Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1442–1487) SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) have an increased risk of serious infections that varies with the severity of the disease, use of immunosuppressives, including glucocorticoids (GC), and damage, among others. Estimating the infection risk in these patients is important to balance the immunosuppression but there is no evidence-based and suitable tool available to make a prediction of severe infection in these patients.
The SLESIS score had been previously developed for the prediction of severe infections in SLE and was initially validated in an external cohort1. This score had 7 predictors, including the Katz index (SKI), a severity score for SLE with a limited degree of validation and difficult to implement in daily practice. Moreover, its performance was only moderate, with an AUC of 0.63 (95% CI: 0.56 – 0.70).
The objective of our study was to improve the SLESIS score in terms of prediction accuracy and feasibility.
Methods: We used the prospective phase of RELESSER (RELESSER-P), the SLE register of the Spanish Society of Rheumatology, a register that includes patients with SLE or incomplete SLE (91%≥4 ACR 1997 criteria) from 45 centers. The outcome variable was any serious infection identified over the first year of follow up, with serious infection being defined as one leading to hospitalization or death.
The sample was randomly divided into development and validation cohorts. A multivariable logistic model was populated with those variables already forming the SLESIS score, including clinical characteristics, demographic features, hospitalization by SLE comorbidities and treatments 2 plus all other potential predictors identified by literature review and available in the first visit of RELESSER-P.
The most parsimonious model with the least information criteria (AIC and BIC) were chosen as the final model. The performance of the final model was analyzed with C-statistics and AUC. Internal validation was tested using bootstrap techniques.
Results: A total of 1459 patients who had completed visit 2 (one year of follow up),or had information on infections or death in the period, were included in the development cohort (mean age of 49 ± 13, 90% females). Twenty-five (1.7%) had experienced at least one serious infection.
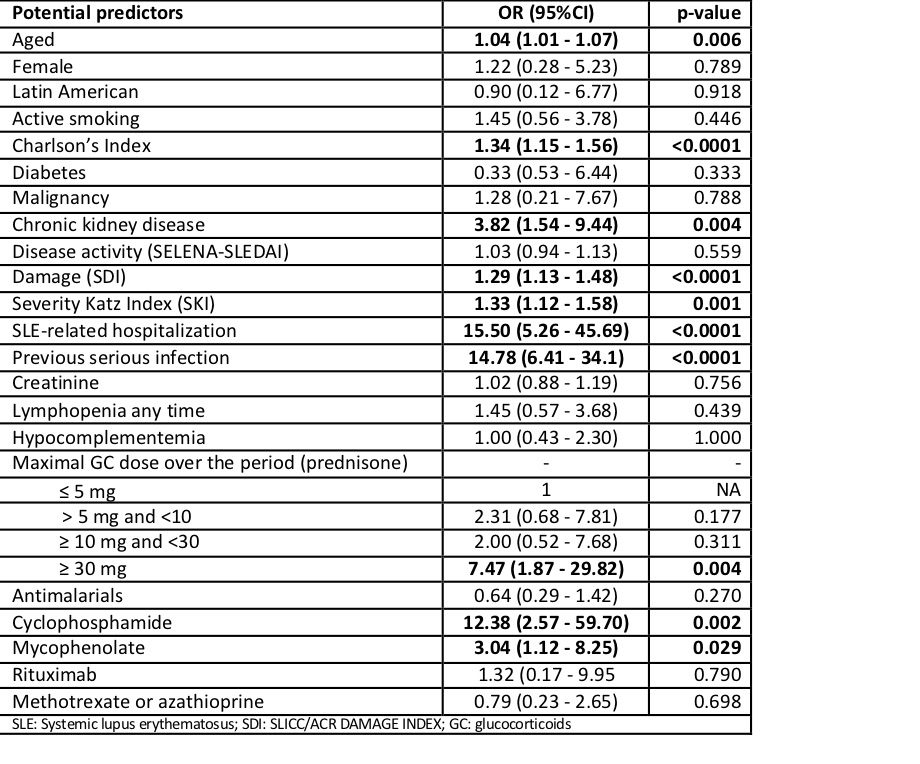
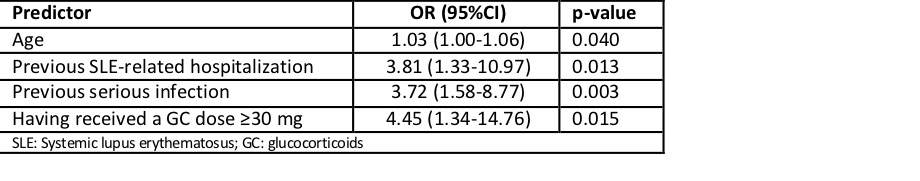
The results of univariate analysis are shown in Table 1.According our final, adjusted multivariate model, serious infection in SLE could be predicted from 4 variables (Table 2) and the SKI could be excluded from the model. The model correctly classified 97% of the infections with C-statistic = 0.82 (0.67 – 0.92) and a Hosmer-Lemeshow p=0.997. The AUC was 0.88 (0.80 – 0.96).
Conclusion: The revised SLESIS score (SLESIS-R) is a fairly accurate and feasible instrument to predict infections in SLE patients in the daily clinical practice that could help making informed decisions on the use of immunosuppressive or biological therapy in SLE patients.
1Tejera-Segura B, Rúa-Figueroa I, Pego-Reigosa JM, et al. Can we validate a clinical score to predict the risk of severe infection in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus? A longitudinal retrospective study in a British CohortBMJ Open 2019;14;9(6):e028697.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rúa-Figueroa I, Garcia de Yebenes M, MARTINEZ BARRIO J, Galindo-Izquierdo M, Calvo- Alén J, Fernandez-Nebro A, Menor-Almagro R, Tomero Muriel E, Freire González M, Sanguesa Gomez C, Horcada L, Blanco R, Uriarte Isacelaya E, García-Villanueva M, Narvaez J, Rosas J, Gómez-Sabater S, Moriano Morales C, Andreu-Sánchez J, Torrente-Segarra V, Aurrecoechea Aguinaga E, Pérez Gómez A, Novoa Medina J, Salgado-Pérez E, Lozano Rivas N, Montilla-Morales C, ruiz-lucea m, Arévalo Salaet M, Iñíguez C, Expósito L, Ibáñez-Barceló M, Bonilla G, Carrión-Barberà I, Erausquin C, Pecondon-Español A, Toyos Sáenz de Miera F, Cobo T, Muñoz A, Fragio J, Oller J, Tejera Segura B, Pego-Reigosa J. SLESIS-R: An Improved Score for Prediction of Serious Infection in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Based on the RELESSER Prospective Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/slesis-r-an-improved-score-for-prediction-of-serious-infection-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-based-on-the-relesser-prospective-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/slesis-r-an-improved-score-for-prediction-of-serious-infection-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-based-on-the-relesser-prospective-cohort/