Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: 4M119: Sjögrenʼs Syndrome – Basic & Clinical Science (1902–1907)
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Primary Sjögren’s syndrome (pSS) is the second most frequent systemic autoimmune disease affecting 0.1% of the general population. No specific immunomodulatory drug has demonstrated efficacy for this disease, and no biomarker is available to identify patients at risk of developing systemic complications. To enable a precision medicine approach, we explored the molecular stratification of the disease in an unsupervised systems biological manner.
Methods: Blood transcriptomes and genotypes of 351 pSS patients from a multi-center prospective clinical ASSESS cohort were analyzed. Clinical phenotype, immunological profile and yearly follow-up of disease course for 5 years of these patients were carefully assessed. Replication of the transcriptomic results was performed using 3 independent cohorts (n= 523 patients). Circulating IFN-alpha (IFNɑ) and IFN-gamma (IFNγ) protein concentrations were determined using ultrasensitive digital ELISA (SIMOA) and patients were genotyped using Immunochip in the ASSESS cohort.
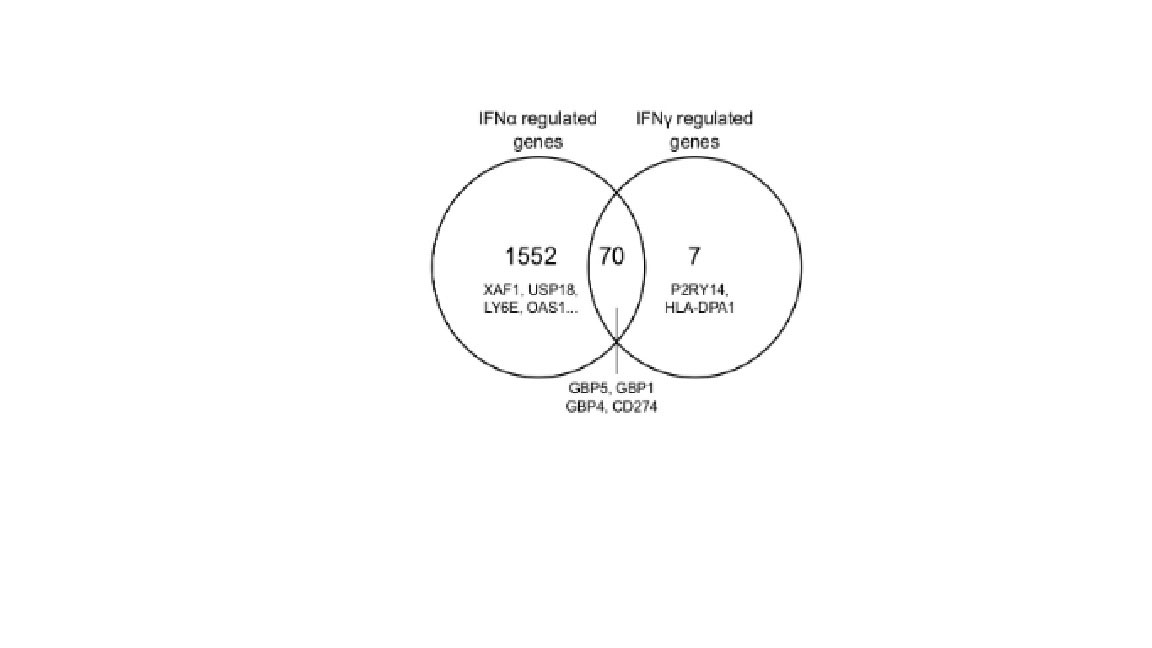
Results: Transcriptomic analysis of the prospective cohort enabled patient stratification that matched clinical assessments, and showed a strong IFN gene signature in more than half of the patients. This finding was replicated in three independent cohorts. As gene expression analysis did not discriminate between type I and II interferons, we applied digital ELISA to assess serum levels of IFNγ. The IFN transcriptomic signature was regulated by circulating IFNɑ, and not IFNγ, protein levels. 95% of the interferon-inducible genes (1552 genes) were specifically modulated by serum IFNα concentration, while only 7 genes were specifically regulated by serum IFNγ concentration. 70 genes were regulated by both IFNα and IFNγ concentrations (Figure 1).
