Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Secukinumab (SEC), a fully human anti-interleukin-17A monoclonal antibody, significantly improved signs and symptoms and inhibited radiographic progression versus placebo (PBO) at Week (Wk) 24 in patients (pts) with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in the FUTURE 5 (NCT02404350) study.1 Here, we report the effects of SEC on radiographic progression, additional efficacy endpoints and safety through 52 wks in the FUTURE 5 study.
Methods: Pts (N=996) with active PsA, were randomized (2:2:2:3) to subcutaneous (sc) SEC 300mg with loading dosage (LD; n=222), 150mg with LD (n=220), 150mg without LD (n=222), or PBO (n=332). All groups received SEC or PBO at baseline (BL), Wks 1, 2, 3, and 4, and then every 4 wks. At Wk 16, PBO non-responders were switched to SEC 300mg or 150mg; remaining PBO pts were switched at Wk 24. Radiographic progression, as assessed by mean change in van der Heijde-modified total Sharp score for PsA (mTSS), was based on hand/wrist/foot radiographs obtained at BL, Wk 16 (non-responders), Wk 24 and Wk 52, assessed by two blinded readers (plus an adjudicator if required). Pts were stratified based on anti-TNF status (naïve/inadequate response [IR]). Radiographic data was analyzed by linear extrapolation at Wk 24 for all PBO non-responders and for all other pts with missing Wk 24 radiographs; Wk 52 radiographic data are based on observed data. In addition, radiographic data for the overall population was analyzed by linear mixed effects model at Wk 24. Additional assessments at Wk 52 included ACR20/50, PASI75 and resolution of dactylitis and enthesitis. Statistical analyses used non-responder imputation for these clinical variables. Safety analyses included all pts who received ≥1 dose of SEC.
Results: 91.9% (204/222; 300mg LD), 91.4% (201/220; 150mg LD) and 86.9% (193/222; 150mg No LD) pts completed 52 wks of treatment. Inhibition of radiographic progression was sustained through 52 Wks (Table). Proportions of pts with no radiographic progression (change from BL in mTSS ≤0.5) with SEC at 52 Wks were 92% (300 mg LD), 85% (150 mg LD), and 87% (150 mg No LD). Mean changes from baseline in mTSS by linear mixed effects model at Wk 24 were 0.03 (P<0.01; 300mg LD), 0.14 (P<0.05; 150mg LD) and -0.10 (P<0.001; 150mg No LD) vs. 0.51 (PBO). Clinical responses were also sustained or improved through 52 Wks (Table). Over the study (mean SEC exposure of 309.0 days), exposure adjusted incidence rates with SEC for selected AEs were: serious infections (1.6), Candida infections (2.2), crohn’s disease (0.2), ulcerative colitis (0.1), major adverse cardiovascular event (0.2) and malignant/unspecified tumors (0.5).
Conclusion: Secukinumab provided sustained inhibition of radiographic progression through 52 wks. Clinical responses were also sustained or improved through 52 wks. The safety profile was consistent with that previously reported.1
References: 1. Mease PJ, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:890-897.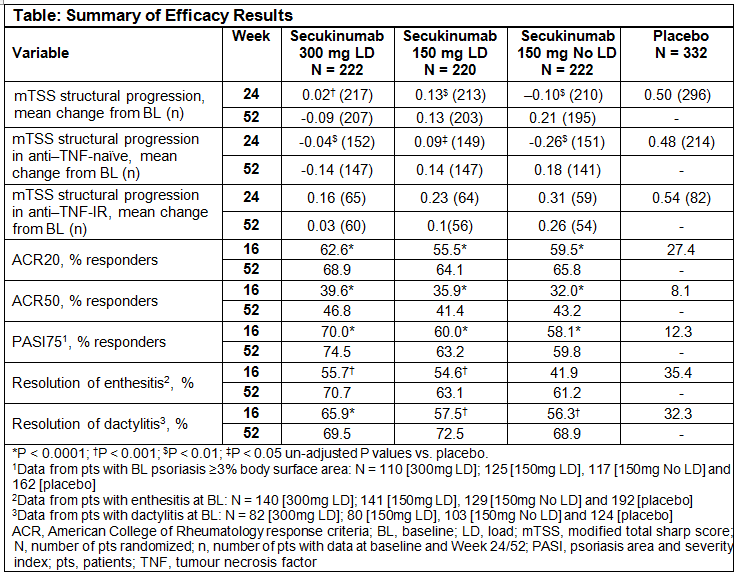
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease PJ, van der Heijde D, Landewé RBM, Mpofu S, Rahman P, Tahir H, Singhal A, Böttcher E, Navarra SV, Zhu X, Readie A, Pricop L, Abrams K. Subcutaneous Secukinumab Provides Sustained Inhibition of Radiographic Progression in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis: 52-Week Results from a Phase 3 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/subcutaneous-secukinumab-provides-sustained-inhibition-of-radiographic-progression-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-52-week-results-from-a-phase-3-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/subcutaneous-secukinumab-provides-sustained-inhibition-of-radiographic-progression-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-52-week-results-from-a-phase-3-study/
