Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: SLE – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: BEL, an approved SLE treatment,1 improved kidney outcomes in initial Phase 3 SLE trials.2,3 This post hoc analysis evaluates the effect of BEL on kidney outcomes in patients (pts) with SLE across a large, integrated population.
Methods: The BEL Summary of Lupus Efficacy (Be-SLE) post hoc analysis evaluated data (collected every 4 weeks [wks]; baseline [BL] to Wk 52) from adults with SLE from 5 BEL trials: BLISS-76, BLISS-52, BLISS-NEA, BLISS-SC, and EMBRACE (GSK Studies BEL110751, BEL110752, BEL113750, BEL112341, and BEL115471). Pts received BEL (10 mg/kg/month intravenously or 200 mg/wk subcutaneously) or placebo (PBO), plus standard therapy. Time to first kidney flare (defined in Table 1), SELENA-SLEDAI and BILAG kidney improvement and worsening, and kidney biomarker changes were assessed.
Results: Among 3086 pts (BEL, N=1869; PBO, N=1217), most were female (94.4%); mean (SD) age was 37.0 (11.64) years. Mean (SD) SLE duration was 6.4 (6.36) years. BL medication use was similar across groups. By Wk 52, 18.8% of BEL and 23.7% of PBO pts had withdrawn from the study.
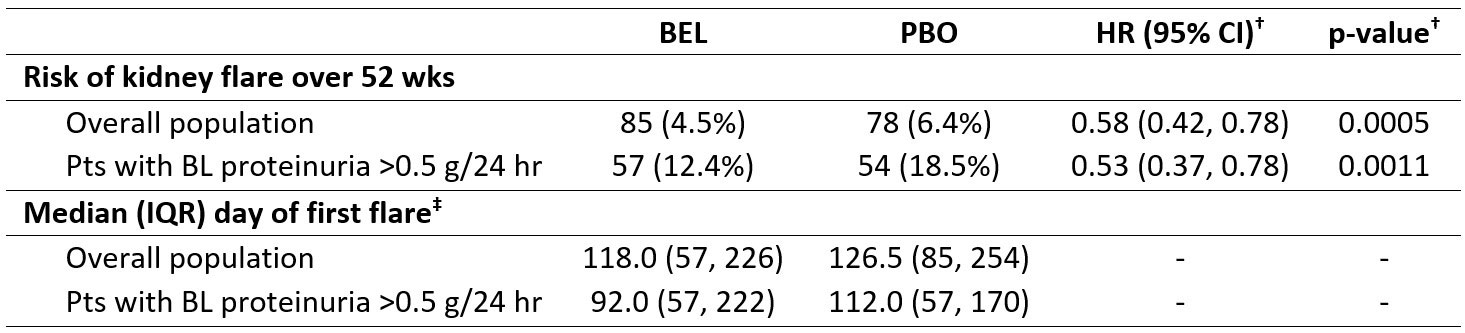
Over 52 wks, fewer BEL vs PBO pts had ≥1 kidney flare in the overall population (4.5% vs 6.4%; hazard ratio, HR [95% confidence interval, CI]: 0.58 [0.42, 0.78]; p=0.0005) and in pts with BL proteinuria >0.5 g/24 hr (BEL, n=461; PBO, n=292; 12.4% vs 18.5%; HR [95% CI]: 0.53 [0.37, 0.78]; p=0.0011; Table 1). Among pts with a kidney flare, BEL vs PBO pts had a shorter median (interquartile range, IQR) time to first flare in the overall population (118 [57, 226] days vs 127 [85, 254] days) and among pts with BL proteinuria >0.5 g/24 hr (92 [57, 222] days vs 112 [57, 170] days).