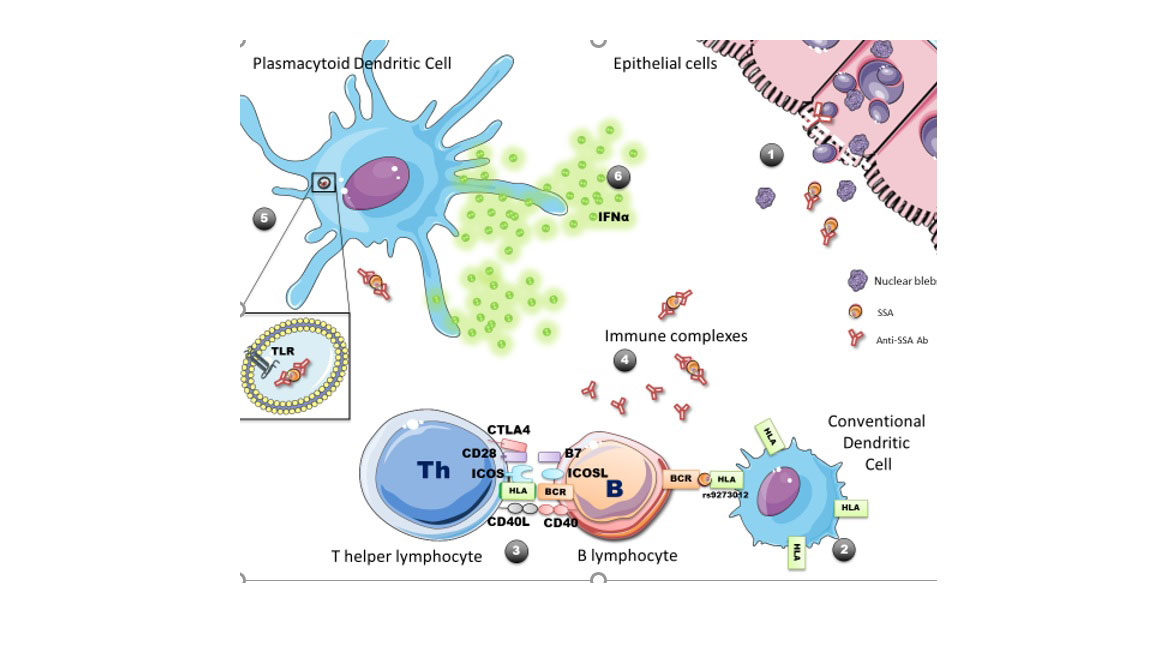
IFNɑ protein levels, detectable in 75% of patients, were significantly associated with clinical and immunological features of disease activity at enrollment (association with anti-SSA: p= 5.09*10-28, anti-SSB: p= 2.45*10-14, RF: R=0.662, p = 1.19 × 10–41) . At enrolment, the mean ESSDAI was higher (4 [0-31] versus 2[1-18], p=0.0004) in patients with detectable IFNɑ blood levels. During the 5-year follow-up, patients with detectable IFNɑ blood levels more frequently developed systemic complications (OR 1.54 [1.14; 2.13]). Genetic analysis revealed a significant association between a specific MHC-II HLA-DQ locus genotype (HLA-DQA1*05:01 allele), anti-SSA antibody (p=4.31 × 10–12) and circulating IFNɑ protein (p=1.70 × 10–8). In multivariate analysis, both HLA DQA1*05:01 and anti-SSA positivity were independently associated with IFNɑ blood concentrations (OR 3.24 [1.78-5.88], p< 0.001, OR 3.08 [1.80-5.29], p< 0.001, respectively). Analyses in healthy controls, and in anti-SSA positive patients using Cytof, suggested that this HLA gene polymorphism acts through upregulation of HLA II molecules on conventional DCs (Figure 2).
Conclusion: This large systems biology analysis emphasizes the crucial role of circulating IFNα in pSS. In addition, we report a new pathogenic mechanism underlying the associations between HLA predisposition, autoantibody production, cytokine secretion and systemic complications of autoimmunity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bost P, Mariette X, Bondet V, Llibre A, Posseme C, Charbit B, Thorball C, Jonsson R, Lessard C, Felten R, Ng F, Silvis K, Chatenoud L, Dumortier H, Fellay J, Brostadt K, Appel S, Tarn J, Quintana-Murci L, Minguenau M, Meyer N, Duffy D, Schwikowski B, Gottenberg J. Systems Biology in 874 Patients with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome Indicates the Predominant Role of Interferon Alpha Compared to Interferon Gamma, Its Association with Systemic Complications, and a New Aspect of the Genetic Contribution of HLA [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/systems-biology-in-874-patients-with-primary-sjogrens-syndrome-indicates-the-predominant-role-of-interferon-alpha-compared-to-interferon-gamma-its-association-with-systemic-complications-and-a-new/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/systems-biology-in-874-patients-with-primary-sjogrens-syndrome-indicates-the-predominant-role-of-interferon-alpha-compared-to-interferon-gamma-its-association-with-systemic-complications-and-a-new/