Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD) is heterogeneous, with varying degrees of severity and risk of disease progression. No consensus-based definitions of disease severity, progression, or risk of progression exist. The purpose of this study was to use expert classification of real-world cases of SSc-ILD to derive definitions of SSc-ILD subsets that can be incorporated into clinical practice and trials.
Methods: All patients included in this study met American College of Rheumatology Criteria for Systemic Sclerosis (N=80).
Patient profiles were developed from participants in the Scleroderma Lung Study-II and ILD patients seen at a Scleroderma Center. Experts in rheumatology, pulmonary medicine, radiology, and members of the OMERACT CTD-ILD Working Group 1 provided key domains to be included in profiles. These included information on demographics, disease features (limited vs. diffuse SSc, ANA status, antibody status), pulmonary function testing, patient-reported assessments, and quantitative analysis of lung involvement on high resolution computerized tomography of the chest (HRCT) for baseline profiles; and for those with follow-up data, how these measures change over time.
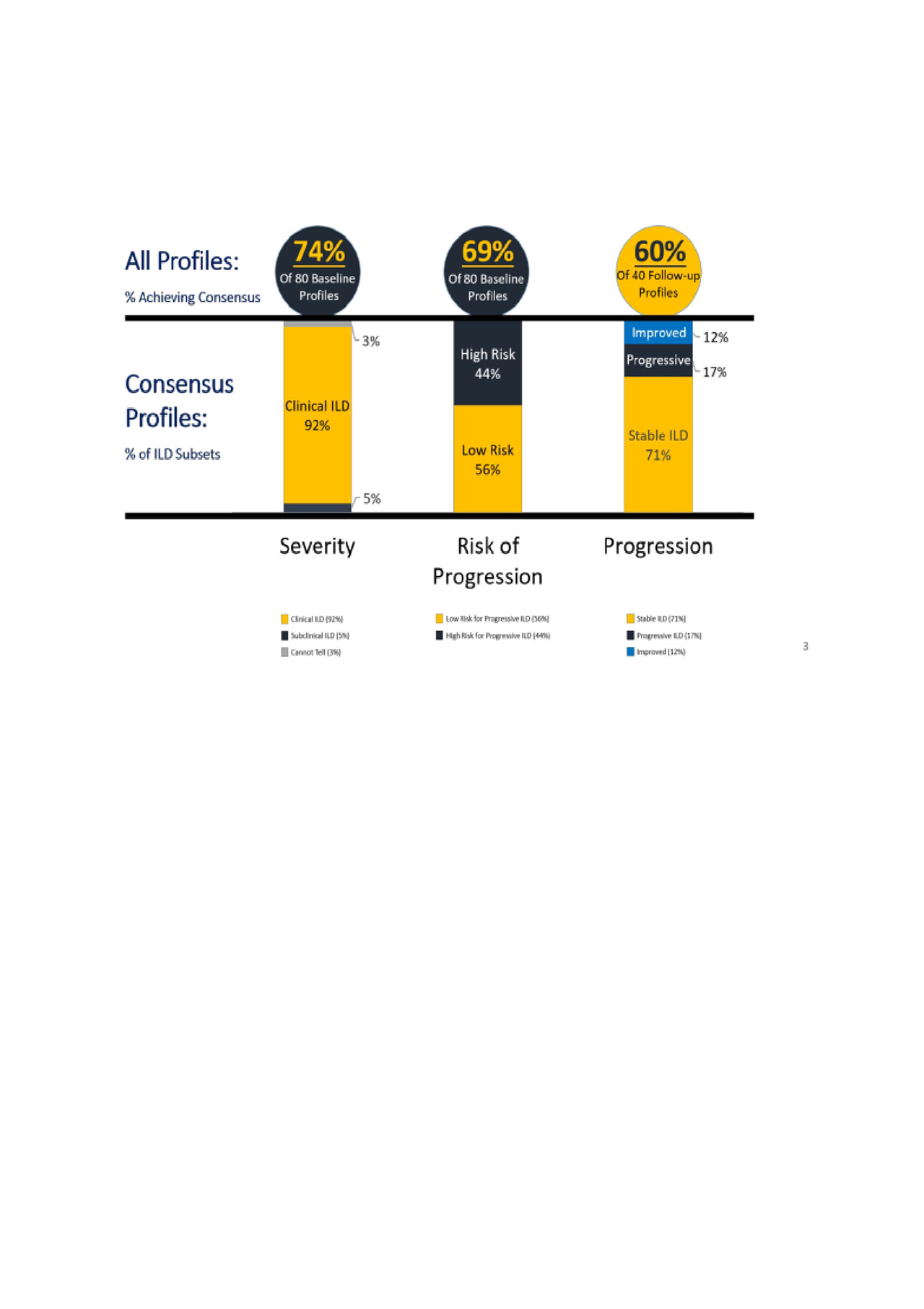
Eighty-three ILD experts were surveyed for classification of 80 baseline and 40 follow-up profiles. Baseline profiles were classified based on: 1- Severity (clinical vs. subclinical) and 2- Risk of Progression (low vs. high); follow-up profiles were classified on 3- Progression over time (stable vs. progressive vs. improved). Each profile was rated by a minimum of 4 experts; consensus on a classification was achieved with 75% concordance. For each profile, experts provided input on the top features that helped in making their classification decision.
Results: Fifty percent (N=42) of invited experts, from 10 countries, completed the survey.
Along the dimensions of severity, risk of progression, and progression, a majority of profiles achieved consensus ratings (Figure). Of those profiles achieving consensus, the majority were classified as “clinical ILD”, “low risk”, and “stable”. Table provides a ranking of the most influential features used in classification on these dimensions.
Conclusion: These data represent the first step in creating operational definitions for ILD subsets. This expert-derived classification advances the characterization of a subset of severity (clinical ILD), subsets of risk of progression (low and high risk), and a subset of progression (stable ILD).
Features used to classify profiles on severity and progression overlapped (forced vital capacity, whole lung involvement on HRCT, dyspnea ratings), whereas the risk of progression was influenced by disease duration, type of SSc, and SSc autoantibodies in addition to the measures endorsed for severity and progression.
The next steps are to reach operational definitions for those ILD subsets not yet reaching consensus (subclinical ILD, progressive ILD, improved ILD).
REFERENCES
- Khanna, D. et al. J. Rheumatol. 42, 2168–2171 (2015)
Acknowledgment: Dr. D. Khanna is funded by NIH/NIAMS K24 AR063120 and RO1 AR070470
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Roofeh D, Brown K, Tashkin D, Assassi S, Barratt S, Bernstein E, Bhatt N, Chung L, Collard H, Conway R, Dellaripa P, Denton C, Distler O, Domsic R, Doyle T, Garcha P, Gupta N, Hoffmann-Vold A, Hsu V, Ingegnoli F, Johannson K, Kahaleh B, Kawano-Dourado L, Kazerooni E, Khanna S, Korsten P, Lin C, Maher T, Mathai S, Martinez F, Matteson E, Nagaraja V, Oddis C, Ovalles-Bonilla J, Pauling J, Raghu G, Rodriguez-Pinto I, Rosas I, Seibold J, Steen V, Strand V, Volkmann E, Vummidi D, Walsh S, Zoz D, Wells A, Khanna D. Subsets in Systemic Sclerosis-ILD: Working Towards Consensus-Based Definitions [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/subsets-in-systemic-sclerosis-ild-working-towards-consensus-based-definitions/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/subsets-in-systemic-sclerosis-ild-working-towards-consensus-based-definitions/