Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: SpA Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in axSpA is considered an overarching outcome, with other disease outcomes contributing to it [1]. To validate a previously proposed model on the relationship between disease outcomes, we aimed to investigate the longitudinal relationship between disease activity and function (independent variables) and HRQoL (outcome).
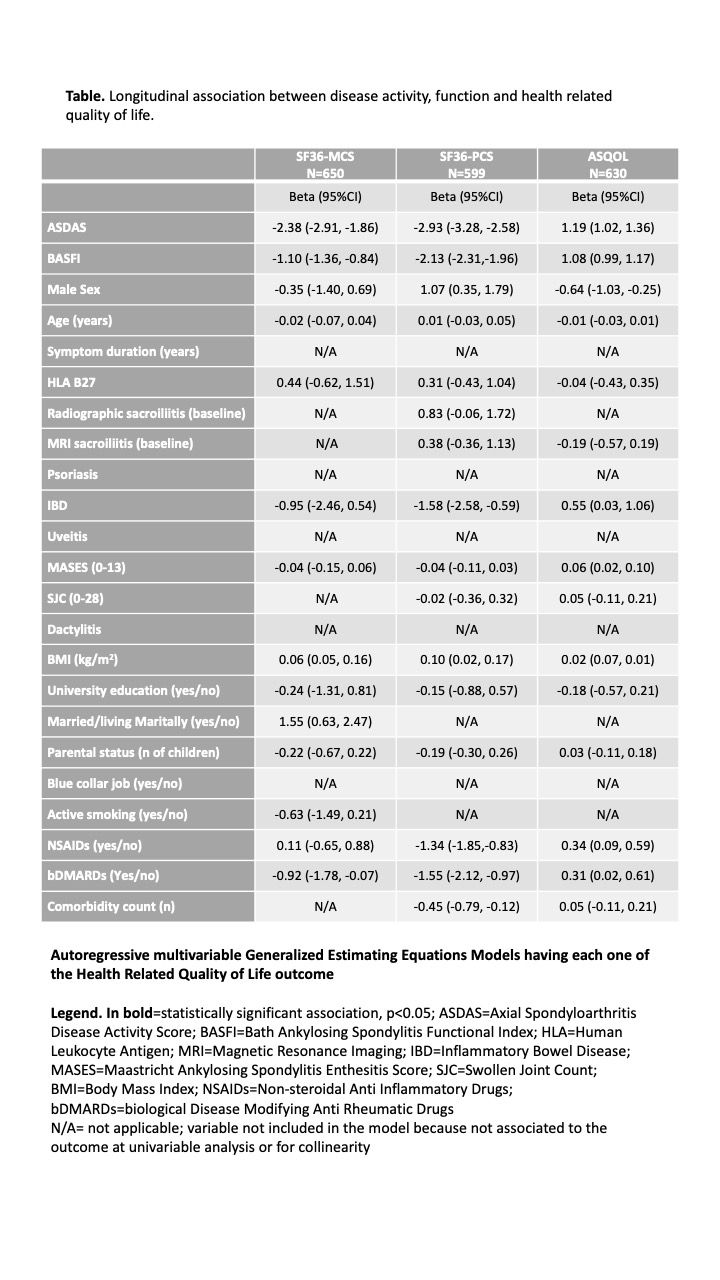
Methods: AxSpA patients with symptoms< 3 years, enrolled in the DESIR cohort, were included. Outcomes were collected longitudinally up to 10 years. The association between disease activity (ASDAS) and physical function (BASFI), on the one hand, and HRQoL (outcome: SF36-MCS, SF36-PCS, ASQoL) was assessed. SpA features, personal and environmental factors, and therapy were collected at baseline (sex, age, HLA-B27 positivity, MRI/radiographic sacroiliitis) or during follow-up (psoriasis, IBD, uveitis, enthesitis, dactylitis, peripheral arthritis, BMI, smoking, job type, education, marital status, parental status, NSAIDs/bDMARDs use, comorbidities) and tested as confounders or effect modifiers. Generalised estimating equations (GEE) were built with SF36-MCS, SF36-PCS, or ASQoL as outcomes (separate models), and ASDAS and BASFI as main independent variables. Covariates were included in the final multivariable models, conducted both as simple GEE models and autoregressive models (corrected for HRQoL at the previous time point). Results were expressed as beta coefficient (Beta) and 95% confidence interval (95% CI).
Results: A total of 663 axSpA patients (46% males, mean age 33.5 [8.6] years) were included. In simple models including only ASDAS and BASFI as independent variables, significant associations were found with SF36-MCS (Beta -2.43[-2.84,-2.04]; -1.23[-1.43,-1.03]), SF36-PCS (-3.07[-3.32,-2.83]; -2.24[-2.37,-2.11]), and ASQoL (1.35[1.23,1.48]; 1.16[1.09,1.22]). These results were confirmed in autoregressive models: effect sizes for ASDAS and BASFI varied modestly when corrected for relevant confounders (Table).
Conclusion: A longitudinal relationship between disease activity and function, on the one hand, and HRQoL as the outcome, has been demonstrated, confirming that HRQoL can be interpreted as an overarching outcome in axSpA.
References. [1] Machado P, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2011;70:1758-64.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ortolan A, van der Heijde D, Gossec L, Ramiro S. The Longitudinal Association Between Disease Activity, Function and Health-Related Quality of Life in Axial Spondyloarthritis: Results from the DESIR Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-longitudinal-association-between-disease-activity-function-and-health-related-quality-of-life-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-results-from-the-desir-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-longitudinal-association-between-disease-activity-function-and-health-related-quality-of-life-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-results-from-the-desir-cohort/