigue VAS was 5.4 (SD:2.7) while the men’s fatigue VAS mean was 4.01 (SD:2.7) (p< 0.05). Fatigue has good correlation with VAS-pain (rho: 0.595), FIRST (rho: 0.513), anxiety (rho: 0.436), depression (rho: 0.388), MASES (rho: 0.297) and it has poor correlation with PASI (rho: 0.073). DAS28 and DAPSA remission, MDA, and VLDA rates were 24.3%, 2.6%, 13.6%, and 2.3%, respectively. The fatigue score was significantly lower in patients with DAS28 remission, DAPSA remission, MDA and VLDA (p< 0.05) and fatigue has a significant correlation with disease activity levels on DAS28 and DAPSA (p< 0.05) (Table 1). The DAS28, DAPSA, and BASDAI scores showed significant between-group differences across the three severity groups of fatigue, being the highest disease activity among patients with severe fatigue (p< 0.05). Significantly higher FIRST, anxiety and depression scores were noted in patients with DAS28 remission and fatigue compared with patients in remission but no fatigue (p< 0.05).
Conclusion: Fatigue is common and associated with disease activity, depression, anxiety, and fibromyalgia in PsA. Patients with remission, according to DAS28, DAPSA, and patients with MDA and VLDA have already mild to moderate fatigue.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Duruoz M, Gezer H, Nas K, Kilic E, Sargin B, Acer Kasman S, Alkan H, Sahin N, Cengiz G, Cuzdan N, Albayrak Gezer I, Keskin D, Mulkoglu C, Resorlu H, Ataman �, Bal A, Kucukakkas O, Yurdakul O, Alkan Melikoglu M, Aydin Y, Ayhan F, Bodur H, Calis M, Capkin E, Devrimsel G, Gök K, Hizmetli S, Kamanli A, Keskin Y, Kocabas H, Kutluk O, Sen N, Sendur O, Tekeoglu I, Tolu S, Toprak M, Tuncer T. The Relationship Between Fatigue and Disease Activity as Determined by Different Indices in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-relationship-between-fatigue-and-disease-activity-as-determined-by-different-indices-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-psa/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-relationship-between-fatigue-and-disease-activity-as-determined-by-different-indices-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-psa/