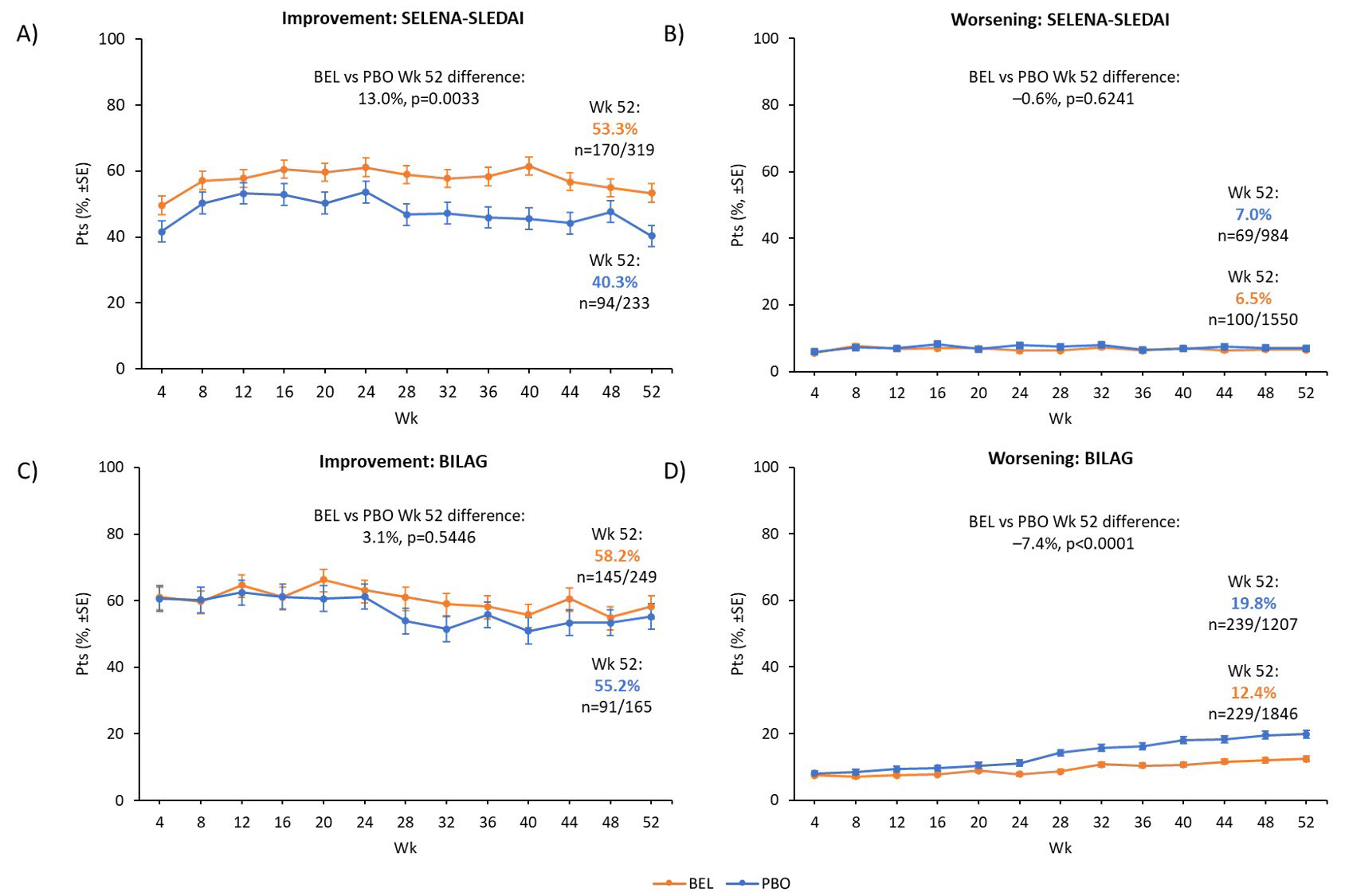
Among pts with BL SELENA-SLEDAI kidney involvement (SELENA-SLEDAI score >0; BEL, n=319; PBO, n=233), significantly more BEL vs PBO pts had kidney improvement at Wk 52 (53.3% vs 40.3%; p=0.0033; Figure 1A); among pts with no BL kidney involvement (SELENA-SLEDAI score =0; BEL, n=1550; PBO, n=984), there was no significant difference in kidney worsening between groups (6.5% vs 7.0%; p=0.6241; Figure 1B). Among pts with BL kidney BILAG =A/B (BEL, n=249; PBO, n=165), there was no significant difference in kidney improvement (BILAG A score change to B/C/D/E, or from B to C/D/E) between groups at Wk 52 (58.2% vs 55.2%; p=0.5446; Figure 1C); among pts with BL kidney BILAG =B/C/D/E (BEL, n=1846; PBO, n=1207), significantly fewer BEL vs PBO pts had kidney worsening (BILAG B/C/D/E score change to A/B) at Wk 52 (12.4% vs 19.8%; p< 0.0001; Figure 1D).
