Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
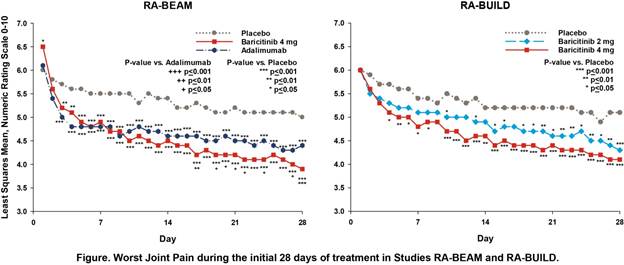
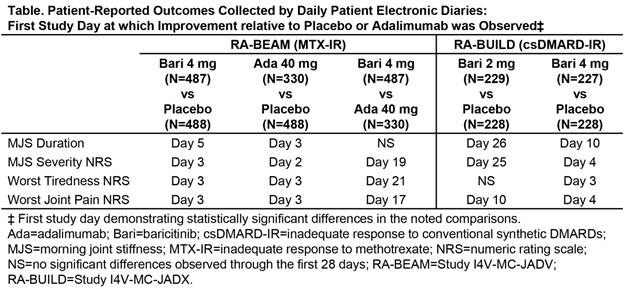
Background/Purpose: Baricitinib (bari), an oral Janus kinase (JAK) 1/JAK2 selective inhibitor, has demonstrated clinical efficacy with a satisfactory safety profile when administered once daily in 4 completed Phase 3 studies in patients with RA1,2,3,4. In 2 studies, RA-BEAM (52-week study in patients with inadequate response (IR) to MTX) and RA-BUILD (24-week study in patients with IR to conventional synthetic [cs] DMARDs), patients recorded their worst joint pain, duration and severity of morning joint stiffness (MJS), and worst tiredness each day for 12 weeks using electronic diaries. In previous analyses based on weekly averages of daily scores3, bari produced significant improvements in patient-reported outcomes (PROs) compared to placebo (pbo) as early as Week 1 and compared to adalimumab (ada) as early as Weeks 2‑4. The aim of these analyses was to explore the kinetics of response using daily diary scores without weekly averaging.
Methods: PRO data were analyzed by study day after randomization (Day 1) – Day 28 for all treated patients. Mixed models for repeated measures analysis were applied (with MJS duration by nonparametric methods).
Results: Consistent with the original weekly-averaged data3, daily diary scores showed significant improvement in patients receiving bari compared to pbo and ada. Improvements relative to pbo were apparent as early as the 3rd day of treatment for MJS severity, worst tiredness, and worst joint pain, and by Day 5 for MJS duration (Figure and Table). Improvements relative to ada were apparent as early as Day 19 for MJS severity, Day 21 for worst tiredness, and Day 17 for worst joint pain. The greatest rapidity and magnitude of benefit was seen with the bari 4-mg daily dose.
Conclusion: In this post hoc analysis from Phase 3 studies of patients with RA with inadequate response to MTX or other csDMARDs, treatment with bari produced rapid improvements in PROs compared to pbo and ada, with significant differences appearing within the initial days of treatment. References: 1Dougados et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74(S2):79; 2Fleischmann et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2015;67(S10):1360-1361; 3Taylor et al. presented at ACR 2015; 4Genovese et al. N Engl J Med 2016;374(13):1243-1252.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Taylor PC, Wright GC, Gaich CL, DeLozier AM, de Bono S, Schlichting DE, Rooney T, Liu J, Beattie SD, Dougados M. Speed of Onset of Effect on Patient-Reported Outcomes Assessed through Daily Electronic Patient Diaries in the Baricitinib Phase 3 RA Clinical Program [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/speed-of-onset-of-effect-on-patient-reported-outcomes-assessed-through-daily-electronic-patient-diaries-in-the-baricitinib-phase-3-ra-clinical-program/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/speed-of-onset-of-effect-on-patient-reported-outcomes-assessed-through-daily-electronic-patient-diaries-in-the-baricitinib-phase-3-ra-clinical-program/