Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) are a heterogeneous group of rare diseases characterized by chronic muscle inflammation and multiple organ involvement. These serious clinical manifestations can be associated with significant impairment of quality of life including sexual life. The aim of this study was to assess sexual functioning in female IIM patients compared to age-/sex-matched healthy controls (HC) and to determine the association between sexual health impairment and physical and psychological aspects of the disease.
Methods: In total, 62 women (45 currently have a partner) with IIM [mean age: 53.1, disease duration: 5.2 years, dermatomyositis (DM, 29)/ polymyositis (PM, 27)/ necrotizing myopathy (IMNM, 5)/ inclusion body myositis (IBM, 1)], who fulfilled the Bohan/Peter 1975 criteria for DM/PM, or ENMC criteria for IMNM or IBM, and 62 healthy controls (HC) (51 currently have a partner, mean age: 53.1) without rheumatic diseases filled in 11 well-established and validated questionnaires assessing sexual function (FSFI, SFQ28, BISF-W), quality of sexual life (SQoL-F), pelvic floor function (PFIQ-7, PISQ-12), fatigue [Fatigue impact scale (FIS)], physical activity [Human activity profile (HAP)], depression [Beck’s depression inventory II (BDI-II)], quality of life [36-item Short form survey (SF-36)], and disability [Health assessment questionnaire (HAQ)]. A routine laboratory testing was performed. Data are presented as median (IQR).
Results: Patients with IIMs reported significantly greater prevalence and severity of sexual dysfunction (FSFI, BISF-W, SFQ28, SQoL-F) and pelvic floor dysfunction (PISQ-12) compared to HC (table). When we analyzed only sexually active patients compared to sexually active HC, the difference between patients and HC remained significant (table). The prevalence of sexual dysfunction in patients with IIM according to the FSFI cut-off score was 59%. Worse scores in IIM patients were associated with greater muscle weakness of m. gluteus maximus [MMT8: FSFI (r=0.289, p=0.035), PFIQ-7 (r=-0.407, p=0.003)], m. gluteus medius [MMT8: PFIQ-7 (r=-0.381, p=0.005)], greater fatigue [FIF: FSFI arousal subscale (r=-0.343, p=0.007), SQoL-F (r=-0.412, p=0.003)], severer depression [BDI-II: SQoL-F (r=-0.459, p=0.0007)], increased disability and deteriorated quality of life [HAQ: FSFI (r=-0.436, p=0.005); SF-36 D1: BISF-W (0.449, p=0.0005), SF-36 D5: SQoL-F (0.428, p=0.002], and worse ability to perform physical activities [HAP: FSFI (r=0.403, p=0.001), SQoL-F (r=0.368, p=0.007)]. We did not observe any associations with disease duration, current prednisone dose, or serum levels of muscle enzymes. Furthermore, no significant differences between DM and PM were found.
Conclusion: Women with IIM reported significantly impaired sexual function and pelvic floor function compared to healthy females with identical age. The prevalence of sexual dysfunction in IIM patients was 59%. Worse scores in IIM were associated with muscle weakness, decreased physical activity, greater fatigue, severer depression, increased disability and deteriorated quality of life.
Acknowledgements: Supported by MHCR 023728, GA UK 1578119 and SVV 260373
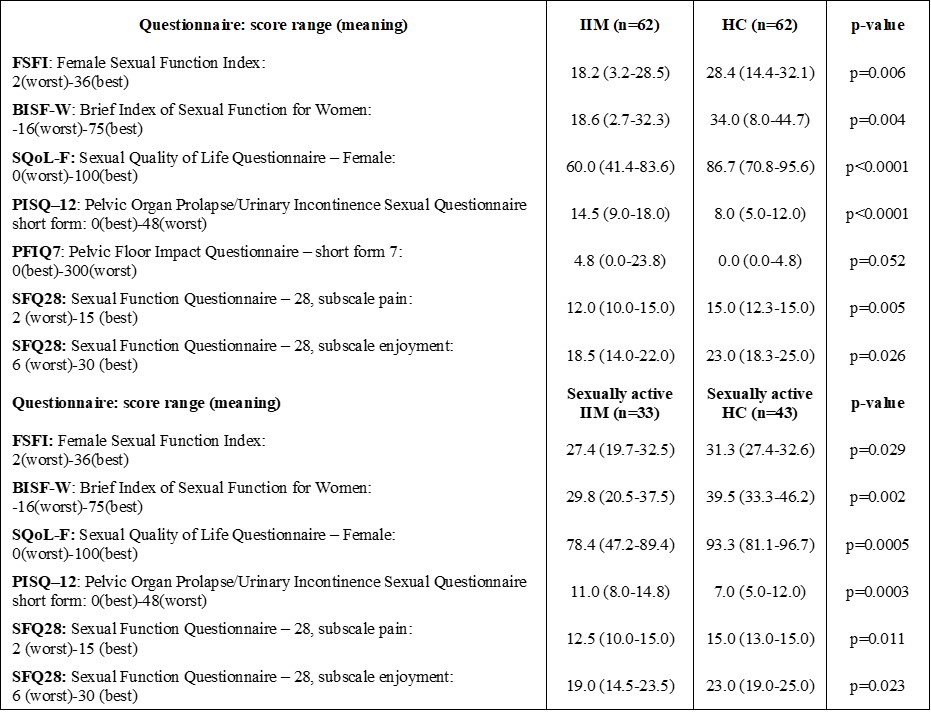 Table. Sexual function and pelvic floor function in women with IIM and healthy controls
Table. Sexual function and pelvic floor function in women with IIM and healthy controls
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hermankova B, Spiritovic M, Oreska S, Storkanova H, Smucrova H, Komarc M, Klein M, Pavelka K, Šenolt L, Vencovský J, Mann H, Tomcik M. Sexual Health Impairment in 62 Female Patients with Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sexual-health-impairment-in-62-female-patients-with-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sexual-health-impairment-in-62-female-patients-with-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies/