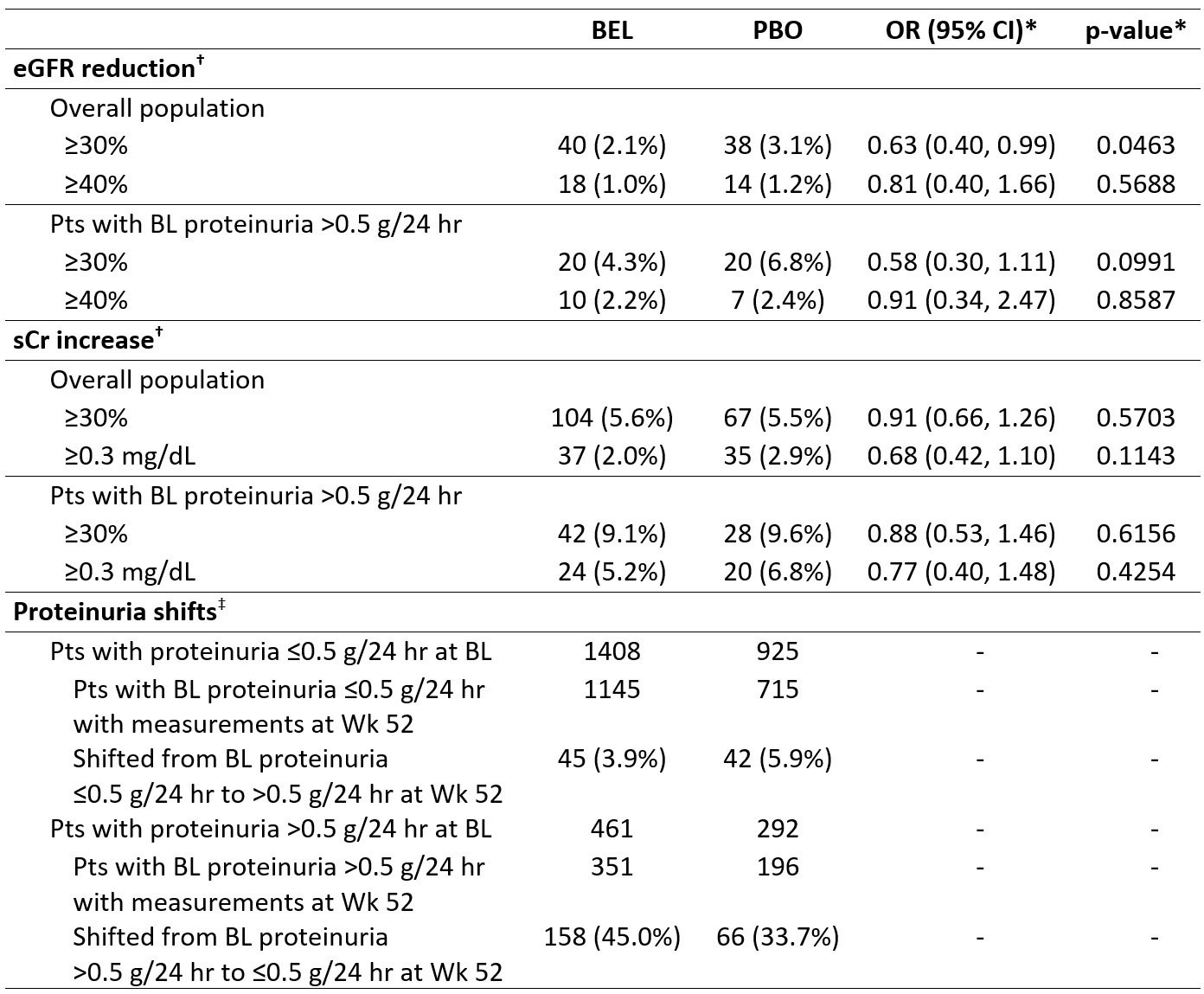
At Wk 52, in the overall population, significantly fewer BEL vs PBO pts had a ≥30% estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) reduction (2.1% vs 3.1%; p=0.0463), while the proportion of pts with ≥30% serum creatinine (sCr) increase was similar (5.6% vs 5.5%; p=0.5703; Table 2). In pts with BL proteinuria >0.5 g/24 hr, more BEL vs PBO pts shifted to ≤0.5 g/24 hr (45.0% vs 33.7%).
