Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
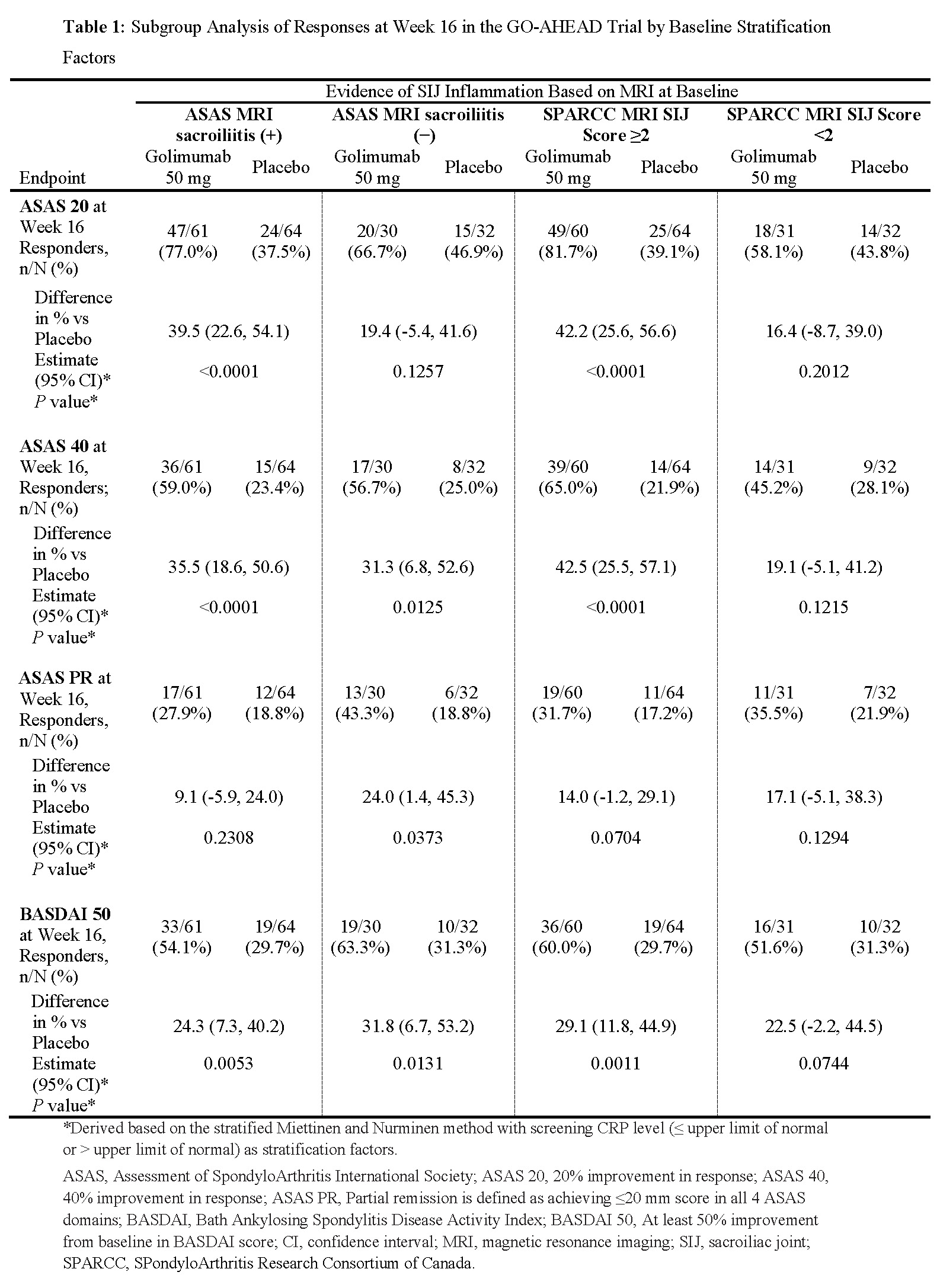
Background/Purpose: Golimumab (GLM) was shown to be effective for nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA) in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study (GO-AHEAD; NCT01453725).1 The SPondyloArthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC MRI index for SI joint (SIJ) inflammation score assesses inflammation in a dichotomous manner in SIJ quadrants. Both Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS) MRI SIJ positivity and the SPARCC SIJ score cut-off of ≥2 reflect positivity for MRI in nr-axSpA, yet each relies on different methodologies with different levels of scientific precision. We analyzed whether the SPARCC SIJ score cut-off of ≥2 is a better predictor of treatment responsiveness to GLM in the GO-AHEAD trial than is ASAS MRI SIJ positivity.
Methods: Patients with nr-axSpA (ASAS criteria, centrally read SIJ X-rays, disease duration ≤5 years, chronic back pain ≥3 months, high disease activity, and inadequate response or intolerance to NSAIDs) were randomized (with ASAS-defined MRI sacroiliitis by a single central reader [yes, SIJ+; no, SIJ–] and CRP level [≤ULN or >ULN] as stratification factors) to GLM 50 mg SC or placebo Q4W for 16 weeks. Baseline ASAS MRI SIJ positivity was assessed by one blinded reader. The SPARCC SIJ score was scored by two independent blinded readers. SPARCC SIJ adjudicated score (if it existed) was used. If no adjudication was required, the mean of the two independent readers’ score assessments was used.
Results: In total, 197 patients were treated (GLM=97; placebo=100). Treatment-group differences in ASAS 20, ASAS 40, ASAS PR, BASDAI 50, and SPARCC SIJ score responses were greater in patients with baseline SPARCC SIJ score ≥2 than in those with ASAS-defined MRI SIJ positivity (Tables). By contrast with the ASAS MRI–negative group, no GLM treatment benefit was observed in patients with baseline SPARCC SIJ score <2. Results should be interpreted with caution given the small subgroups, absence of multiplicity control, and post-hoc nature of the analysis.
Conclusion: Compared with ASAS MRI SIJ positivity, the categorization of patients according to a more standardized definition of MRI positivity, as defined by the SPARCC ≥2 cut-off, may provide a more accurate reflection of responsiveness to GLM in patients with nr-axSpA. Reference
1. Sieper J, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2015;67,2702–12.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Maksymowych W, Tzontcheva A, Philip G, Bergman G, Huyck S, Curtis SP. Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) Baseline MRI SI Joint Score ≥2 Better Predicts Response to Golimumab Than Does Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society (ASAS) MRI Positivity in Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/spondyloarthritis-research-consortium-of-canada-sparcc-baseline-mri-si-joint-score-%e2%89%a52-better-predicts-response-to-golimumab-than-does-assessment-of-spondyloarthritis-international-socie/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/spondyloarthritis-research-consortium-of-canada-sparcc-baseline-mri-si-joint-score-%e2%89%a52-better-predicts-response-to-golimumab-than-does-assessment-of-spondyloarthritis-international-socie/