Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
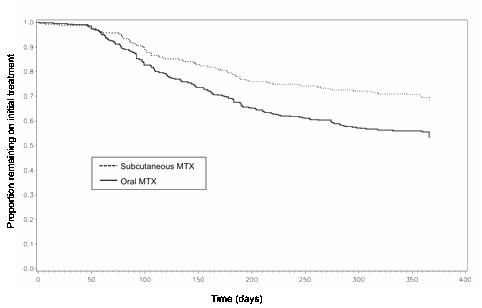
Results: 674 patients were included (418 oral MTX, 256 sc MTX); mean age 53, 72% female, mean symptom duration 5.2 months, mean baseline DAS-28 5.5. Patients treated with sc MTX were less likely to receive other DMARDs (56% vs. 71%, p<0.01), and had a higher mean starting dose of MTX (23 mg vs. 17 mg, p<0.01). Other characteristics were similar between groups. Unadjusted Kaplan-Meier curves showed significantly improved survival with sc MTX (figure 1, log-rank p<0.001). After adjusting for confounders the association remained significant (Hazard ratio (HR) for treatment failure: 0.58 (95%CI: 0.37-0.92, p=0.02). Older age (HR: 0.98 (95%CI: 0.97-0.99) per year of age) and the use of other DMARDs in combination (HR: 0.53 (0.35-0.81)) were also associated with improved survival. The starting dose of MTX (HR: 0.98 (0.94-1.02)) and all other covariates demonstrated no significant association.
Disclosure:
G. S. Hazlewood,
None;
J. C. Thorne,
None;
J. E. Pope,
None;
J. Xiong,
None;
G. Boire,
None;
B. Haraoui,
None;
C. A. Hitchon,
None;
E. C. Keystone,
None;
D. Tin,
None;
V. P. Bykerk,
Amgen, Pfizer,
2,
, Roche, UCB, BMS, Abbvie, Janssen ,
2.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/subcutaneous-delivery-of-methotrexate-is-associated-with-improved-treatment-survival-compared-to-oral-administration-for-the-initial-treatment-of-patients-with-early-rheumatoid-arthritis/