Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Open-label studies provided evidence for possible efficacy of rituximab (RTX) in systemic sclerosis (SSc). Previously, we reported on a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial in early SSc showing no significant difference in clinical outcomes. In rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematodus, clinical efficacy of RTX is associated with the extent of B cell depletion. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the effect of rituximab in SSc on B cells in peripheral blood and skin, as possible explanation for lack of clinical efficacy.
Methods: Sixteen patients fulfilling ARA criteria for SSc were randomized to either placebo or 1000 mg RTX IV on day 1, 15 and at 6 months and followed for 24 months. Immunophenotyping of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) by flow cytometry for presence of CD19+CD27- naïve B cells, CD19+CD27+ memory B cells, CD19+CD20-CD27++ plasmablasts and detection of antibody secreting cells (ASC) by Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSpot assay (ELISPOT) was performed at baseline, months 3, 6, 12 and 24. 4 mm skin biopsies of the dorsal forearm were assessed for presence of B cells by immunohistochemistry with CD79a at baseline and 3 months.
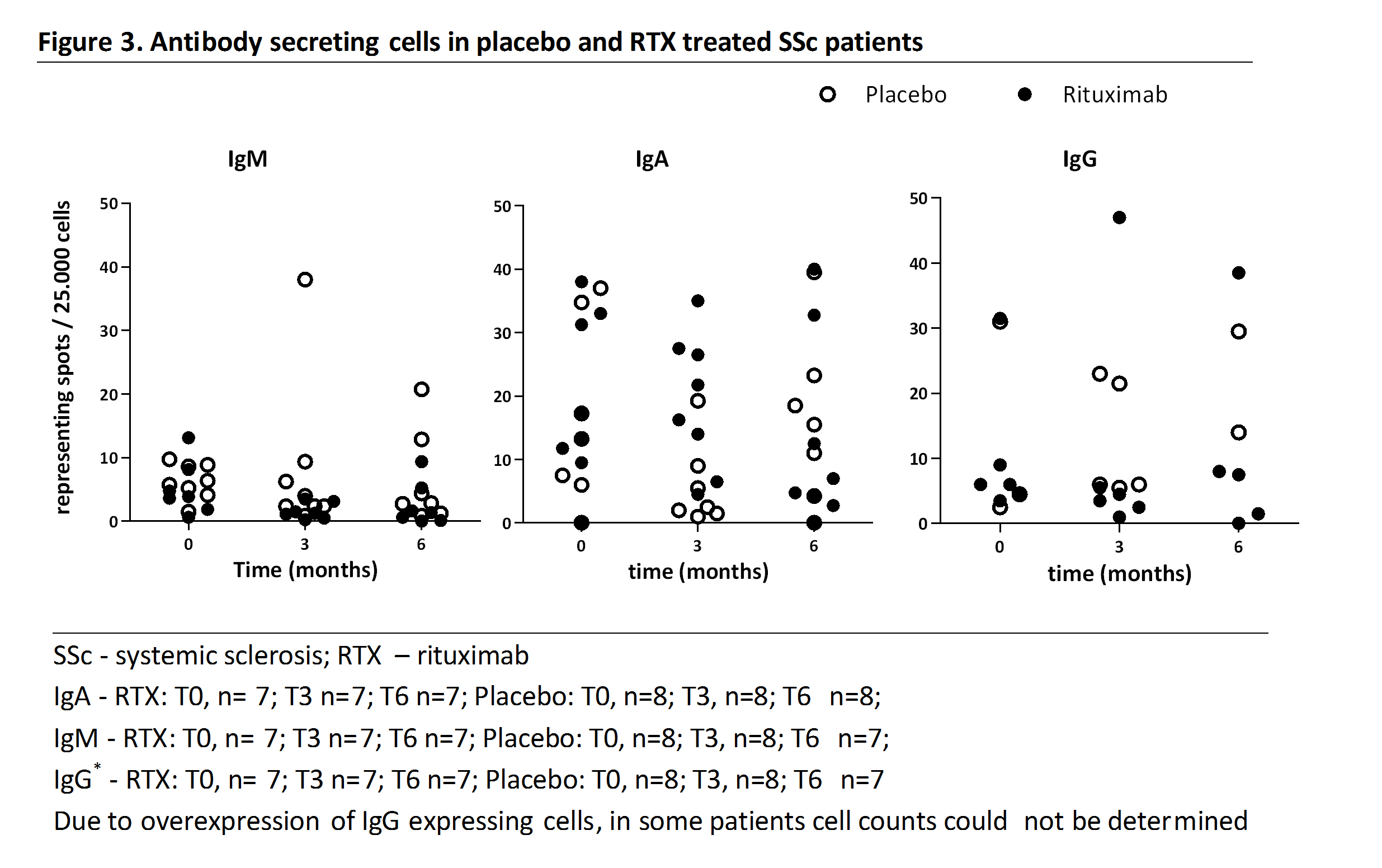
Results: Mean age was 44.5 years (SE 5.6), 87.5 % of patients had diffuse cutaneous SSc, median disease duration since non-Raynaud was 1.2 years (interquartile range 0.8-2.8). At month 3, depletion of naïve and memory B cells to very low B cell counts was achieved with RTX. Naïve B cells repopulated first and were clearly detectable at month 12, while memory B cells reached pre-treatment levels only at month 24 (Figure 1). Some patients achieved undetectable counts of naïve B cells or plasmablasts, though no patient had undetectable B cells in all subsets (Figure 2). Persistence of ASC was confirmed by ELISPOT (Figure 3). Scattered B cells (range 2-7) were seen in skin biopsies at baseline (placebo 3 of 8; RTX 2 of 7 biopsies) and at 3 months (placebo 4 of 7; RTX 4 of 7 biopsies).
Conclusion: Treatment with RTX resulted in depletion of peripheral blood B cells to very low, though still detectable counts. Despite this depletion, no clinical effect was observed. Persistence of ASC and persistent detection of B cells in skin at 3 months provide evidence for treatment-resistant populations of B cells in SSc, which might influence treatment response.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Boonstra M, Dorjée AL, Quint KD, Huizinga TWJ, Scherer HU, de Vries-Bouwstra JK. The Effect of Rituximab on B Cells in Skin and Peripheral Blood in Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effect-of-rituximab-on-b-cells-in-skin-and-peripheral-blood-in-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effect-of-rituximab-on-b-cells-in-skin-and-peripheral-blood-in-systemic-sclerosis/