Conclusion: Favorable kidney outcomes were observed for BEL vs PBO in pts with SLE, including fewer kidney flares, greater kidney improvement (SELENA-SLEDAI), less kidney worsening (BILAG), and improved eGFR.
Funding: GSK
References
1GlaxoSmithKline. Benlysta US prescribing information. 2021
2Dooley MA, et al. Lupus. 2013;22:63–72
3Manzi S, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71:1833–8
*Kidney improvement by SELENA-SLEDAI is defined as a decrease in kidney SELENA-SLEDAI score compared with BL. Kidney improvement by BILAG is defined as a kidney BILAG score change from A to B/C/D/E, or B to C/D/E; †kidney involvement is defined as either a SELENA-SLEDAI score >0 in the kidney organ system, or as a BILAG kidney score of A/B at BL; ‡kidney worsening by SELENA-SLEDAI is defined as an increase in SELENA-SLEDAI kidney score compared with BL; kidney worsening by BILAG is defined as a kidney score change from B to A, or from C/D/E to A/B.
Treatment groups were compared using Fisher’s exact test.
SE, standard error
*Kidney flare was defined as the development of ≥1 of the following 3 factors: increased proteinuria (reproducible increase in 24 hr urine protein levels to >1.0 g if BL value was <0.2 g, >2 g if BL value was 0.2–1.0 g, or more than twice the value at BL if BL value was >1.0 g), impaired kidney function (reproducible increase in sCr of >20% or an increase of at least 0.3 mg/dL/reproducible >20% decrease in GFR, accompanied by proteinuria [>1.0 g/24 hr], hematuria [≥4 RBCs/hpf], and/or cellular [RBC and WBC] casts), and new hematuria (11–20 RBCs/hpf or a reproducible increase in hematuria by 2 grades vs BL, associated with >25% dysmorphic RBCs [glomerular in origin, exclusive of menses] accompanied by an 800 mg increase in 24 hr urinary protein levels or new RBC casts). In the EMBRACE study, new hematuria was not required; †a Cox proportional hazards model was used for the comparison between treatment groups, adjusting for study and BL SELENA-SLEDAI score (≤9 vs ≥10); ‡among pts who experienced a kidney flare in the overall population (BEL, n=85; PBO, n=78) and among pts with BL proteinuria >0.5 g/24 hr (BEL, n=57; PBO, n=54).
hpf, high power field; RBC, red blood cell; WBC, white blood cell
*Logistic regression models were used to compare treatment groups for eGFR reductions and sCr increase with covariates for treatment group, study, BL eGFR/sCr value and BL SELENA SLEDAI score (≤9 vs ≥10). Analyses were not adjusted for multiplicity; †calculated based on last observation carried forward; ‡among pts who completed Wk 52 of the study.
OR, odds ratio
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dall'Era M, Fava A, Henning C, Jones-Leone A, Carroll A, Harris J, Hammer A, Levy R, Magder L, Petri M. The Effect of Belimumab (BEL) on Kidney Outcomes in SLE: Results of a Large Integrated Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effect-of-belimumab-bel-on-kidney-outcomes-in-sle-results-of-a-large-integrated-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effect-of-belimumab-bel-on-kidney-outcomes-in-sle-results-of-a-large-integrated-analysis/