Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Title: 3S104 ACR Abstract: Infection-Related Rheumatic Disease (946–951)
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Brazil faced a new yellow fever (YFV) outbreak that reached the state of Sao Paulo in December 2016. The fractional dose was used in this campaign to extend vaccine supplies. Due to the YF high risk of fatality, the vaccination may be also indicated for autoimmune rheumatic disease (ARD) patients under low immunosuppression. There is, however, no prospective evaluation of YFV safety in these patients. The aim of this study was to evaluate the short-term safety of immunization with the fractional YFV in patients with ARDs.
Methods: One hundred and sixty adult ARD patients [65 systemic lupus erythematosus, 11 rheumatoid arthritis, 8 ankylosing spondylitis, 16 systemic sclerosis, 2 psoriatic arthritis, 8 Behçet’s disease, 4 mixed connective tissue disease, 13 primary antiphospholipid syndrome, 7 dermatomyositis/polymyositis, 11 primary Sjögren’s syndrome, 3 Takayasu’s arteritis, and 2 granulomatosis with polyangiitis, 10 juvenile idiopathic arthritis] and 160 age and gender-matched healthy controls were vaccinated with a 5-fold fractional-dose (0.1mL, subcutaneous route) of the 17DD YFV. All participants were evaluated at entry (D0), 5 days (D5), 10 days (D10) and 30 days (D30) post-vaccination for clinical and laboratory parameters (AST, ALT, complete blood count, CRP) and disease activity according to specific tools for each ARD. Participants were instructed to seek medical attention, if necessary, and a rigorous follow-up of adverse events was performed during the first 30 days after vaccination. Serious adverse events were defined as those resulting in hospitalization or death. ANOVA was performed for longitudinal analysis of laboratory exams.
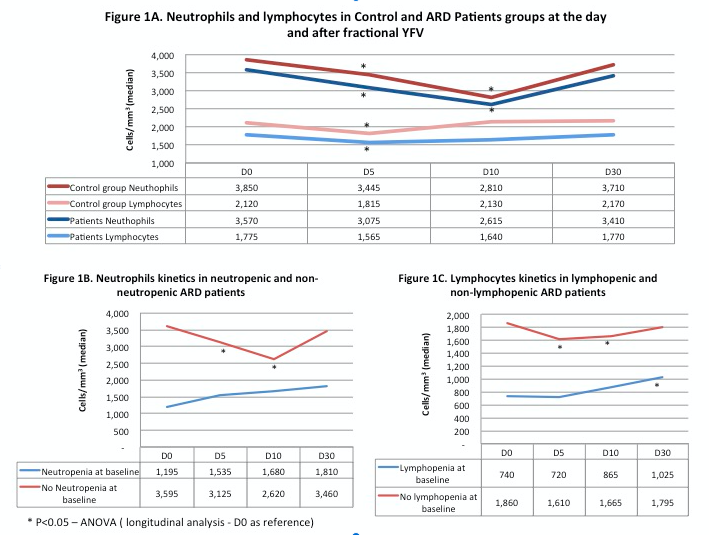
Results: All disease activity parameters of ARD patients (SLEDAI-2K, DAS28, BASDAI, ASDAS, BR-BDCAF, MMT, ESSDAI, BVAS, ESR and CRP) remained stable 30 days after YFV (P<0.05). ARD patients had higher frequencies of fever, muscle pain, abdominal pain, arthralgia and diarrhea compared to controls (p<0.05). Kinetics of neutrophils and lymphocytes in patients and controls had a similar pattern (r=+0.99 and r=+0.81) characterized by a significant transient decrease in neutrophils (D10) and lymphocytes (D5) and a full recovery to baseline levels for both in D30 (Figure 1A). In contrast, kinetics of ARD patients with neutropenia/lymphopenia at baseline had a distinct pattern with stable/increase in levels of these cells (Figures 1B and 1C). No serious adverse effect was reported neither mild abnormalities in liver enzymes or renal function.
Conclusion: The 17DD YFV was safe and did not induce flares in ARD patients with low immunosuppression and may be indicated in yellow fever outbreak situations. Further studies are necessary to determine if the observed distinct immune microenvironment kinetics will be relevant for YFV viremia and/or vaccine seroconversion (ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT03430388)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tonacio AC, Pedrosa TN, Ferreira Filho JC, Sampaio-Barros MM, Fuller R, Lopes M, Borba EF, Pasoto SG, Neves E, Silva CA, Pereira RMR, Sampaio-Barros P, Andrade D, Ribeiro AC, Moraes JC, Shinjo SK, Miossi R, Higashino H, Costa S, Duarte A, Leon EP, Lopes M, Aikawa NE, Bonfa E. Short-Term Safety of Fractional-Dose Yellow Fever Vaccination in Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases and Kinetics of White Blood Cells [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/short-term-safety-of-fractional-dose-yellow-fever-vaccination-in-autoimmune-rheumatic-diseases-and-kinetics-of-white-blood-cells/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/short-term-safety-of-fractional-dose-yellow-fever-vaccination-in-autoimmune-rheumatic-diseases-and-kinetics-of-white-blood-cells/