Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Clinical Poster II: Clinical/Epidemiology Studies
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
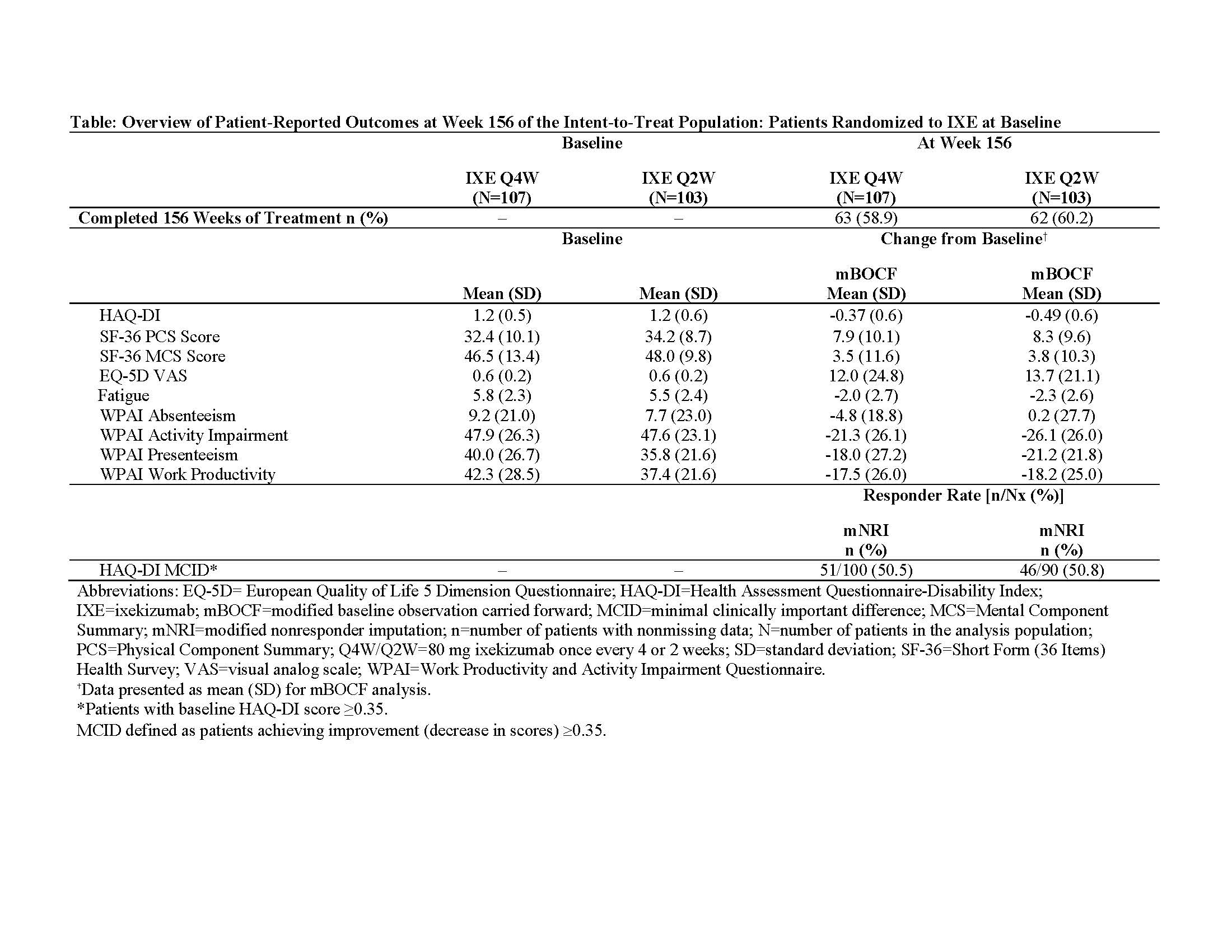
Background/Purpose: Ixekizumab (IXE), a high-affinity mAb that selectively targets IL-17A, has shown improvements compared to placebo not only in disease activity but also in various patient-reported outcomes (PROs) assessing physical function, fatigue, quality of life, and work productivity in PsA patients treated for 24 weeks.1 Herein, we report the effects of treatment with IXE on these PROs after up to 3 years of treatment.
Methods: In SPIRIT-P11 (NCT01695239), a Phase 3 trial, 417 biologic-DMARD-naive patients with active PsA were randomized to IXE 80 mg every 4 weeks (IXE Q4W; N=107) or every 2 weeks (IXE Q2W; N=103), adalimumab 40 mg every 2 weeks (ADA; N=101), or placebo (PBO; N=106) in the double-blind treatment period (Weeks 0-24). Both IXE regimens had a starting dose of 160 mg. Results are reported from a subset of the intent-to-treat population defined as patients randomized to IXE at baseline (Week 0). The following PROs were assessed in the study (during Weeks 0-156): HAQ-DI (minimally clinically important difference [MCID]: improvement ≥0.35 from baseline), medical outcomes survey Short Form-36 (SF-36) Physical and Mental Component Summary (PCS and MCS), European Quality of Life 5 Dimensions Visual Analog Scale (EQ-5D VAS; 0-100 scale), fatigue Numeric Rating Scale (NRS; 0 [no fatigue] to 10 [as bad as you can imagine] scale), and Work Productivity and Activity Impairment Questionnaire-Specific Health Problem (WPAI-SHP; absenteeism, presenteeism, work productivity, and activity impairment). Missing values were imputed by modified nonresponder imputation (mNRI) for categorical data and by modified baseline observation carried forward (mBOCF) for continuous data.
Results: Mean baseline (Week 0) scores for HAQ-DI, SF-36 (PCS and MCS), fatigue NRS, WPAI-SHP, and EQ-5D VAS (Table) indicated impaired physical function and quality of life. Patients receiving IXE up to 3 years reported improvements in SF-36 (PCS and MCS), EQ-5D VAS, fatigue NRS, and WPAI-SHP (presenteeism, work productivity, and activity impairment) (Table). The percentage of IXE patients achieving MCID for HAQ DI (improvement >0.35) was sustained at 3 years.
Conclusion: In bDMARD-naive patients with active PsA, improvements with IXE in all the measured PROs, including physical and mental function, quality of life, fatigue, and work productivity are maintained up to 3 years.
Reference:
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fleischmann R, Chandran V, Lespessailles E, Birt J, Benichou O, Erickson J, Shuler C. Sustained Improvements in Physical Function, Quality of Life, and Work Productivity after Ixekizumab Therapy in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis: 3-Year Results [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sustained-improvements-in-physical-function-quality-of-life-and-work-productivity-after-ixekizumab-therapy-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-3-year-results/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sustained-improvements-in-physical-function-quality-of-life-and-work-productivity-after-ixekizumab-therapy-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-3-year-results/