Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Treatment with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors has the effect of slowing radiographic progression by improving symptoms and reducing inflammation in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS). However, the inflammation is still not controlled in some patients even if their symptoms improve with the TNF inhibitor treatment. The purpose of this study was to analyze the relationship between inflammation and radiographic progression in patients with AS, whose symptoms were well controlled by a TNF inhibitor treatment in a real-world observational data.
Methods: Of the 1,280 patients who were followed-up for 18 years in a single center, the electronic medical data of 590 patients treated with TNF inhibitors were included. Among them, 333 patients with bath ankylosing spondylitis disease activity Index (BASDAI) < 4 measured at all the time points following the first TNF inhibitor dosing were included. From these patients, 898 intervals were obtained, which was the period of administration of the TNF inhibitor. To determine the relationship between the modified stoke ankylosing spondylitis spinal score (mSASSS) and inflammatory markers such as c-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and disease activities such as Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS)-ESR and ASDAS-CRP over time, we fitted linear mixed models with mSASSS as response variable, baseline mSASS and inflammatory marker with different lag times as fixed effects, and patients as random effects. With the inflammatory marker and the lag time with statistically significant beta coefficient, , its association with the mSASSS was further investigated with linear mixed model that includes additional clinical variables.
Results: The relationship between mSASSS and past inflammatory markers and disease activities were examined for up to 36 months using linear mixed models (Fig. 1). The cumulative sums of log CRP for the previous 18, 24, 30, and 36 months showed significantly positive correlation with mSASSS (Fig. 1E). From these results, the cumulative sum of the previous 24 months’ log CRP as the main independent variable was used in the linear mixed model with mSASSS at 24 months as the outcome (Table 1). Baseline mSASSS (b=1.047, 95% CI: 1.013 to 1.080, p< 0.001), time (b=0.466, 95% CI: 0.433 to 0.500 p< 0.001), and cumulative sum of the previous 24 months' log CRP (b=0.043, 95% CI: 0.014 to 0.071, p=0.004) were significantly associated with mSASSS at 24 months.
Conclusion: The symptoms were well controlled because BASDAI was maintained below 4; however, those with a high cumulative sum of CRP showed an increased mSASSS change. In order to slow the radiographic progression in patients with AS, inflammation rather than disease activity should be targeted and actively controlled during treatment with TNF inhibitors.
 Figure 1. Relationship between mSASSS and inflammatory markers and disease activities over time using an autoregressive model
Figure 1. Relationship between mSASSS and inflammatory markers and disease activities over time using an autoregressive model
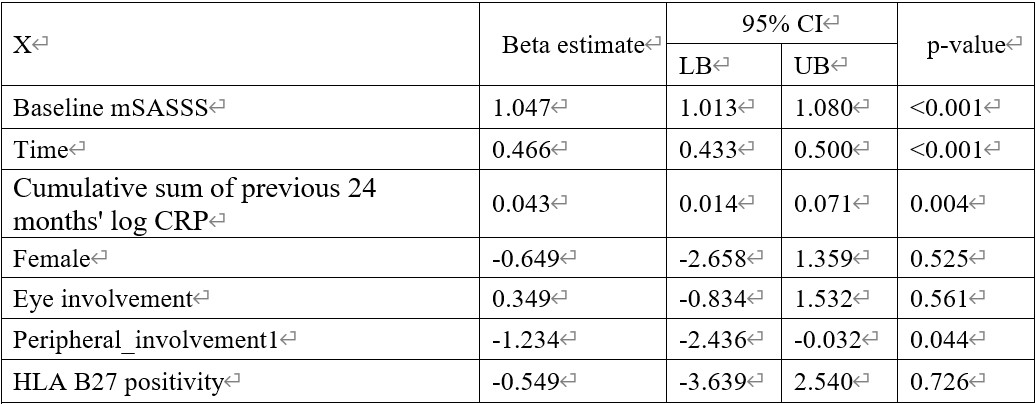 Table 1. Linear mixed model with the cumulative sum of log CRP up to 24 months as main independent variable and mSASSS at 24 months as outcome
Table 1. Linear mixed model with the cumulative sum of log CRP up to 24 months as main independent variable and mSASSS at 24 months as outcome
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Koo B, Oh J, Park S, Shin J, Nam B, Lee S, Joo K, Kim T. Suppressing Inflammation Rather Than Lowering the Disease Activity Score Should Be Targeted During TNF Inhibitor Treatment to Slow Radiographic Changes in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/suppressing-inflammation-rather-than-lowering-the-disease-activity-score-should-be-targeted-during-tnf-inhibitor-treatment-to-slow-radiographic-changes-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/suppressing-inflammation-rather-than-lowering-the-disease-activity-score-should-be-targeted-during-tnf-inhibitor-treatment-to-slow-radiographic-changes-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis/
