Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1554–1578) Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Few studies have assessed patient-reported outcome measures in Takayasu arteritis (TAK), a rare large vessel vasculitis. We prospectively analysed fatigue and fibromyalgia in TAK and its relationship with disease activity in a large cohort of TAK from India.
Methods: Patients with TAK satisfying ACR 1990 criteria or 2012 Chapel Hill consensus conference definition for TAK and age- and gender-similar healthy controls (HC) were enrolled after written informed consent. Disease activity scores (using DEI.TAK, ITAS2010 and NIH disease activity scores), fatigue [using Multidimensional Fatigue Inventory (MFI), FACIT Fatigue Scale (Version 4)] and fibromyalgia (using 2019 American College of Rheumatology diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia) were assessed at baseline and 6 months.
TAK were compared with healthy controls using unpaired student’s t-test or Chi squared test. Comparisons between TAK at baseline and at 6 months follow-up were performed using paired student’s t-test or Chi squared test. Pearson’s correlation coefficient was computed for the association of fatigue and fibromyalgia scores with disease activity scores. p values < 0.05 were considered as statistically significant.
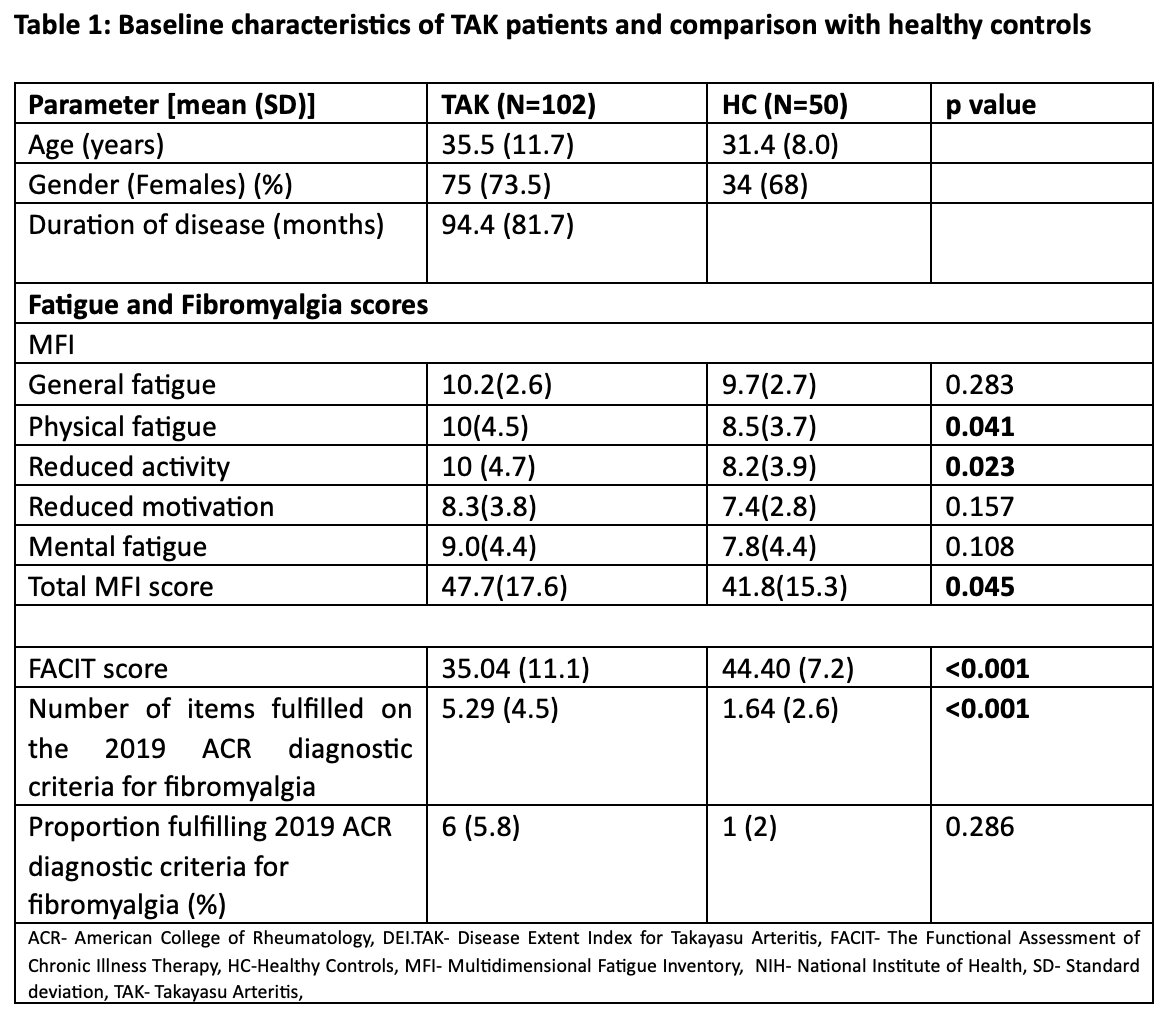
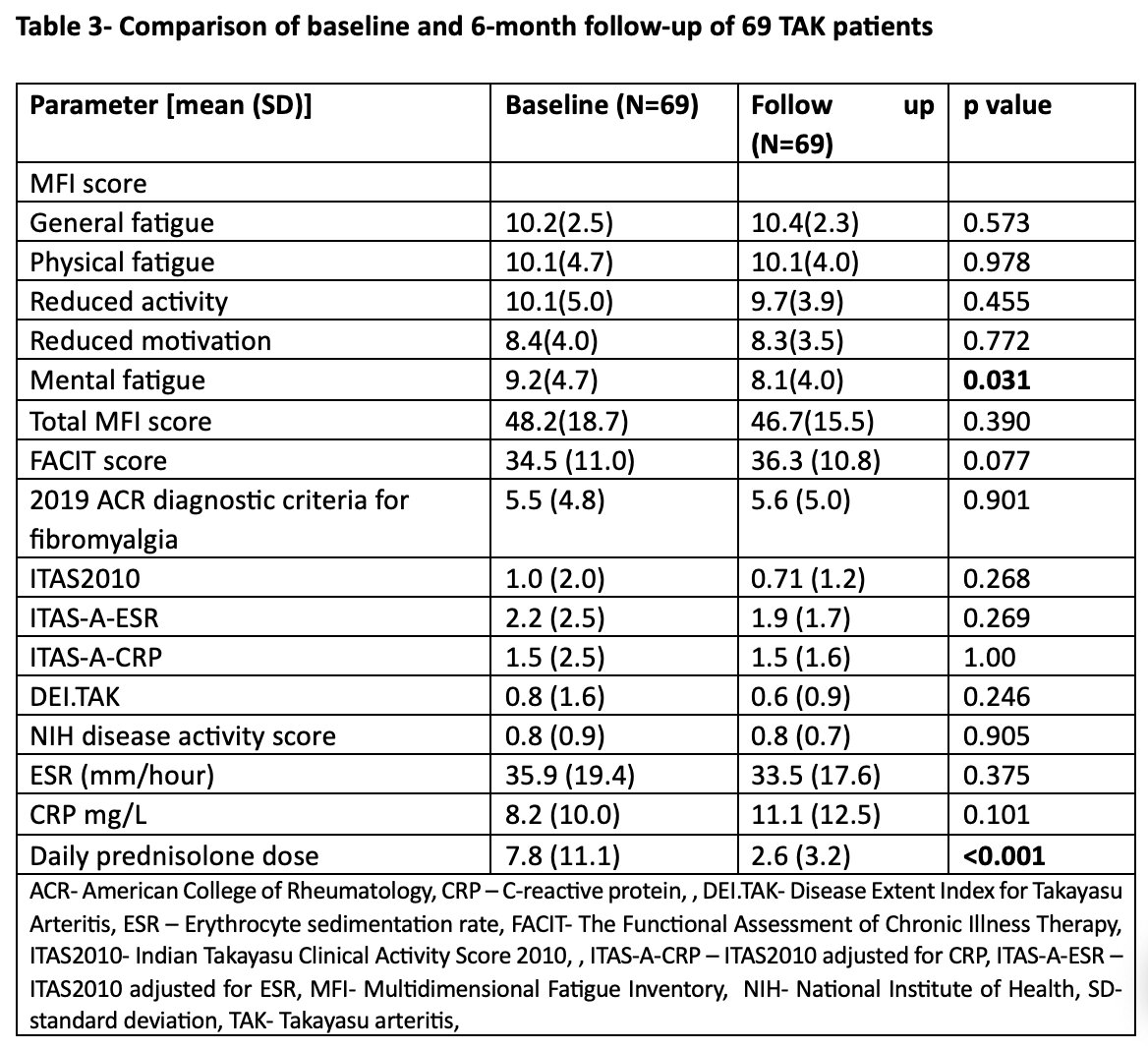
Results: One hundred and two TAK patients (Females-73.5%, mean age-35.5 years, mean disease duration-94.4 months) and fifty healthy controls (Females-68%, mean age-31.4 years) were enrolled. Hata’s Type V was the most common angiographic subtype (63.7%) and 17.6% had active disease