Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Aiming at rapid decrease of disease activity, there has been a trend to start with higher doses of methotrexate (MTX) for newly diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, not only for MTX monotherapy, but also in combination with other antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). We hypothesized that in combination with other very effective medication, there might be no additional benefit of high over low doses of MTX. We studied the relationship with early clinical response of high versus low doses of MTX in mono- and combination therapy in DMARD naive early RA patients.
Methods: RA patients included in the observational international METEOR cohort with symptom duration ≤5 years, time between diagnosis and first visit ≤2 months, MTX prescribed at first visit, no medication change within 3 to 6 months and available disease activity information were selected. Patients were divided into 4 medication groups: MTX monotherapy, MTX + synthetic (cs)DMARDs, MTX + oral glucocorticoid (+ possibly csDMARDs) or MTX + biologic (b)DMARDs (+ possibly csDMARDs). Missing data were imputed using multivariate normal imputation. MTX dose was dichotomized: low dose ≤10 mg/week & high dose ≥15 mg/week. A propensity score (PS) was calculated to adjust the relationship between MTX doses and outcome for potential confounding by indication. Linear mixed model analyses for DAS, DAS28, and HAQ were performed for each medication group, with ‘MTX-dose’ & ‘days between visit and baseline assessment (time)’ as co-variates. Associations were adjusted for the PS. Random intercept and slope were used to account for irregular time intervals between visits. Each model was tested for the presence of an interaction between ‘MTX dose’ and ‘time’.
Results: Patients on MTX monotherapy had lower baseline disease activity and fewer were erosive and autoantibody positive; other baseline characteristics were comparable between medication groups. The number of patients on combination therapy with bDMARDs was too small to perform analyses (n visits=26, n patients=11). For patients on MTX monotherapy, no differences in efficacy between high and low MTX dose were seen for DAS28 and HAQ. Only DAS decreased slightly less in the high dose initial MTX compared to the low dose group (β=0.0021, 95% CI=0.00012; 0.0041) for interaction between MTX dose and time). No differences in clinical response between high or low dose MTX were seen in patients on combination therapy with csDMARDs or glucocorticoids (table 1).
Conclusion: In DMARD naive early RA patients, there seems to be no early clinical benefit of high over low initial MTX doses, neither for MTX monotherapy nor for combination therapy with MTX/csDMARDs or glucocorticoids. Contrary to expectations, DAS (but not DAS28 or HAQ) even appeared to decrease slightly less after higher doses of MTX monotherapy. However, this effect was very small and may be explained by unmeasured baseline differences between high and low MTX dose groups not captured by the PS. 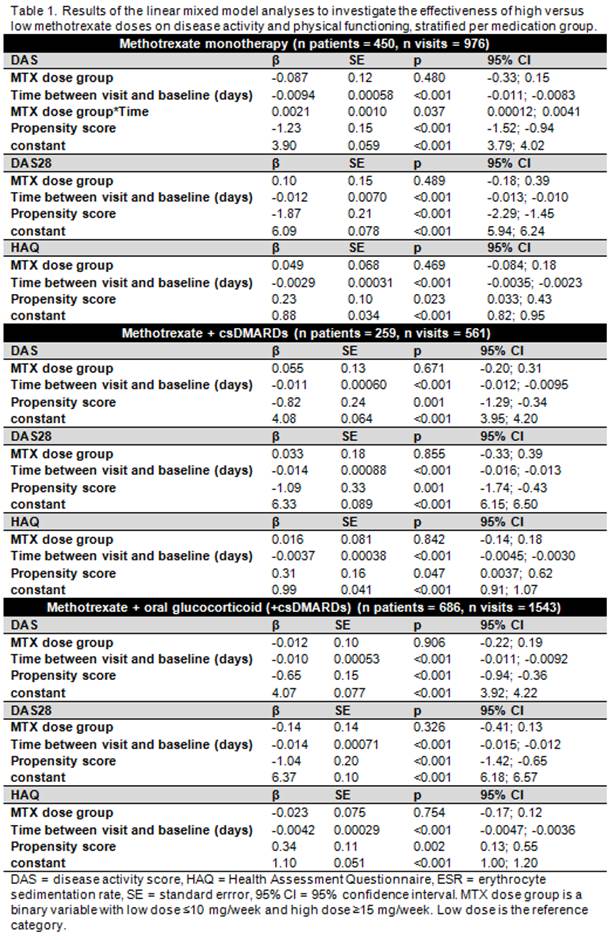
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bergstra S, Allaart C, van den Berg R, Chopra A, Govind N, Santos M, Huizinga T, Landewé R. Short Term Clinical Response to Initial Treatment with High Versus Low Dose Methotrexate in Mono- and Combination Therapy in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/short-term-clinical-response-to-initial-treatment-with-high-versus-low-dose-methotrexate-in-mono-and-combination-therapy-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/short-term-clinical-response-to-initial-treatment-with-high-versus-low-dose-methotrexate-in-mono-and-combination-therapy-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/
