Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: High titers of rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody (ACCP) are poor prognostic factors for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. Only few studies have investigated the detailed clinical subtypes or radiographic changes based on serologic status; double (RF/ACCP) positive (+ve), RF or ACCP +ve, double negative (-ve) (seronegative, SN). We aimed to analyze the clinical and radiographic features of RA patients with robust disease activity, based on their serologic status.
Methods: RA patients registered in the Korean College of Rheumatology Biologics Registry (KOBIO), a nationwide inception cohort, were analyzed. Data regarding patient demographics, comorbidity, disease activity, medication, imaging and laboratory exams were utilized. After adjusting for gender, age, disease duration, and smoking history, we analyzed the association of seropositivity and bony erosion (hands and feet X-ray), and the association of the ACCP titer and joint damage, both at baseline (initiation of biologics) presented as odd ratio (OR) and its 95% confidence interval [95% CI].
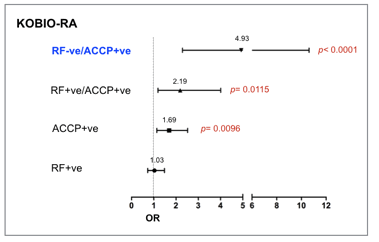
Results: Data of 1198 RA patients were investigated. Mean age was 57.2 years, and disease duration was 8.3 +/- 7.6 years. Mean DAS28-ESR was 5.71, and erosion were found in 40.1% of patients. Being ACCP+ve was significantly associated with bony erosions (OR 1.69 [95% CI 1.13-2.52], p= 0.0096), compared with RF+ve (OR 1.03 p= 0.83), or RF+ve/ACCP+ve (OR 2.19 [95% CI 1.19-4.01], p= 0.012). Of note, being ACCP+ve/RF-ve was strongly associated with radiographic damage (OR 4.93 [95% CI 2.29-10.61], p< 0.0001) in our analysis (figure). In contrast, a multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that baseline ACCP titers were not positively associated with joint damage; a multivariate linear regression model revealed disease duration (estimate -3.95, p< 0.0001) and RF titer (estimate +0.0665, p= 0.0157) were associated with ACCP titers.
Conclusion: Our data demonstrate the significance of ACCP in predicting radiographic damage in established Korean RA patients with persistently high disease activity. Longitudinal studies would be needed to clarify the impact of ACCP titers on radiographic progression.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Shin K, Ha S, Jung I, Kim HA, Lee SS. Seroprevalence and Its Impact on Radiographic Damage in Korean Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Starting Biologics [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/seroprevalence-and-its-impact-on-radiographic-damage-in-korean-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-starting-biologics/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/seroprevalence-and-its-impact-on-radiographic-damage-in-korean-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-starting-biologics/