Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The pathogenesis of interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis (SSc-ILD) is not completely elucidated, although it is believed that chronic alveolar inflammation leads to increasing fibrosis. Treatment strategies using cyclophosphamide (CYC) have been focusing on the inflammatory pathway of SSc-ILD. We hypothesized that CYC is more effective in patients that are in the early, inflammatory phase. The objectives of this study are analyze the effects of intravenously CYC pulses (750mg/m2) on pulmonary function (FVC, DLCO) in SSc-ILD after 12, 24 and 36 months, and whether this effect is dependent on the extent of ILD, the proportion of ground glass compared to fibrosis, SSc disease duration or baseline DLCO <60%.
Methods: Patients with SSc-ILD receiving CYC pulses between 2003 and 2015 were classified by the Goh (2008) criteria in either limited or extensive ILD, using HRCT at baseline independently judged by two raters. Pulmonary function tests were performed at 0, 6, 12, 24 and 36 months. Missing outcome data due to drop-out were replaced by last observation carried forward, except in case of death.
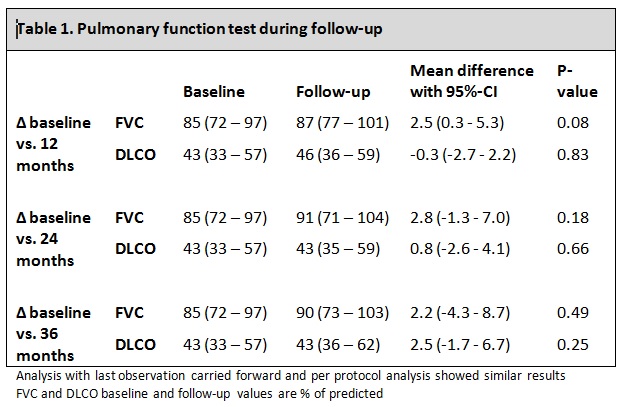
Results: Seventy-five patients were included, 33 with limited ILD, 42 with extensive ILD. There were no baseline differences in age, gender, SSc subtype classification, disease duration or autoantibody status. FVC and DLCO were stable after 12, 24 and 36 months of follow-up (table 1).
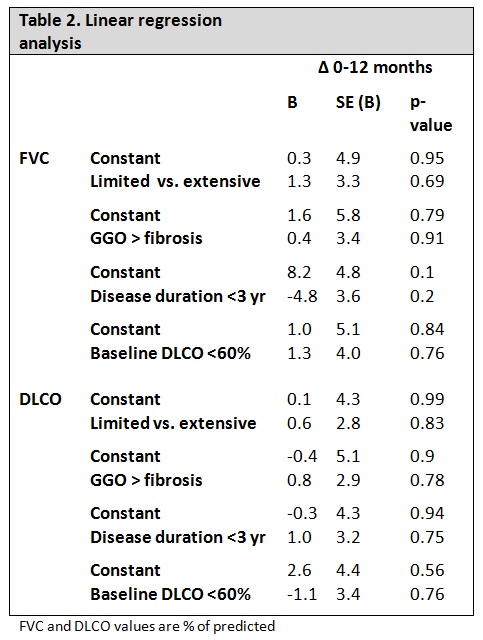
There was no effect in the degree of change in FVC and DLCO for the different effect modifiers (table 2): the extent of ILD, proportion of ground glass compared to fibrosis, short SSc disease duration or baseline DLCO <60%.
Conclusion: Pulmonary function in SSc-related ILD was stable during 36 months of follow-up after cyclophosphamide pulse therapy. The extent of ILD, proportion of ground glass, SSc disease duration and baseline DLCO <60% did not influence the effect of CYC on pulmonary function. It could not be shown that CYC is more effective in the early phase of SSc-ILD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
van den Hombergh W, Teesselink E, Knaapen-Hans H, van den Hoogen F, Simons SO, Fransen J, Vonk M. The Effect of Cyclophosphamide on Pulmonary Function and Dependence on Disease Activity of Interstitial Lung Disease Associated with Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effect-of-cyclophosphamide-on-pulmonary-function-and-dependence-on-disease-activity-of-interstitial-lung-disease-associated-with-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effect-of-cyclophosphamide-on-pulmonary-function-and-dependence-on-disease-activity-of-interstitial-lung-disease-associated-with-systemic-sclerosis/