Background/Purpose: The S100 proteins (S100A8/9 complex and S100A12) are calcium binding proteins expressed during myeloid differentiation. S100 proteins are phagocyte-specific proteins that have been demonstrated to be markers of early recruited phagocytes in various inflammatory disorders. We previously demonstrated that gene expression of the S100A8/A9 and S100A12 are significantly elevated in temporal arteries in patients with giant cell arteritis (GCA), compared to controls. Furthermore, serum concentrations of S100A8/A9 and S100A12 are higher in patients with GCA compared to healthy controls. We aimed to assess the association of S100 proteins in disease activity in GCA and their value in predicting disease activity as compared to standard inflammatory markers (CRP and ESR).
Methods: Fifty-nine patients with GCA were selected from the Vasculitis Clinical Research Consortium Longitudinal Study of GCA. Mean age was 72.3 and 44 (75%) were female. Serum concentrations of S100A8/A9 complex and S100A12 were measured by ELISA in 106 samples at times of active or inactive disease. Data on ESR and CRP values were available for 100 and 94 samples, respectively. Mixed effects model, accounting for repeat measurements, was used to compare S100A8/A9 or S100A12 levels between active and inactive disease. ROC curves were created to compare the utility of CRP and ESR, S100 proteins or a combination of all markers in predicting disease activity.
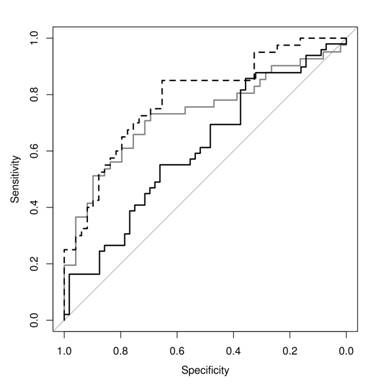
Results: Estimated mean serum S100A8/9 was significantly higher during active disease (1446 ng/mL) vs. inactive disease (1096 ng/mL), p=0.003. Mean serum S100A12 was also significantly higher during active disease (163 ng/mL) vs. inactive disease (117 ng/mL), p=0.016. The AUC for the combination of S100 proteins and standard markers of inflammation was higher than the AUC for either alone (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Estimated ROC curves for prediction of disease activity in patients with GCA. The grey line is for predictions based on CRP and ESR (AUC = 0.73). The black line is for predictions based on S100A12 and S100A8/9 (AUC = 0.61). The dashed line is the model involving all measurements (AUC = 0.79)
Conclusion:
Serum S100A8/A9 and S100A12 are both significantly elevated during active disease in GCA. The combination of S100 proteins measurements with ESR and CRP enhanced the predictive value of disease activity in GCA.
Disclosure:
J. Springer,
None;
D. Holzinger,
None;
G. S. Hoffman,
None;
P. A. Monach,
Genentech and Biogen IDEC Inc.,
2;
T. Hamilton,
None;
C. A. Langford,
Bristol-Myers Squibb,
9,
Genentech and Biogen IDEC Inc.,
9;
D. Foell,
None;
D. Cuthbertson,
None;
C. O’Rourke,
None;
S. Carette,
None;
N. A. Khalidi,
None;
C. McAlear,
None;
C. Pagnoux,
None;
P. Seo,
None;
K. J. Warrington,
None;
S. R. Ytterberg,
None;
T. Vogl,
None;
P. A. Merkel,
None;
J. Roth,
None;
R. Hajj-Ali,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-s100a8s100a9-and-s100a12-as-a-marker-of-disease-activity-in-giant-cell-arteritis/