Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster I: Comorbidities
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Lung disease is described in 5–20% of pts (pts) with RA and affects parenchyma, pleura, airways and vasculature; drug-induced pulmonary disease also occurs. It is associated with a higher mortality and identification of safe and effective drugs is essential.
Methods:
Retrospective analysis of the electronic records from RA cohort followed at University College Hospital. Lung involvement was based on high resolution computed tomography. Demographic data, smoking status, complementary exams at baseline/follow-up and therapies used were analysed. A sub-analysis of pts treated with rituximab (RTX) evaluated response at 12, 24 and 36 months. Declines of 15% in gas transfer from baseline and/or 10% in forced vital capacity were recognized.
Results:
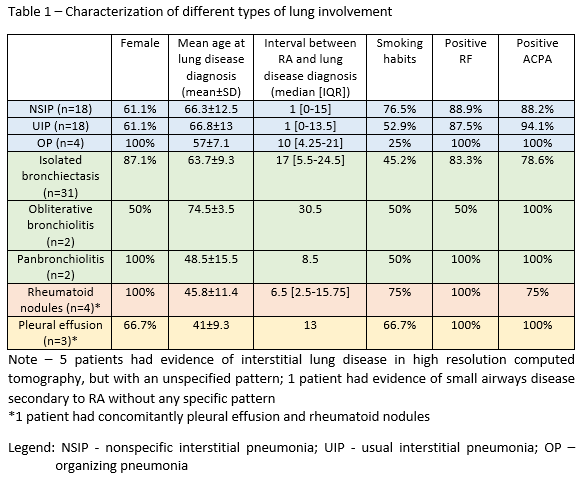
From 1129 RA pts, 87 (7.7%) had documented lung involvement. Mean age at last follow-up was 68.3±12 years, 74.7% were female and 85.1% Caucasian. Median disease duration was 14 (IQR 8-29) years. 54% of pts had erosive disease. RF was positive in 88.1% and ACPA in 87.8%. 23 pts had positive ANAs (25 missing data) and 4 anti-Ro52, 2 anti-Scl70, 2 anti-PL12. Secondary SS occurred in 6.9%, cutaneous rheumatoid nodules in 5.7% and cutaneous vasculitis in 1.1%. 11.5% and 43.7% were current and previous smokers, respectively.
Mean interval between articular and pulmonary symptoms was 12.3 years; 2 pts had lung disease as a prior manifestation. Types of lung involvement are shown in table 1.
At last follow-up appointment 22 pts were still on MTX and 27 had previously received it. MTX-acute pneumonitis occurred in 2 pts, both in the 1st year of treatment.
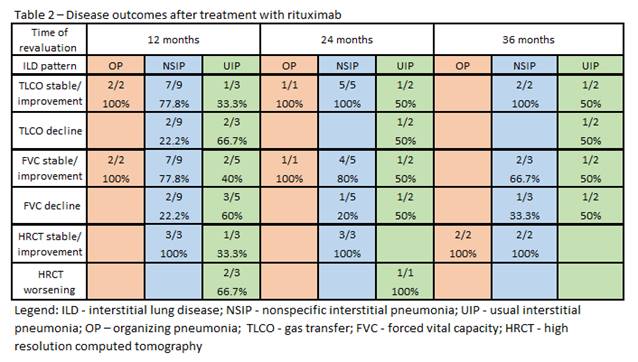
RTX was used in 26pts (57.8%) with ILD (14 nonspecific interstitial pneumonia-NSIP, 8 usual interstitial pneumonia-UIP, 2 organising pneumonia-OP). The mean number of cycles was 4 (range 1-12). Two pts were concomitantly receiving MMF and 1 AZA. RTX treatment outcomes are shown in table 2.
In the cohort there were 18 (20.7%) deaths. Seven of them were related to ILD (4 UIP, 3 NSIP) and occurred 8.8 years after the ILD diagnosis. Two were due to infection, but none was felt to be directly related to immunosuppressive therapy.
Conclusion:
Lung disease occurred in 7.7% of our cohort, with ILD being the commonest presentation (51.7%).
MTX was widely used in pts with lung disease with only 2 cases of acute pneumonitis. Although the number of ILD-pts treated with RTX was small, the drug improved/stabilized the disease in most NSIP and OP pts. UIP pattern was associated with disease progression, despite RTX, and worse outcome.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Duarte AC, Leandro MJ, Porter J. The Lung in an English Cohort of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients – an Overview of Different Types of Involvement and Treatment [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-lung-in-an-english-cohort-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-an-overview-of-different-types-of-involvement-and-treatment/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-lung-in-an-english-cohort-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-an-overview-of-different-types-of-involvement-and-treatment/