Session Information
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: International guidelines for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treatment emphasize that all treatment decisions should be made through a shared decision making (SDM) process between clinicians and patients (1,2). Observations of routine clinical practice are needed to obtain insight into the actual implementation of SDM. The aim of this study was to assess the level of SDM in RA treatment from an observer perspective and the association with characteristics of the clinician, patient, and consultation.
Methods: Audio-recordings of 168 unique consultations with RA patients were available. The level of SDM was assessed by scoring the audio-recorded consultations with the 5-item observation-based OPTION scale (3). The OPTION scores ranged from 0 to 100 with higher scores indicating higher levels of SDM. Descriptive statistics were computed. First, associations with characteristics of the clinician (age, sex), patient (age, sex, educational level, disease duration, comorbidities, medication beliefs, health status), and consultation (length, type of treatment decision) were assessed using univariate regression analyses. Thereafter, variables with a p-value < 0.2 were included in a multilevel model with random intercepts. Statistical significance was set at P < 0.05.
Results: Characteristics of the clinician, patient, and consultation are shown in table 1. The mean OPTION score was 28.3 ± 15.1. The multilevel model included 4 variables, namely the clinician’s age, patient’s age, consultation length, and type of treatment decision. The level of SDM was significantly associated with the consultation length (B=0.63, P=0.01), decision for stopping and/or starting medication (B=14.3, P=0.00), decision for adjusting doses (B=8.38, P=0.00), and decision for administering single dose glucocorticoids (B=15.03, P=0.00). No other significant associations were found.
Conclusion: A higher level of SDM is associated with a longer consultation length and the type of treatment decision. Overall, the level of SDM in RA treatment leaves room for improvement. However, an observer’s assessment of the efforts of clinicians to involve patients in decision making may not be congruent with clinicians’ and patients’ perspectives of SDM.
References:
(1) Smolen JS, Landewé R, Bijlsma J, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann Rheum Dis 2017;76:960-77.
(2) Singh JA, Saag KG, Bridges SL Jr, et al. 2015 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 2016;68:1-26.
(3) Elwyn G, Tsulukidze M, Edwards A, et al. Using a ‘talk’ model of shared decision making to propose an observation-based measure: Observer OPTION 5 Item. Patient Educ Couns 2013;93:265-71.
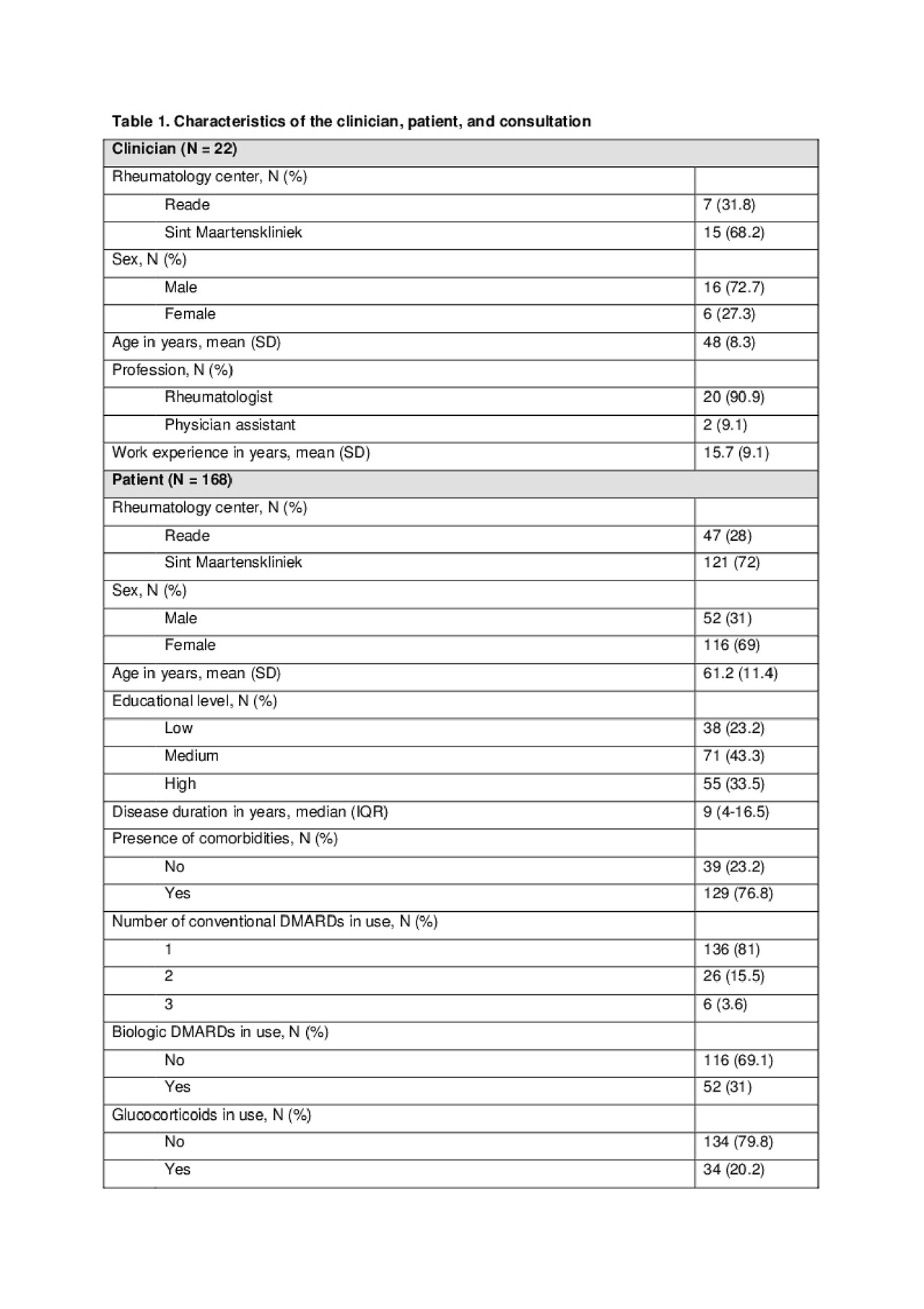
Table 1. Characteristics of the clinician, patient, and consultation
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mathijssen E, Vriezekolk J, van den Bemt B. Shared Decision Making in Routine Clinical Practice: An Assessment of Audio-recorded Consultations with Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/shared-decision-making-in-routine-clinical-practice-an-assessment-of-audio-recorded-consultations-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/shared-decision-making-in-routine-clinical-practice-an-assessment-of-audio-recorded-consultations-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/
