Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: B Cell Biology & Targets In Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease Poster
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Elevated IgG4 concentrations are used to support a diagnosis of IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD). IgG4 concentrations are reported to be higher in male IgG4-RD patients than in female patients and higher in Asian patients than in non-Asian patients. Similar observations have been made in studies of other immunoglobulin concentrations but were limited by relying on small cohorts with similar conditions/exposures or by excluding certain races. There are scarce data on demographic differences in IgG4 concentrations. We assessed IgG4 concentration differences according to sex and race in a large cohort with demographic diversity.
Methods: The Partners Research Patient Data Registry (RPDR) was queried to identify patients who had ≥ one IgG subclass concentrations measured between January 1, 1989 and March 15, 2018 within the Partners HealthCare Network. Immunoglobulin (Ig) concentration test results, sex, date of birth, self-reported race, billing ZIP code (to estimate socioeconomic status [SES]), and diagnostic billing codes (to determine clinical indication for testing) were extracted. The distributions of IgG4 concentrations were compared across race and sex categories using t-tests and ANOVA tests, as appropriate. Multivariate-adjusted differences in IgG4 concentrations and the proportion of subjects with results above the reference range across race and sex subgroups were estimated using linear and logistic regression, respectively.
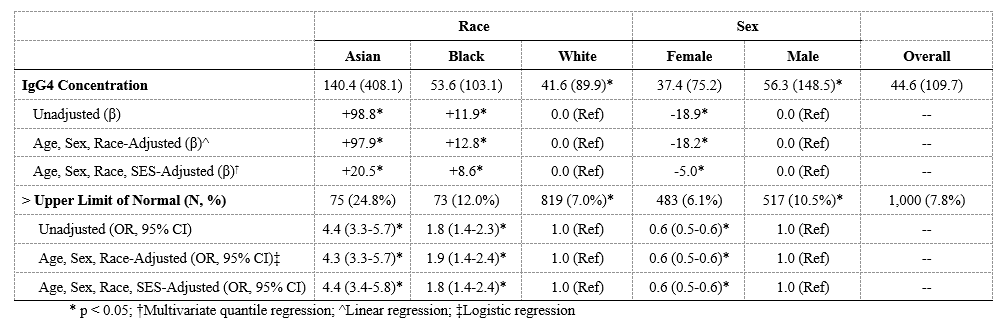
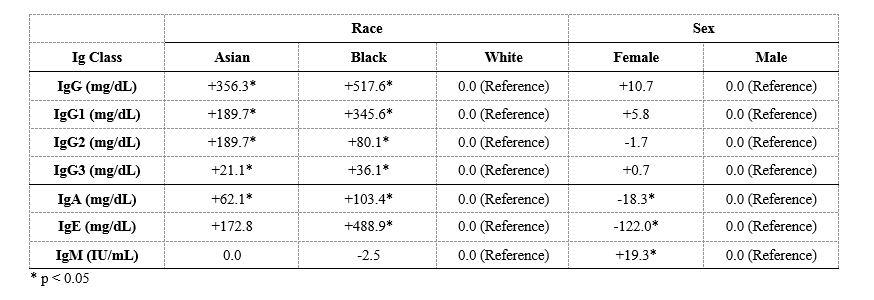
Results: Of the 12,851 subjects, the mean age was 54.7 (±18.3) years, 7,917 (62%) were female, 11,673 (91%) were White, 611 (5%) were Black, and 302 (2%) were Asian (Table 1). Asian and Black subjects, compared to White subjects, had higher IgG4 concentrations (mean 140.4 and 53.6 vs. 41.6 mg/dL, p< 0.001) and more often had IgG4 concentrations above the ULN (24.8% and 12.0% vs. 7.0%; p< 0.001). In age- and sex-adjusted analyses, Asian subjects had over a 4-fold higher odds (aOR 4.3, 95% CI 3.3-5.7) and Black subjects had a2-fold higher odds (aOR 1.9, 95% CI 1.4-2.4) of having an IgG4 above the ULN than White subjects. Males had higher IgG4 concentrations than females (mean 56.3 vs. 37.4 mg/dL, p< 0.001) and more often had IgG4 concentrations above the upper limit of normal (ULN) than females (10.5% vs 6.1%, p< 0.001; Table 2). In age- and race-adjusted analyses, females were 40% less likely than males to have an IgG4 above the ULN (aOR 0.6, 95% CI 0.5-0.6). These differences persisted but were attenuated after adjustment for SES (Table 2). Our findings were similar when we stratified according to clinical indication. Similar observations were made when evaluating IgG, IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgA, and IgE concentrations (Table 3).
Conclusion: IgG4 concentrations differ according to race and sex and reflect similar differences observed in other Ig concentrations. These similarities suggest that a non-specific activation of Ig-producing B cells by environmental or genetic factors is responsible for these observations. These results have implications both for the interpretation of IgG4 concentration testing for the diagnosis of IgG4-RD and for the use of Ig concentrations in other clinical settings and research.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Harkness T, Fu X, Zhang Y, Choi H, Stone J, Blumenthal K, Wallace Z. Serum IgG4 Concentrations Differ According to Race and Sex [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-igg4-concentrations-differ-according-to-race-and-sex/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-igg4-concentrations-differ-according-to-race-and-sex/