Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0510–0542) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment: AxSpA Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Despite multiple pharmacological options for axSpA are available, still one out of three patients do not achieve the recommended treatment target (1), highlighting the need to understand better the difficult-to-treat (D2T) axSpA profile. The aim of this study was to identify the characteristics of D2T-axSpA patients compared to “good responders” (GR) and determine predictive factors for D2T-axSpA.
Methods: Data from an observational prospective cohort recruiting consecutively patients diagnosed of axSpA initiating the first bDMARD from La Paz University Hospital between 2004 and 2019 were analysed. Patients were classified as D2T if they failed to at least two b/tsDMARDs or as GR if they continued treatment with the first bDMARD for at least 3 years or stopped it due to disease control. Clinical characteristics, laboratory tests, concomitant treatment and disease activity measures prior to starting the first bDMARD (baseline) and after 6 months were collected. Also, b/tsDMARD courses were registered. Chi-square or Fisher test and unpaired t-student were used for descriptive analyses. Logistic regression models were used to identify associated factors with D2T-axSpA. Finally, a Classification And Regression Tree (‘CART’) was created to predict D2T-axSpA.
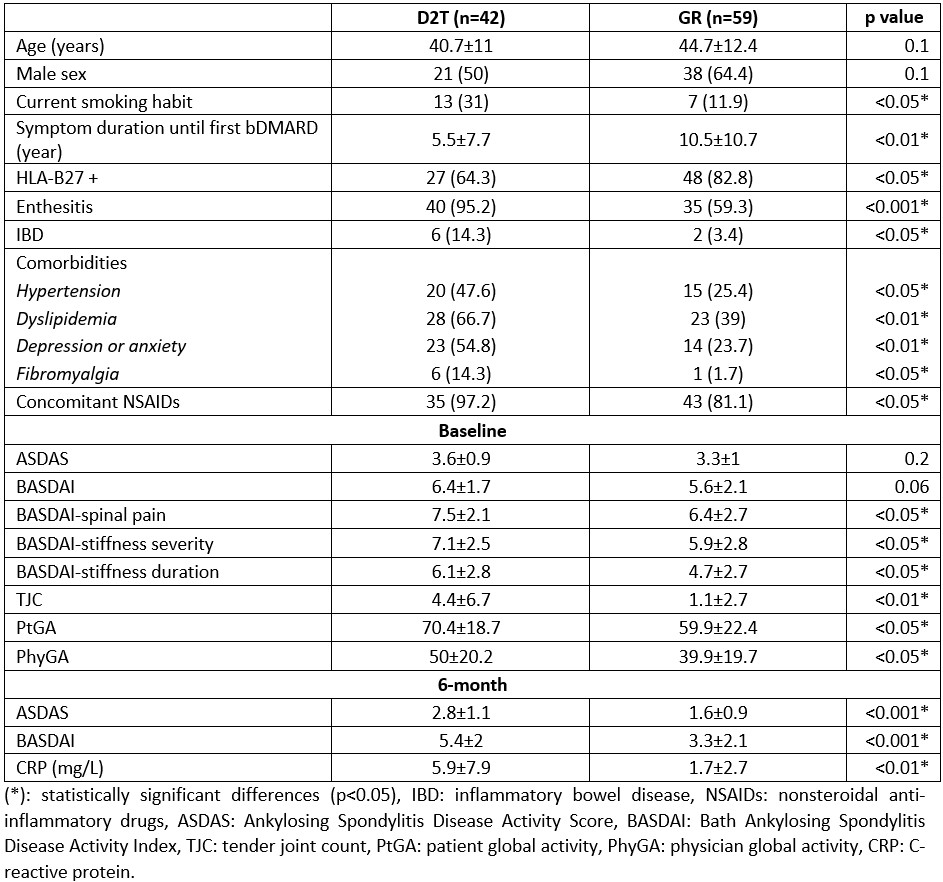
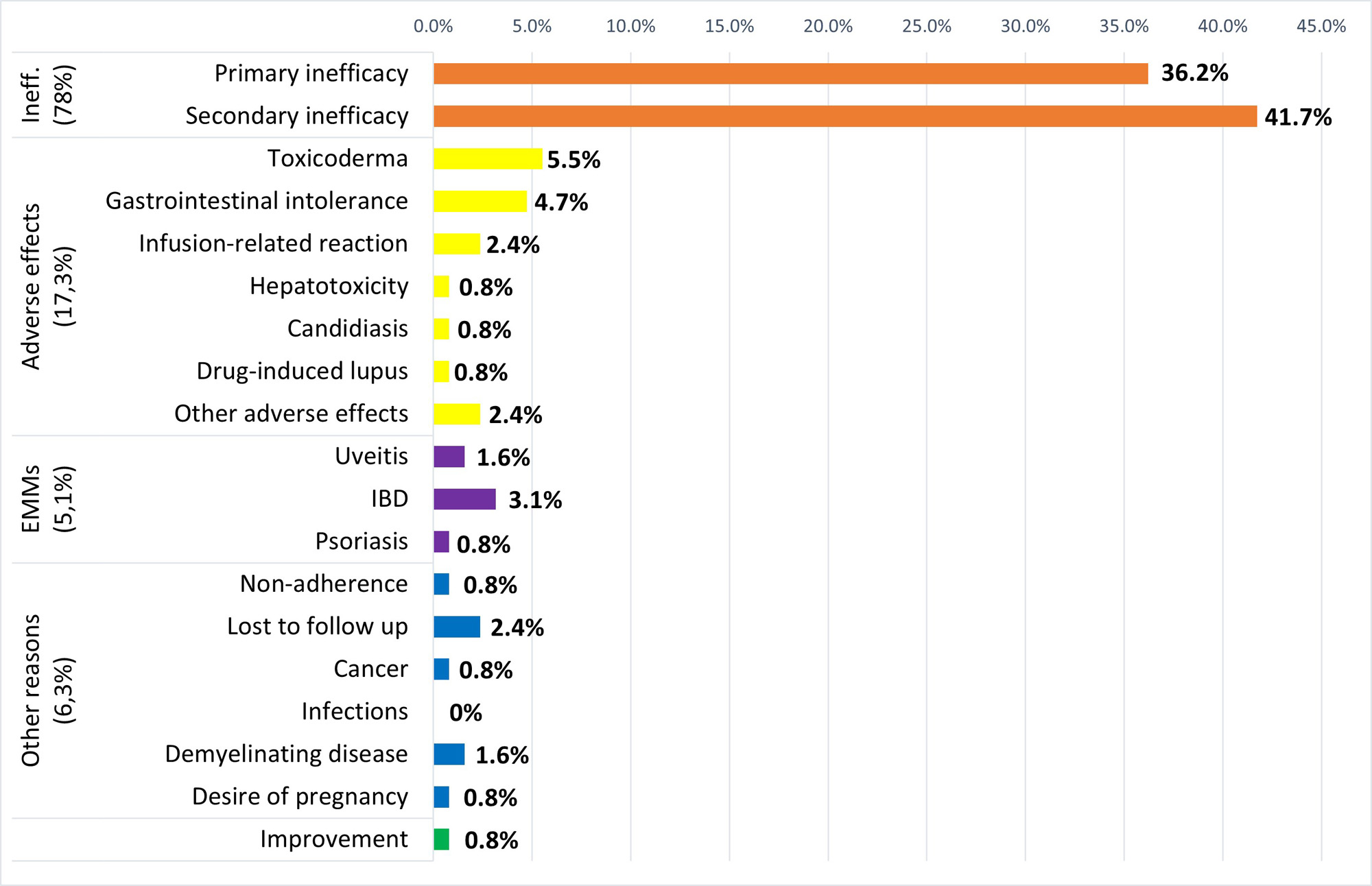
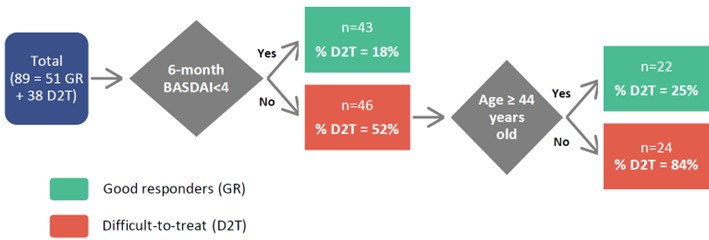
Results: Out of 101 patients included, 42 (41.6%) were classified as D2T and 59 (58.4%) as GR. D2T patients were more frequently HLA-B27 negative and smokers, had significant shorter symptom duration and more enthesitis, IBD, concomitant NSAIDs and comorbidities (hypertension, dyslipidemia, depression or anxiety and fibromyalgia) (Table 1). However, no significant differences were found in age, sex, BMI, dactylitis, arthritis, uveitis, psoriasis, concomitant csDMARDs, diabetes mellitus or cardiopathy. Furthermore, while