Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Methotrexate (MTX) is commonly used in the treatment of RA, psoriasis, and psoriatic arthritis. Subcutaneously administered MTX is well absorbed and appears to overcome the problems associated with oral administration, including variable absorption and saturation of the absorption mechanism with increasing doses.
The purpose of this study was to investigate the relative bioavailability of MTX administered by subcutaneous (SC) injection with a prefilled MTX autoinjector pen (MTX pen) as compared to oral administration.
Methods: A single center, open label, randomized, 2-period, 2-sequence, single dose crossover study in 4 dose groups (7.5 mg, 15 mg, 22.5 mg, and 30 mg) with healthy subjects aged 18 to 55 years. A subject participated in only 1 of the 4 dose groups and received a single dose of the test product (MTX pen) and the reference product (methotrexate tablets, USP (Dava)). Pharmacokinetic blood samples were collected predose and at 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 16, 24, and 48 h postdose.
Results:
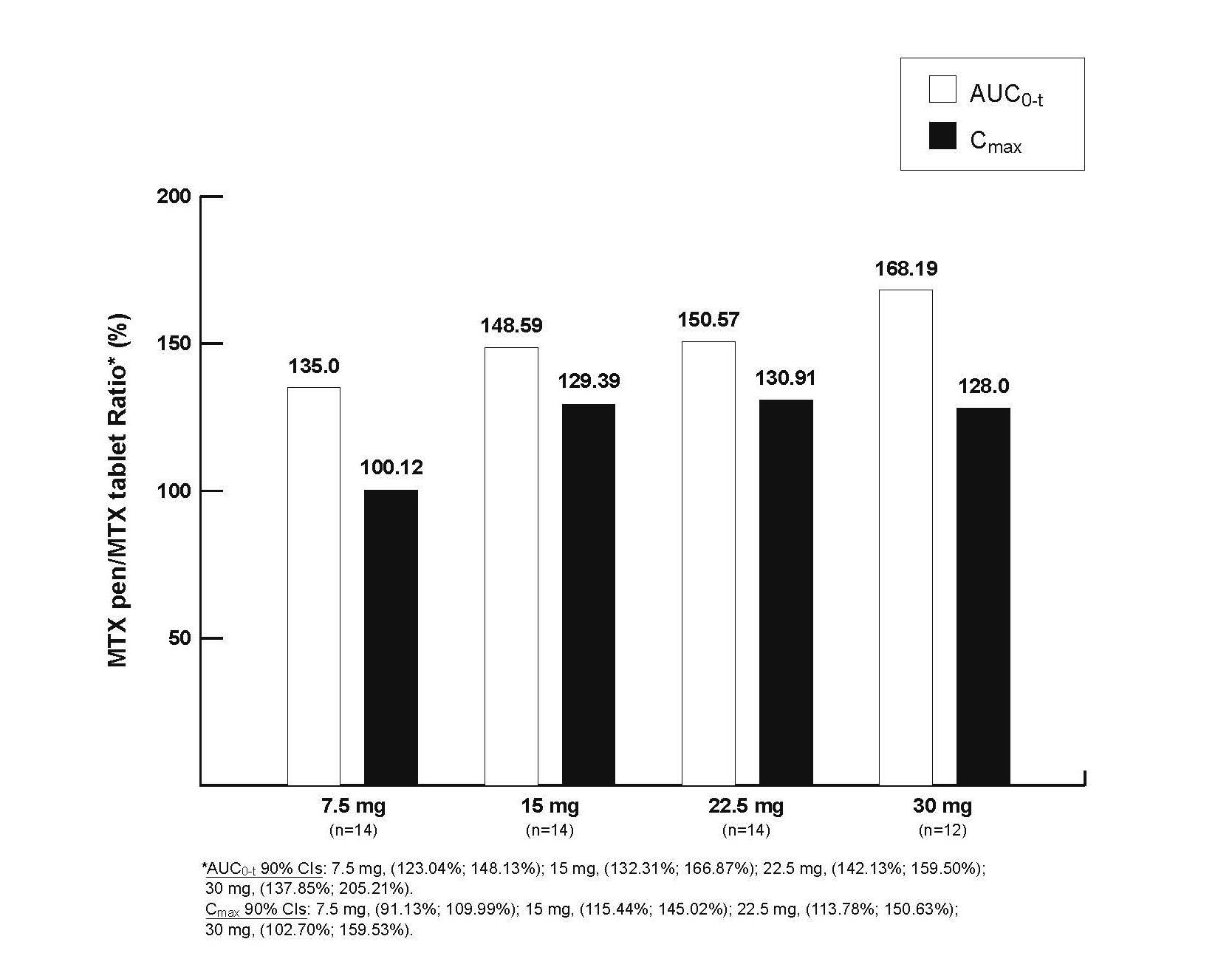
Bioavailability of MTX administered SC with the MTX pen compared with MTX tablets
|
Dose
|
MTX pen AUC0-t (h·ng/mL) |
MTX tablet AUC0-t (h·ng/mL) |
MTX pen Cmax (ng/mL) |
MTX tablet Cmax (ng/mL) |
|
7.5 mg |
782.73 |
579.79 |
185.99 |
185.77 |
|
15 mg |
1594.84 |
1073.32 |
392.00 |
302.96 |
|
22.5 mg |
2272.55 |
1509.34 |
512.71 |
391.64 |
|
30 mg |
2824.72 |
1679.47 |
576.26 |
450.20 |
The safety results were in line with the current knowledge about the safety profile of MTX. No serious adverse events were reported after SC administration of MTX. A total of 80 adverse events were reported by 35 of the 62 subjects, of which 63 were mild and 17 were moderate events. None of these were serious. Differences in the safety profile were related to the route of administration, i.e., more GI disorders were observed after oral administration (15% vs. 28%) whereas injection site reactions were observed after administration with the MTX pen. Overall, single administrations with the MTX pen were locally well tolerated. No redness or swelling occurred, and only 2 subjects had a mild hematoma. Mild pain or burning sensation at the injection site was reported by 5 of the 59 subjects.
Conclusion: Administration of MTX with the MTX pen resulted in a higher relative bioavailability compared to oral administration of MTX after single doses of 7.5, 15, 22.5, and 30 mg.
· AUC0-t was higher after MTX pen compared to oral administration for all dose groups
· MTX pen administration resulted in a higher Cmax compared to oral administration for all dose groups, with the exception of the lowest dose
· AUC0-t ratios increased with ascending doses whereas Cmax ratios did not increase with ascending doses
Disclosure:
U. Pichlmeier,
medac,
3;
K. U. Heuer,
medac,
3.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/subcutaneous-administration-of-methotrexate-with-a-prefilled-autoinjector-pen-results-in-a-higher-relative-bioavailability-compared-to-oral-administration-of-methotrexate/