Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
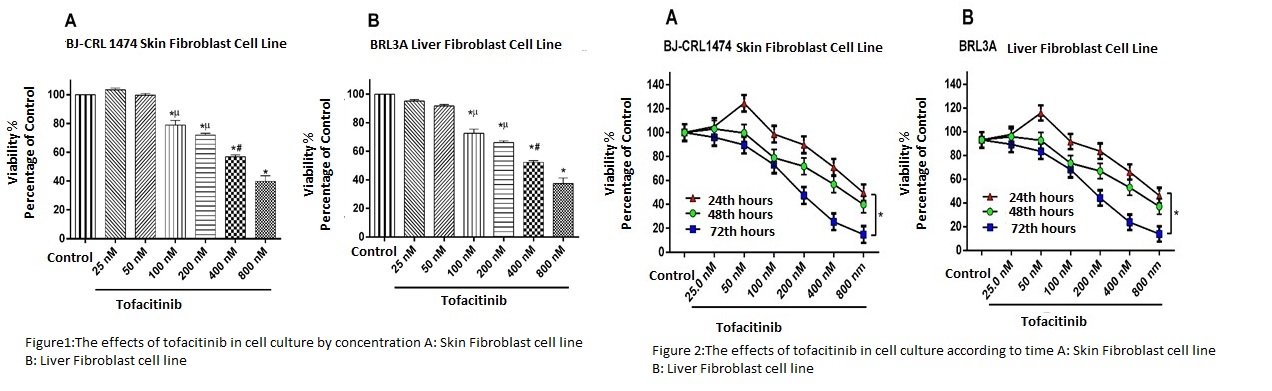
Background/Purpose: Uncontrolled collagen synthesis and deposition occur in various diseases such as hepatic fibrosis, scleroderma.Tofacitinib is a selective JAK-kinase (1/3)inhibitor.Currently it is used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.The aim of the study is to investigate the effect of JAK-STAT signal pathway inhibition on collagen biosynthesis in fibroblast cell-culture.Methods: BJ-CRL1474®(skin) and BRL3A®(hepatic) fibroblast cell cultures were proliferated in the appropriate medium.Tofacitinib was administered to fibroblast cells proliferating on 96-well flasks at concentrations of 25nM,50nM,100nM,200nM,400Nm and 800nM, respectively.Cell viability and quantity were read by spectrophotometer.Tissue metalloproteinase inhibitor(TIMP-1),matrixmetalloproteinase-3(MMP-3), transforming growth factor (TGF-1β) and hydroxyproline levels were measured by ELISA method.Results: The cytotoxic effect of tofacitinib started at 100 nM concentration(p<0.05). The highest effect was obtained at 800nM.The cytotoxic effect at concentrations of 400nM and 800nM was higher than at 100nM and 200nM concentrations(p<0.05)(Figure1).The time-dependent cytotoxic effect of tofacitinib was significantly higher at 72th hours than at 24th and 48th hours at all concentrations(p<0.05)(Figure1).TFG-1β,the major stimulus of collagen synthesis, was found to be significantly low even at 25 nM concentration(p<0.05).The lowest concentration was reached at 800nM(p<0.05).There was a significant decrease in MMP-3, TIMP-1 and hydroxyproline levels respectively(p<0.05).The decline in all three biomarkers started at a concentration of 100nM.The maximum decrease in the levels of four biomarkers was observed at a concentration of 800nM(Figure).The results in both cell cultures were similar and not statistically significant(p>0.05).Conclusion:Tofacitinib was shown to reduce fibroblast proliferation and viability in fibroblast cell culture.The decrease in the levels of TGF-β, which is also the main stimulus of collagen synthesis and is also released from fibroblasts, may be due to reduced release of TGF-β.The level of hydroxyproline in the collagen structure is expected to decrease.We found that the level of MMP-3 was also reduced.MMP-3 was not needed in conditions such as collagen synthesis decreased and in vitro.We found a decrease in TIMP-1, an inhibitor of MMP-3. JAK kinase inhibitor, tofacitinib inhibited fibroblast cell proliferation in fibroblast cell culture by time and concentration.
Table-1: Effect of Tofacitinib on levels of TGF-1β, MMP-3,TIMP-1 and hydroxyproline.
|
Tofacitinib |
TGF-1β (pg/mg) |
MMP-3 |
TIMP-1 (pg/ml) |
Hydroxyproline (Ratio of control) |
|
Control |
23,4±2,6 |
12,9±2,6 |
860,5±23,3 |
1 |
|
25 nM |
18,6±3,5* |
11,3±2,8 |
840,2±21,9 |
0,91±0,13 |
|
50 nM |
17,2±1,9* |
10,8±1,9 |
800,0±20,3 |
0,85±0,08 |
|
100 nM |
11,3±2,1** |
4,2±1,1* |
621,3±25,6* |
0,61±0,07* |
|
200 nM |
10,6±1,8** |
3,8±0,9* |
324,3±17,5** |
0,52±0,05* |
|
400 nM |
3,6±0,9# |
3,6±0,6* |
321,9±16,2** |
0,48±0,03* |
|
800 nM |
2,1±0,7# |
1,2±0,4** |
310,2±18,8** |
0,12±0,02** |
*p<0.05, **p<0.05 , #p<0.005
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
ŞAHİN M, AYDIN H, ALTUN A, DERİN ME, Şahin A. The Effects of the Jak-Stat Signal Pathway Inhibition on Collagen Biosynthesis in Fibroblast Cell Culture [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effects-of-the-jak-stat-signal-pathway-inhibition-on-collagen-biosynthesis-in-fibroblast-cell-culture/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effects-of-the-jak-stat-signal-pathway-inhibition-on-collagen-biosynthesis-in-fibroblast-cell-culture/