no differences were found for disease activity composite measures (ASDAS, BASDAI) and CRP or ESR at baseline, D2T patients had greater scores in BASDAI questions for pain and morning stiffness, TJC, PtGA and PhyGA. After 6 months of starting the first bDMARD, the scores for all disease activity measures, including ASDAS, BASDAI, CRP and ESR were significantly higher in D2T patients. Reasons for b/tsDMARDs discontinuation in D2T patients are shown in Figure 1. Two different multivariable models were obtained due to collinearity between ASDAS and BASDAI/CRP.These multivariable logistic regression models showed that 6-month BASDAI (odds ratio [OR]=1.49, p=0.001) and 6-month CRP (OR=1.15, p< 0.05) or 6-month ASDAS (OR=3.16, p< 0.001) were independently associated with D2T-axSpA. The CART model (Figure 2), incorporating 6-month BASDAI and age at diagnosis, demonstrated the best predictive performance, with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.84 (95% confidence interval 0.87-1).
Conclusion: D2T-axSpA patients often have known predictors of poor therapeutic response (smoking and HLA-B27 negative) and worse response to first bDMARD already after 6 months. Disease activity at this point is independently associated with failure to consecutive b/tsDMARDs. The proposed CART model is simple to apply and useful for predicting D2T-axSpA after 6 months of bDMARD therapy.
References:
1. Smolen JS, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Juárez M, Benavent D, Navarro-Compán V, Díaz-Almirón M, Novella-Navarro M, Peiteado D, Villalba A, Monjo I, Nuño L, Balsa A, Plasencia-Rodríguez C. The Challenge of Identifying Difficult-To-Treat Axial Spondyloarthritis in Clinical Practice: Results from La Paz-SpA Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-challenge-of-identifying-difficult-to-treat-axial-spondyloarthritis-in-clinical-practice-results-from-la-paz-spa-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-challenge-of-identifying-difficult-to-treat-axial-spondyloarthritis-in-clinical-practice-results-from-la-paz-spa-cohort/