Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: Pediatric Rheumatology – ePoster I: Basic Science, Biomarkers, & Sclerodermic Fever
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: IL2RA has been identified as a JIA-associated risk locus using both candidate gene and genetic fine mapping approaches. However, numerous gene expression studies comparing children with active JIA to healthy control children have failed to identifyIL2RAas a differentially expressed gene. Furthermore, the SNPs used to identifyIL2RAlie within the first intron of the IL2RAgene, not its promoter or coding regions. The risk haplotype is marked by prominent H3K4me1/H3K27ac histone marks, suggesting that genetic risk may be mediated through enhancer function. We therefore sought to confirm whether this region is a functional enhancer and whether the enhancer operates in lymphoid cells, myeloid cells, or both. We also examined the effects of genetic variants on enhancer function at the IL2RAlocus.
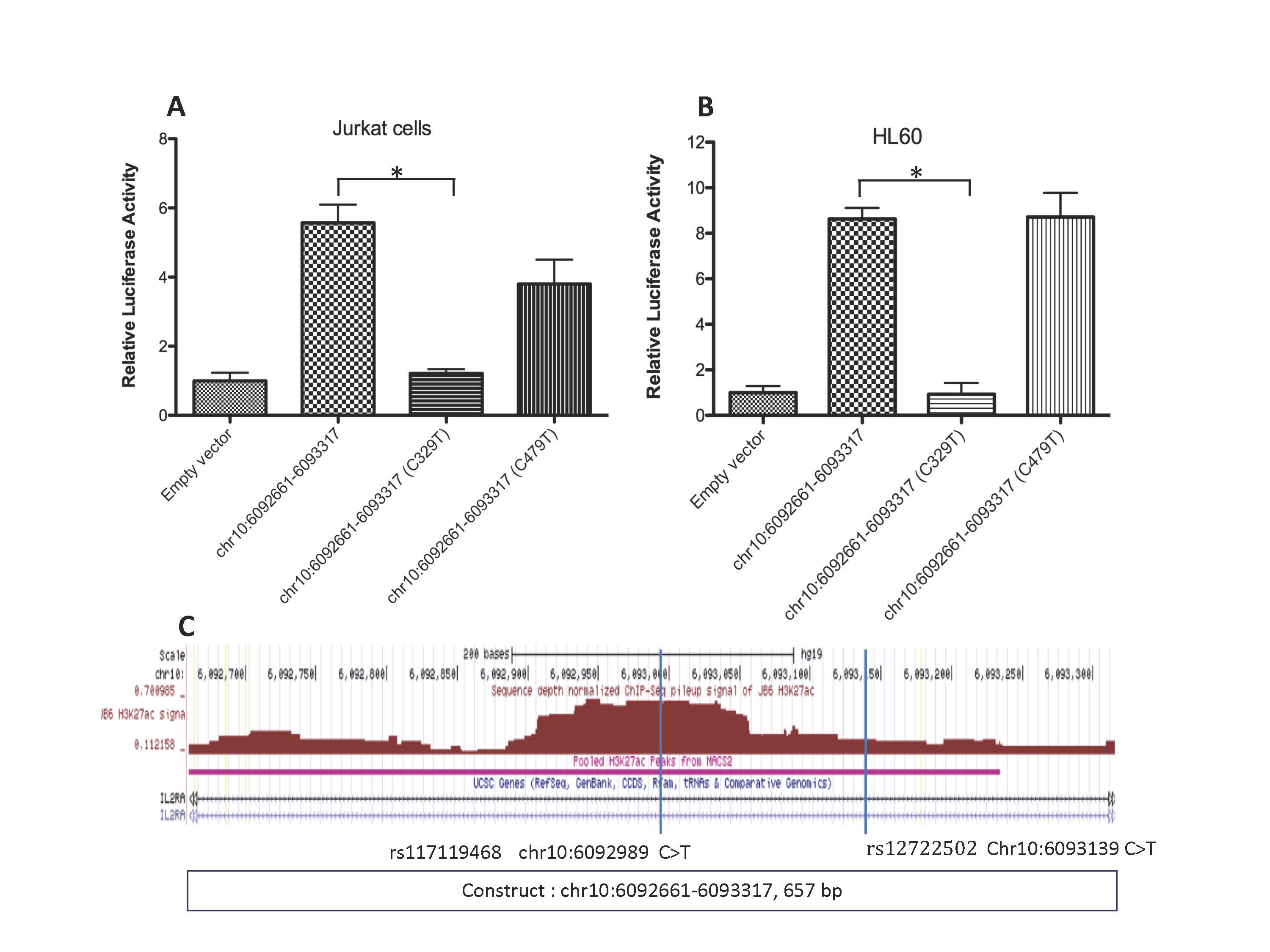
Methods: We used the pGL4 reporter system to query enhancer effects across a 1,000 bp region within the first intron of the IL2RAgene marked by H3K4me1 and H3K27ac histone marks in both CD4+ T cells and neutrophils. This region is within the linkage disequilbrium block that includes the SNPs used on both candidate gene and genetic fine mapping studies that identified IL2RAas a JIA risk locus. The pGL3 vector contains a minimal SV40 promoter that is, by itself, inefficient at driving luciferase function. We tiled three 500 bp constructs across the region of interest and cloned these constructs into pGL3 vectors, which were then transfected into Jurkat T cells and myeloid HL60. Cells were incubated for 24 hr, after which luciferase production was assessed using standard methods. We repeated these same experiments using constructs containing genetic variants (rs117119468 C- >T and rs12722502 C- >T) that we identified in children with JIA using whole genome sequencing.
Results: Within the H3K4me1/H3K27ac-marked region within the first intron of IL2RA, we observed enhancer activity across a 657 bp region from chr10:6092661 to chr10:6093317 in both Jurkat T cells and HL60 myeloid cells. The reporter constructs enhanced luciferase activity by 5-8 fold in Jurkat T cells (compared with a control vector that contained only the minimal SV40 promoter and the luciferase gene) and 4-6 fold in HL60 cells. A construct carrying a sequence within the first intron of the IL2RAgene that was not marked by the H3K4me1/H23K27ac histone signature showed no enhancement of luciferase expression compared to background. Constructs containing the JIA-associated rs117119468 C- >T allele abolished the enhancer activity within the IL2RAlocus, while the construct containing the rs12722502 C- >T allele reduced luciferase activity by 30%.
Conclusion: The JIA-associated risk locus,IL2RA, contains an intronic enhancer that is active in both lymphoid and myeloid cells. JIA-associated genetic variants identified by WGS attenuate or abolish enhancer activity at this locus. These findings demonstrate the importance of assessing the non-coding functions of JIA risk loci, even where the coding function a specific gene might be plausibly implicated. Our findings also underline the potential importance of rare genetic variants, which may have stronger biological effects than GWAS SNPs, in complex traits like JIA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jiang K, Park Y, Evan T, Liu T, Jarvis J. The Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis-Associated IL2RA Haplotype Contains an Intronic Enhancer Whose Function Is Diminished by JIA-Associated Genetic Variants [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-associated-il2ra-haplotype-contains-an-intronic-enhancer-whose-function-is-diminished-by-jia-associated-genetic-variants/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-associated-il2ra-haplotype-contains-an-intronic-enhancer-whose-function-is-diminished-by-jia-associated-genetic-variants/