Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2015
Title: Cytokines, Mediators, Cell-cell Adhesion, Cell Trafficking and Angiogenesis Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
S100A12, a neutrophil protein, has proinflammatory effects on immune cells and can activate endothelial cells. The mechanism of action suggests vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) as a marker of synovial neovascularization in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). S100A12 and VEGF have both been associated with disease activity in RA. We wanted to compare S100A12 and VEGF as biomarkers in a large longitudinal study of RA patients, and explore their association with inflammatory activity expressed as synovial power Doppler (PD) scores.
Methods:
A total of 141 patients with RA (all met the ACR 1987 criteria, 81% women, mean (SD) age 52 (12) years, 79% anti-CCP positive) were examined clinically and with ultrasound (US) before starting biologic treatment (67% anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy) and after 1, 2, 3, 6 and 12 months. Inflammation of wrist (radiocarpal, intercarpal, radioulnar), metacarpophalangeals 1-5, proximal interphalangeals 2-3, elbow, knee, ankle, metatarsophalangeals 1-5, extensor carpi ulnaris and tibialis posterior tendons bilaterally, expressed as gray scale (GS) and PD scores, was scored semiquantitatively 0-3. C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) were analyzed by in-house methodology. Sera from all examinations were frozen at -80 ˚C and S100A12 was analyzed by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and VEGF by multiplex analysis. A total of 141 blood donors were controls (81% women, mean (SD) age 52 (12) years). Mann-Whitney test was used to evaluate differences between patients and controls, Wilcoxon signed rank test to study changes from baseline and Spearman’s rank test for correlation analysis.
Results:
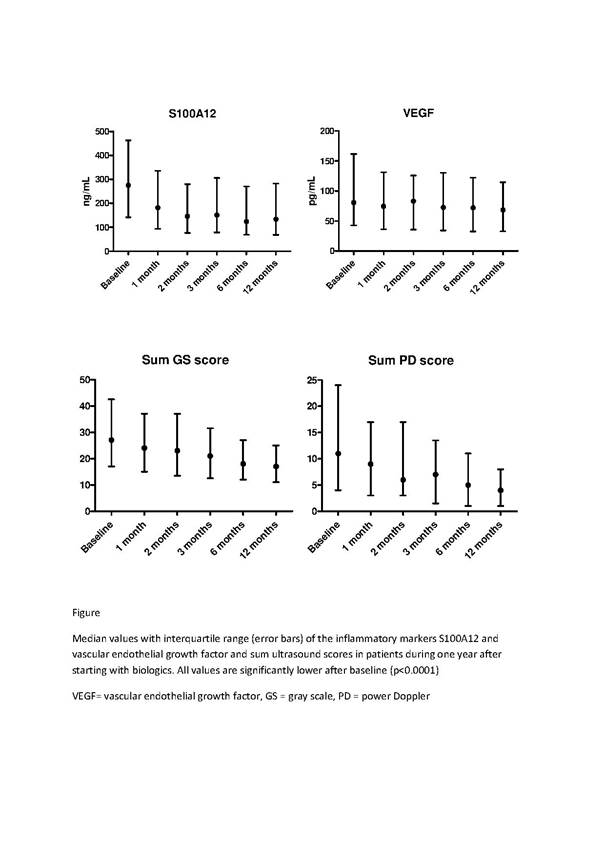
At baseline, median (interquartile range) values of S100A12 were 275 (142-463) ng/mL in patients and 129 (75-222) ng/mL in controls (p<0.0001), while VEGF values were 81 (43-162) pg/mL in patients and 68 (46-108) pg/mL in controls (p=0.08). S100A12, VEGF, CRP, ESR, DAS28, sum GS and PD scores were reduced from baseline at all time points (all p<0.0001). S100A12 correlated with ESR and CRP at all times (r=0.23-0.56, p≤0.003) except with CRP after 12 months. VEGF did not correlate with ESR/CRP at any examination, except with CRP at 2 months (r=0.17, p=0.05). S100A12 correlated with DAS28 at all times (r=0.27-0.35, p≤0.001), with sum GS scores (r=0.26-0.39, p≤0.002) except after 12 months, and with sum PD scores at all times (r=0.17-0.42, p ≤0.04). No correlations were found between VEGF and DAS28. VEGF correlated with sum GS scores (r=0.18-0.21, p≤0.03) before 12 months and with sum PD scores (r=0.17-0.19, p≤0.05) only before 3 months.
Conclusion:
S100A12 was a stronger biomarker than VEGF in RA patients treated with biologic medication during one year, having significant associations with clinical and US examinations. VEGF was expected to be associated with PD activity, but only weak correlations were presently found.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nordal HH, Hammer HB. The Neutrophil Protein S100A12 Has Stronger Associations with a Comprehensive Ultrasound Score of Synovitis Than Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in a Longitudinal Study of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-neutrophil-protein-s100a12-has-stronger-associations-with-a-comprehensive-ultrasound-score-of-synovitis-than-vascular-endothelial-growth-factor-in-a-longitudinal-study-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-pati/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-neutrophil-protein-s100a12-has-stronger-associations-with-a-comprehensive-ultrasound-score-of-synovitis-than-vascular-endothelial-growth-factor-in-a-longitudinal-study-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-pati/