Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: 5T109 ACR Abstract: RA–Treatments V: Beyond Individual Compounds (2874–2879)
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: RA patients who are intolerant or have an inadequate response to conventional synthetic DMARDs (csDMARDs) can be treated with a biologic DMARD (bDMARD). Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) are often used first-line but non-TNFi bDMARDs are also used. Data comparing the effectiveness of TNFi and non-TNFi following csDMARDs are limited; we therefore sought to compare the real-world effectiveness of TNFi and non-TNFi agents in bDMARD-naïve patients.
Methods: Demographic, clinical, disease characteristic, and patient-reported outcomes (PROs) were collected for patients enrolled in a large US registry (Corrona) from Jan 1, 2001 to Jan 20, 2018 with diagnosis of RA, ≥18 years at diagnosis, initiating (mono- or combination therapy) with a TNFi or non-TNFi bDMARD, and with follow-up 6–15 months after initiation. Non-TNFi and TNFi patients were propensity score matched (PSM) on a 1:4 basis by age, RA duration, cardiovascular and hypertension history, prior cancer, private insurance, Medicare, marital status, smoking status, work status, ACR functional class, and concomitant csDMARDs; variables with >10% missing data were omitted. The PSM used no replacement matching. Baseline characteristics after PSM were compared using two-sample t-tests (continuous) and Chi-squared tests (categorical). Outcomes were assessed after 12 months of therapy; for patients switching therapy last-visit outcomes were carried forward. Random effect linear (continuous) and random effect logistic (binary) regression were used to compare outcomes at 12 months between matched populations further adjusted by baseline value, concomitant csDMARD, and prednisone use. A number of outcome covariates were assessed as potential effect modifiers using interaction terms in multivariable mixed models.
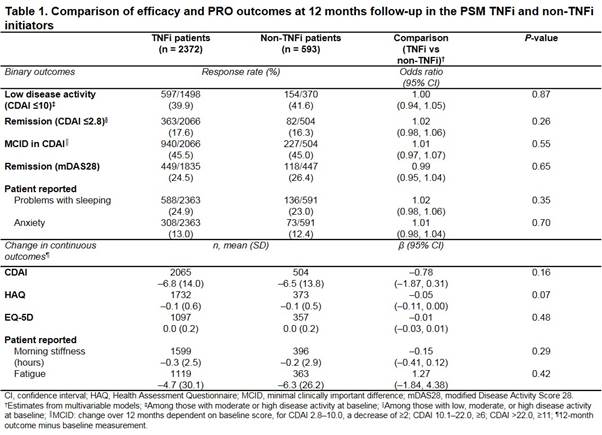
Results: Of the bDMARD-naïve patients, 4186 initiated a TNFi and 630 a non-TNFi. After PSM, 2372 TNFi and 593 non-TNFi patients were included. Respectively, mean (SD) age was 61.0 (12.9) vs 62.3 (12.8) years (P = 0.03); 76.8% vs 79.8% female (P = 0.12); mean (SD) duration of RA 8.2 (9.3) vs 8.7 (9.5) years (P = 0.24); RF positive 70.2% vs 70.4% (P = 0.95); mean (SD) BMI 30.0 (7.1) vs 29.8 (7.3) (P = 0.41); concomitant csDMARD 78.0% vs 76.7% (P = 0.83); prednisone use 31.7% vs 31.2% (P = 0.81); mean (SD) clinical disease activity index (CDAI) 19.8 (13.2) vs 20.1 (13.1) (P = 0.72); and mean (SD) HAQ 1.1 (0.6) vs 1.1 (0.6) (P = 0.96). No significant differences were observed in 12-month outcomes for TNFi and non-TNFi initiators (Table). No significant effect modification was observed between cohorts for outcomes including achievement of low CDAI and remission, PROs (sleep, anxiety, fatigue, and morning stiffness) and change in CDAI, HAQ, and EuroQoL-5 dimensions (EQ-5D) (data not shown).
Conclusion: No differences in clinical responses were observed in patients with RA initiating a TNFi or non-TNFi as their first bDMARD in this large real-world US cohort.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pappas DA, St. John G, Etzel CJ, Fiore S, Blachley T, Kimura T, Punekar R, Emeanuru K, Boklage S, Kremer J. The Comparative Effectiveness of First-Line Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor (TNFi) Compared with Non-TNFi Agents in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results from the Corrona Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-comparative-effectiveness-of-first-line-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitor-tnfi-compared-with-non-tnfi-agents-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-from-the-corrona-registry/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-comparative-effectiveness-of-first-line-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitor-tnfi-compared-with-non-tnfi-agents-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-from-the-corrona-registry/