Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose
Compared to the general population, patients (pts) with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) suffer greater amounts of disability and substantially lower employment rates.1 The previous results from the RAPID-PsA study indicate significant improvements in work and household productivity and social participation with certolizumab pegol (CZP) vs placebo (PBO) up to Week (Wk) 24, which were maintained to Wk48.2 The purpose of this report is to examine the long-term effect of CZP on workplace and household productivity in RAPID-PsA up to Wk96.
Methods
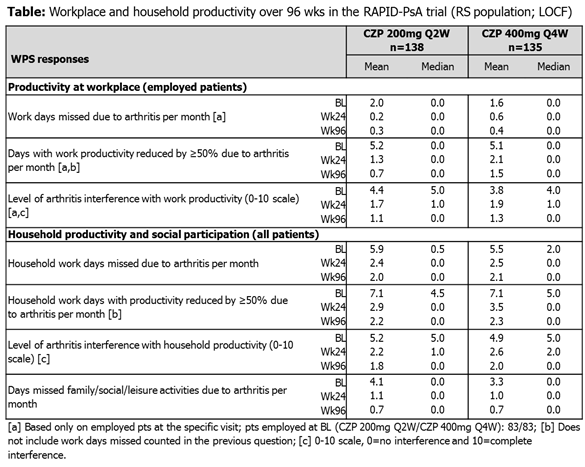
The ongoing RAPID-PsA trial (NCT01087788) is double-blind and PBO-controlled to Wk24, dose-blind to Wk48 and open-label to Wk216.3 Pts had active PsA and had failed ≥1 DMARD. Pts originally randomized to CZP (200mg Q2W or 400mg Q4W, following 400mg loading dose [LD] at Wks 0, 2, 4) continued on their assigned dose in the OLE; PBO pts entering dose-blind phase were re-randomized to CZP LD followed by CZP 200mg Q2W or 400mg Q4W after Wk24 or, for non-responders, Wk16. The validated arthritis-specific Work Productivity Survey (WPS),4 administered Q4W from baseline (BL), assessed the impact of PsA on workplace and household productivity in the randomized set (RS). WPS responses (LOCF imputation) in pts originally randomized to CZP groups are summarized descriptively over 96 wks.
Results
409 pts were randomized, of which 273 were assigned to CZP 200mg Q2W or CZP 400mg Q4W. Of the pts randomized to CZP, 91% completed Wk24, 87% Wk48 and 80% Wk96; 60.1% and 61.5% were employed at BL in the CZP 200mg Q2W and CZP 400mg Q4W groups, respectively. At BL, pts randomized to CZP reported on average ~1 wk of paid work, ~2 wks of household duties, and mean 3.7 days of social activities affected over previous month. In employed pts in both CZP groups, decreases in absenteeism and presenteeism reported to Wk24 were continued up to Wk96 (Table). The initial improvements in household productivity and increased participation in social activities reported in both CZP groups over 24 wks were maintained up to Wk96 (Table).
Conclusion
The initial improvements with CZP in workplace and household productivity, and participation in social activities were sustained up to 96 wks, suggesting long-term productivity benefits of CZP treatment in PsA pts.
References
1. Mau W. J Rheumatol 2005;32:721-728
2. Kavanaugh A. Arthritis Rheum 2013;65(10):326
3. Mease P. Ann Rhuem Dis 2014;78(1):48-55
4. Osterhaus J. Arth Res Ther 2014 [In press]
Disclosure:
A. Kavanaugh,
Abbott, Amgen, BMS, Pfizer, Roche, Janssen, UCB Pharma,
2;
D. D. Gladman,
Abbott, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Johnson & Johnson, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB Pharma,
2,
Abbott, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Johnson & Johnson, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB Pharma,
5;
D. van der Heijde,
AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Augurex, BMS, Celgene, Centocor, Chugai, Covagen, Daiichi, Eli-Lilly, Galapagos, GSK, Janssen Biologics, Merck, Novartis, Novo-Nordisk, Otsuka, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, Schering-Plough, UCB, Vertex,
5,
Imaging Rheumatology bv,
9;
O. Purcaru,
UCB Pharma,
3;
P. J. Mease,
(Abbott) AbbVie, Amgen, BiogenIdec, BMS, Celgene, Crescendo, Genentech, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Pharma, Vertex.,
2,
(Abbott) AbbVie, Amgen, BiogenIdec, BMS, Celgene, Covagen, Crescendo, Genentech, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Pharma, Vertex,
5,
(Abbott) AbbVie, Amgen, BiogenIdec, BMS, Crescendo, Genentech, Janssen, Lilly, Pfizer, UCB Pharma.,
8.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sustained-improvements-in-workplace-and-household-productivity-and-social-participation-with-certolizumab-pegol-over-96-weeks-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/