as per physician global assessment. TAK had greater severity of fatigue than HC [MFI (p= 0.045), FACIT (p =< 0.001), lower FACIT scores indicate greater fatigue]. The prevalence of fibromyalgia was similar between TAK and HC (p=0.286) (Table 1). Active TAK had higher fatigue scores [MFI (p= 0.002), FACIT (p=0.033)] than inactive TAK (Table 2). At baseline, MFI had weak positive correlation (r=0.231, p=0.019) & FACIT score had weak negative correlation (r=-0.226, p =0.022) with NIH disease activity score but not with ITAS 2010 or DEI TAK. The number of items on the 2019 ACR diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia showed a weak positive correlation with ITAS 2010 (r=0.230, p=0.020), DEI TAK (r=0.227, p=0.022), and NIH disease activity score (r=0.285, p=0.004). No difference was observed in fatigue or fibromyalgia scores at six months of follow-up (Table 3).
Conclusion: Fatigue was more prevalent in TAK than in healthy controls, and correlated with TAK disease activity. Fibromyalgia did not differ between TAK and controls. Fatigue and fibromyalgia remained similar in TAK over time.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Thakare D, Rathore U, Singh K, Agarwal V, Misra D. Takayasu Arteritis Is Associated with Worse Fatigue Than Healthy Controls Which Persists over Time – A Longitudinal Cohort Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/takayasu-arteritis-is-associated-with-worse-fatigue-than-healthy-controls-which-persists-over-time-a-longitudinal-cohort-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/takayasu-arteritis-is-associated-with-worse-fatigue-than-healthy-controls-which-persists-over-time-a-longitudinal-cohort-study/