Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is an immune-mediated inflammatory arthritis associated with psoriasis that can cause remarkable joint damage (1). Subclinical cardiovascular disease (CVD) due to subclinical atherosclerosis is accelerated in PsA leading to overt cardiovascular events with increased mortality in those patients(2). Chronic inflammation plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis in PsA, together with the conventional risk factors (3). Intima-media thickness of the common carotid artery, evaluated by ultrasonography, is a good indicator of generalized atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease, giving early signs of subclinical atherosclerosis (4). We aimed to investigate the role of interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), and insulin level as early predictors of subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with PsA.
Methods: The study included 81 patients with PsA and 69 matched healthy volunteers. Serum IL-1β, HOMA-IR, and insulin levels were assessed. Ultrasonographic measurement of carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) was done for both common carotid arteries and the mean CIMT was calculated.
Results: Our patients and controls were matched regarding age, sex, and body mass index (BMI) (P >0.05). Our study revealed a statistically significant difference between patients and controls regarding IL-1β, HOMA-IR, insulin level, and CIMT (p < 0.05) as illustrated in table (1). There was a statistically significant positive correlation between IL-1β, HOMA-IR, insulin level, and CIMT (p< 0.05), however, no significant correlation could be detected between ESR, CRP, and CIMT (p >0.05) as shown in table (2).
Conclusion: IL-1β, HOMA-IR, and insulin levels are correlated with CIMT in PsA. So, each of them can be used as a predictor of subclinical atherosclerosis in those patients. Consequently, IL-1β targeted therapy may have a pivotal role in the prevention of subclinical CVD in PsA.
REFERENCES:
- J. McHugh, C. Balachrishnan, S. M. Jones. Progression of peripheral joint disease in psoriatic arthritis: a 5-yr prospective study. Rheumatology. 2003;42:778–783.
- Ramonda, A. Lo Nigro, V. Modesti, et al. Atherosclerosis in psoriatic arthritis. Auto-immunity Reviews. 2011;10:773-778.
- M. Tobin, D. J. Veale, O. FitzGerald, et al. Cardiovascular disease and risk factors in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology. 2010; 37:1386–1394.
- Di Minno MN, Ambrosino P, Lupoli R, Di Minno A, Tasso M, Peluso R, et al. Cardiovascular risk markers in patients with psoriatic arthritis: a metaanalysis of literature studies. Ann Med. 2015; 47:346–53.
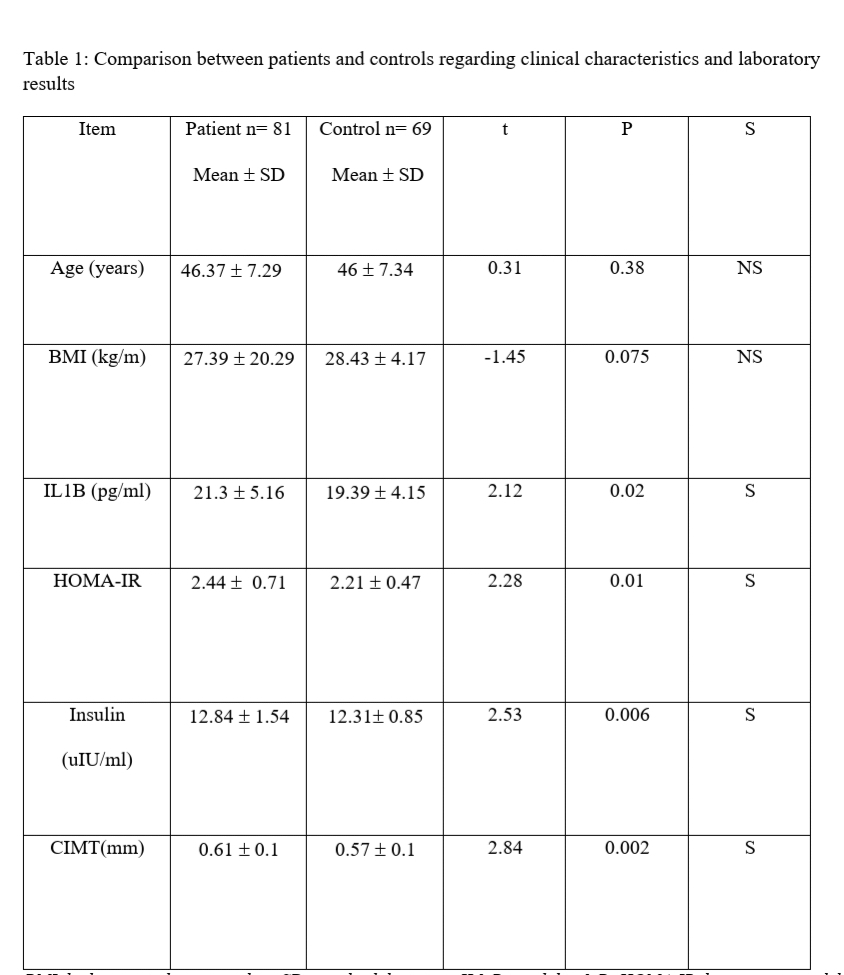 Table 1: Comparison between patients and controls regarding clinical characteristics and laboratory results. BMI, body mass index; n, number; SD, standard deviation; IL1-B,interlukin 1-B; HOMA-IR, homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance; CIMT, carotd intima-media thichkness; kg, kilogram; m, meter; pg, picogram; ml, milliliter; uIU, micro-international unit; mm, millimeter.
Table 1: Comparison between patients and controls regarding clinical characteristics and laboratory results. BMI, body mass index; n, number; SD, standard deviation; IL1-B,interlukin 1-B; HOMA-IR, homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance; CIMT, carotd intima-media thichkness; kg, kilogram; m, meter; pg, picogram; ml, milliliter; uIU, micro-international unit; mm, millimeter.
 Table 2: Correlation between CIMT and some parameters. ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP, c-reactive protein; IL-1B, interlukin-1 beta; HOMA-IR, homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance; CIMT, carotid intima-media thickenss; pg, picogram; ml, milliliter; uIU, micro-international unit; mm, millimeter; mg, milligram; hr, hour; dl, deciliter.
Table 2: Correlation between CIMT and some parameters. ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP, c-reactive protein; IL-1B, interlukin-1 beta; HOMA-IR, homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance; CIMT, carotid intima-media thickenss; pg, picogram; ml, milliliter; uIU, micro-international unit; mm, millimeter; mg, milligram; hr, hour; dl, deciliter.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Farouk M, Moussa S, Abdou R. Subclinical Atherosclerosis Risk in Psoriatic Arthritis: Could It Be Prevented? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/subclinical-atherosclerosis-risk-in-psoriatic-arthritis-could-it-be-prevented/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/subclinical-atherosclerosis-risk-in-psoriatic-arthritis-could-it-be-prevented/
