Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, and Attitudes Poster I: Patient-Reported Outcomes
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Subjective well-being (SWB) is a psychological construct that is synonymous with happiness. Many variables including age, sex, income, employment, and marital status are related to SWB. Health is also an important determinant of SWB that can be adversely affected in patients with chronic conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In this study, we evaluated the SWB of RA patients and compared it with that of healthy controls.
Methods:
We obtained the original dataset from the Quality of Life Survey, 2013, which was conducted by the Economic and Social Research Institute, Cabinet Office, Government of Japan. In this survey, SWB was determined by asking participants to rate their happiness on a scale from 0 (very unhappy) to 10 (very happy). The survey also included a 56-point questionnaire regarding variables related to well-being. This questionnaire was administered to RA patients recruited from Kobe University Hospital. Clinical data regarding disease duration, stage, class, disease activity, health activity, complications, and treatment data were collected simultaneously.
Results:
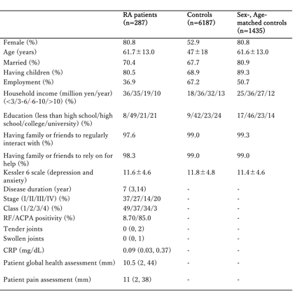
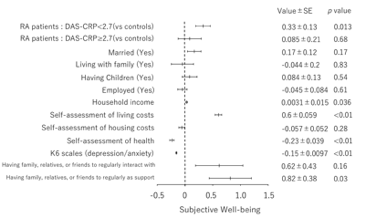
Multivariate analysis revealed that RA patients had significantly better SWB than age- and sex-matched controls (p = 0.025). In addition, RA patients with high or moderate disease activity had SWB scores that were similar to those of controls. However, the SWB scores of RA patients in remission or with low disease activity were higher than those of controls (p=0.013). SWB was associated with household income, financial status, psychological distress, self-assessment of health, and social connection.
Conclusion:
For RA patients, achieving the therapeutic target can result in better SWB. Socioeconomic factors, financial status, psychological stress, self-assessment of health, and social network are also important for better SWB of RA patients.
Table Summary of demographic characteristics of the study cohort
Figure
When RA patients were stratified according to the degree of disease activity (DAS28-CRP _ 2.7 vs DAS28-CRP < 2.7), multivariate analysis shows that RA patients with DAS_2.7 had SWB scores similar to those of controls. However, the SWB of RA patients with DAS<2.7 was higher than that of controls. SWB was also associated with socioeconomic factors, psychological stress, self-assessment of health and social network.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kageyama G, Onishi A, Ueda Y, Akashi K, Sendo S, Saegusa J, Morinobu A. Subjective Well-Being Among Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/subjective-well-being-among-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/subjective-well-being-among-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/