Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To explore the impact of sex and disease classification on outcomes in axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) patients, including both ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and non-radiographic (nr-) axSpA, in males and females respectively.
Methods: AxSpA patients were consecutively recruited from 2 rheumatology outpatient university clinics. We explored how sex and axSpA disease classification affected patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs). Statistical tests were applied for group comparisons and interactions. We analyzed the relationship between tender point count (TPC) and the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI). The prevalence of extra-articular manifestations (EAMs) and the Charlson comorbidity index (CCI) were determined.
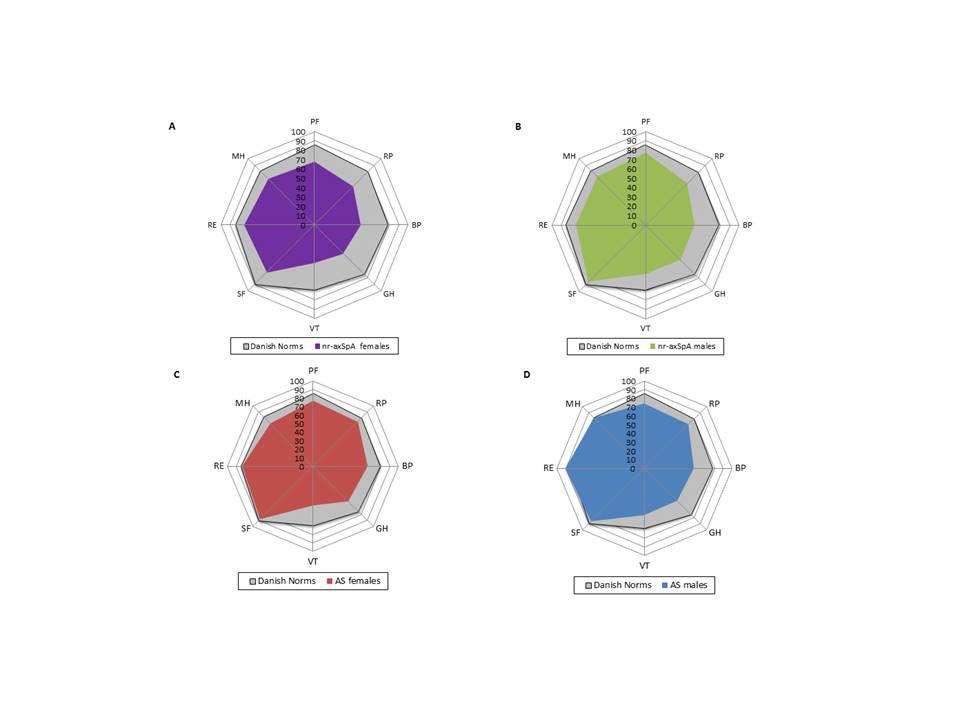
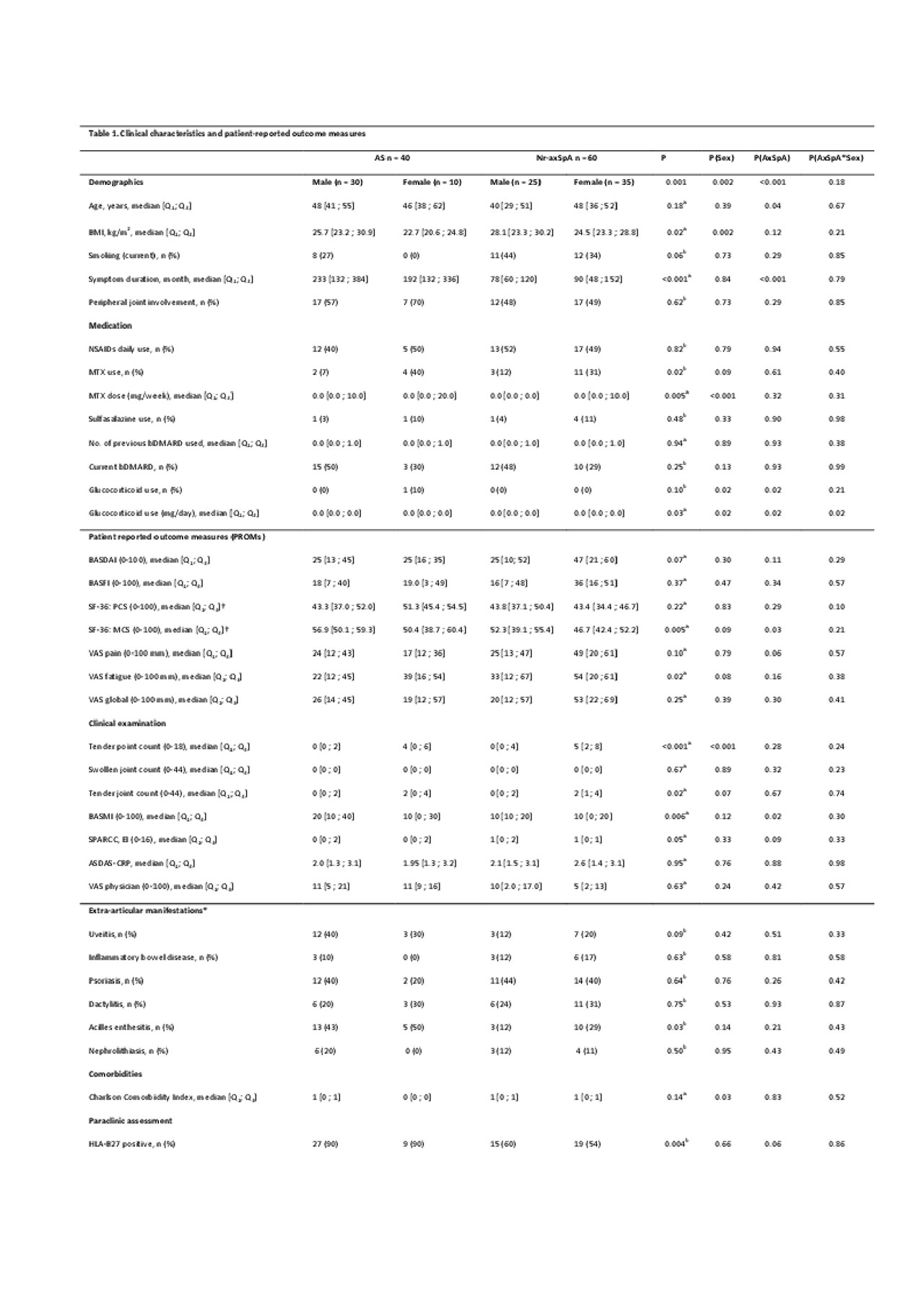
Results: According to the protocol a total of 100 outpatients with axSpA were enrolled (AS males 30; AS females 10; nr-axSpA males 25; nr-axSpA females 35). The BASDAI scores appeared higher among nr-axSpA females (median [Q1; Q3] 47 [21; 60]) compared with the combined median for the three other subgroups 25 [12; 25]. Being classified as nr-axSpA was associated with a lower SF-36 MCS (median SF-36 MCS for the four subgroups: nr-axSpa females: 46.7, nr-axSpA males: 52.3 vs. AS males: 56.9 and AS females: 50.4). Females had a higher tender point count (TPC) compared with females (P< 0.001). TPC and BASDAI were correlated for female nr-axSpA patients (r= 0.44, P=0.008) and male nr-axSpA patients (r= 0.56, P=0.003). EAMs were frequent (up to 50 %) and no difference in the CCI between the subgroups was observed (P=0.14).
Conclusion: This is to our knowledge the first study to evaluate the impact of sex and axSpA classification on PROMs in axSpA patients. AS patients appeared less affected on most PROMs compared with nr-axSpA patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Andreasen R, Kristensen L, Egstrup K, Baraliakos X, Strand V, Horn H, Hansen I, Christensen R, Ellingsen T. The Impact of Sex and Disease Classification on Patient-reported Outcome Measures in Axial Spondyloarthritis: A Descriptive Prospective Cross-sectional Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-sex-and-disease-classification-on-patient-reported-outcome-measures-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-descriptive-prospective-cross-sectional-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-sex-and-disease-classification-on-patient-reported-outcome-measures-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-descriptive-prospective-cross-sectional-study/