Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: B Cell Biology & Targets In Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease Poster
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a severe systemic disease characterized by fibrosis of the skin and visceral organs. While protein biomarkers of lung damage, e.g. krebs von den lungen-6 and surfactant protein D (SPD) have been reported in SSc-ILD, no immunologic predictors of SSc-ILD have been reported. CD21lo B lymphocytes have been implicated as autoimmune-prone cells. We evaluated the relationship of these cells to clinical phenotype in patients with SSc.
Methods: Cryopreserved peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were stored as part of the MYSTIC cohort (VUMC IRB 141415). Detailed clinical phenotyping, including extent of cutaneous involvement and serologic status, was performed at the time of patient enrollment. All patients met the 2013 ACR classification criteria for SSc. The presence of interstitial lung disease was defined as FVC< 79% predicted, isolated DLCO< 79% predicted in the absence of pulmonary hypertension, or radiographic fibrosis on CT scan. PBMCs were thawed and subjected to mass cytometry to investigate B cell phenotypes in patients with SSc (n=40) versus healthy controls (n=21). Data was analyzed with biaxial gating and correlated to clinical phenotypes. Statistical significance was determined using Mann-Whitney U-tests.
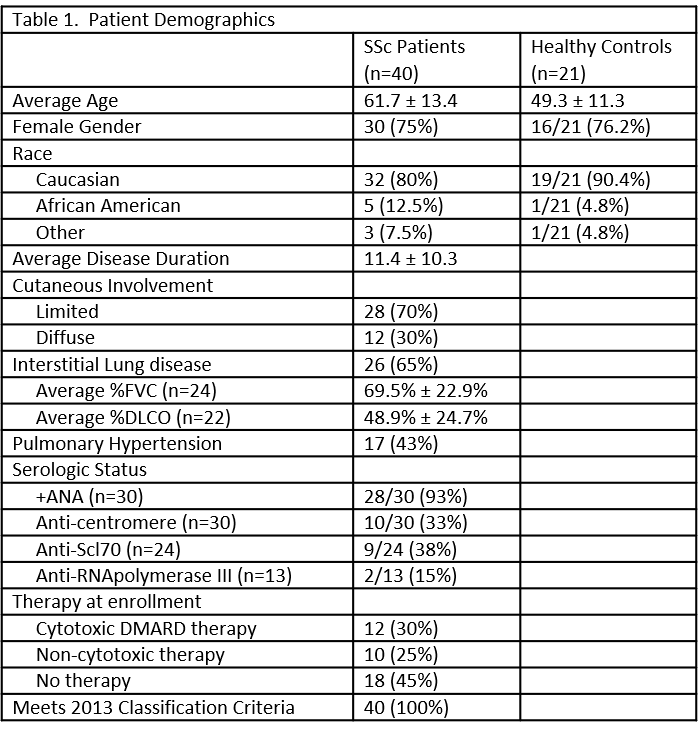
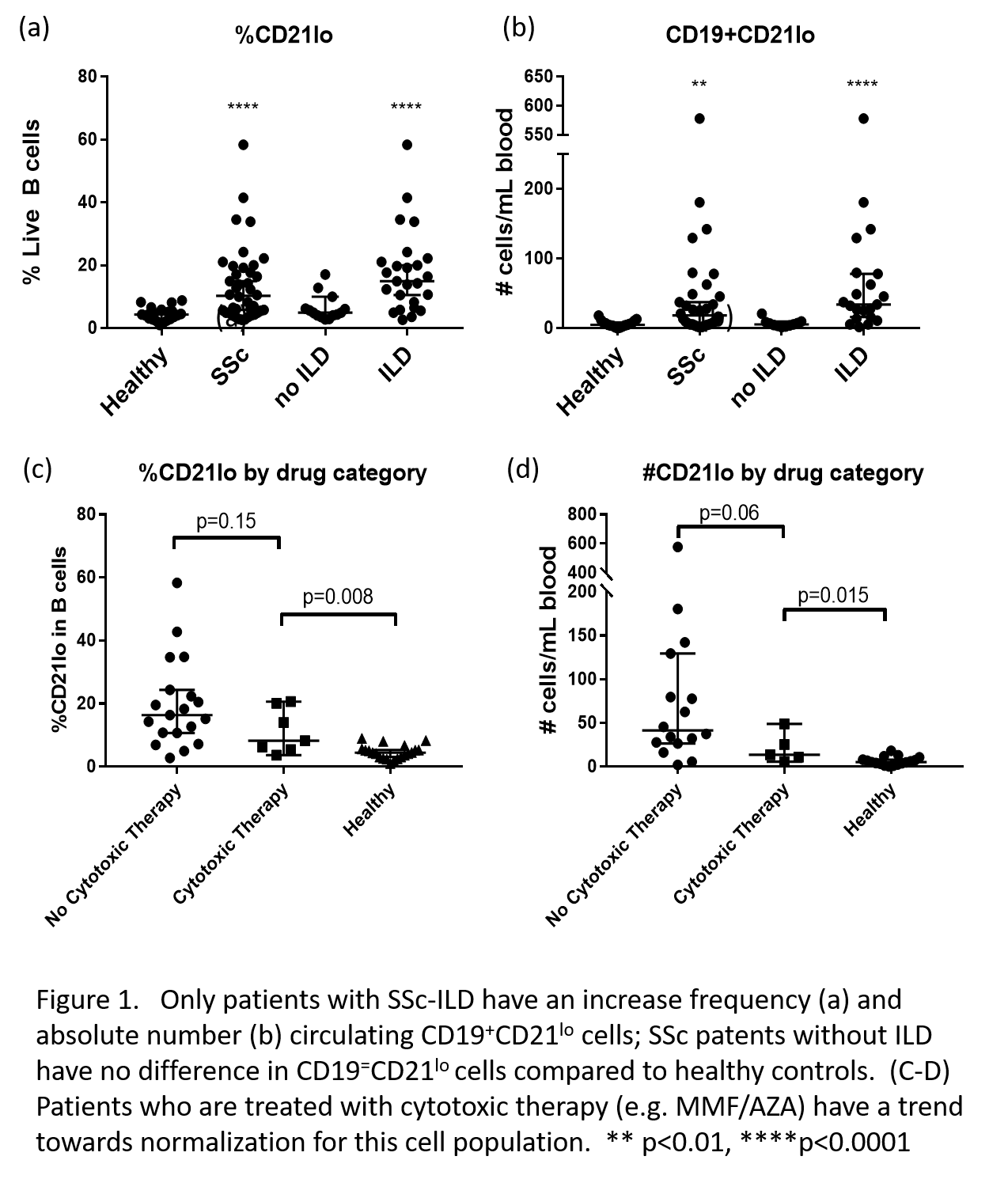
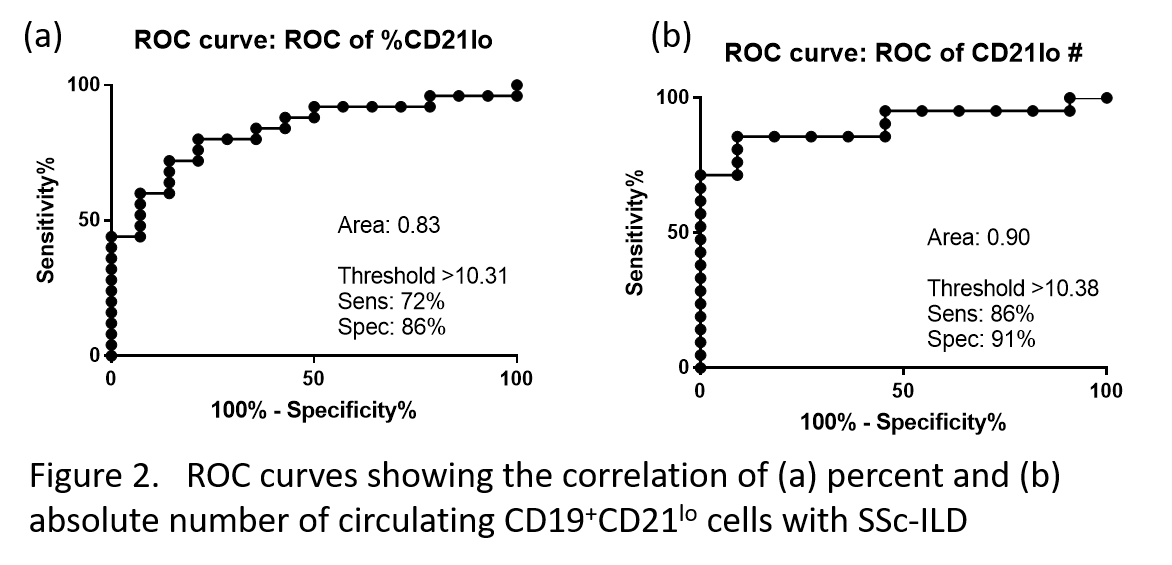
Results: Basic demographics are shown in table 1. Patients with SSc-ILD have a higher percentage of CD19+CD21lo cells compared to patients without interstitial lung disease (15.0% versus 5.0%, p=0.0004); there is no increased CD19+CD21lo frequency for patients with SSc without ILD compared to healthy controls (5.0% v. 4.4%, p=0.22). Similarly, the absolute number of circulating CD19+CD21lo cells is increased for SSc-ILD compared to SSc without ILD or healthy controls (34.0 v. 5.59 v. 5.09 cells/mL, p< 0.0001) (Figure 1A-B). There was no correlation between CD19+CD21lo cells and extent of cutaneous involvement of serologic status. For the subset of patients with ILD treated with mycophenolate mofetil or azathioprine (n=7), there was a trend towards normalization of their CD19+CD21lo frequency (8.2% v. 16.4%, p=0.15) compared to those not treated with these medications (n=19). This trend was even stronger when considering the absolute number of circulating CD19+CD21lo cells for treated versus untreated patients (13.6 v. 41.4 cells/mL, p=0.06) (Figure 1C-D). An ROC curve was generated to predict the presence of ILD. A threshold of 10.3% circulating CD19+CD21lo cells had sensitivity of 76%, specificity of 86%, and AUC 0.87. A threshold of 10.4 cells/mL had a sensitivity of 86%, specificity of 91%, and AUC of 0.90 (Figure 2).
Conclusion: This single center study demonstrated the presence of circulating CD19+CD21lo cells is highly predictive of SSc-ILD. The frequency and absolute number of circulating cells seems to decrease with treatment of ILD. These findings will need to be confirmed in a second large cohort.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wilfong E, Young-Glazer J, Rizzi E, Dudenhofer R, Crofford L, Kendall P. The Presence of Circulating CD19+CD21lo cells Predicts the Presence of Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-presence-of-circulating-cd19cd21lo-cells-predicts-the-presence-of-interstitial-lung-disease-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-presence-of-circulating-cd19cd21lo-cells-predicts-the-presence-of-interstitial-lung-disease-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis/