Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: 3S102: Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies I: Clinical (898–902)
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
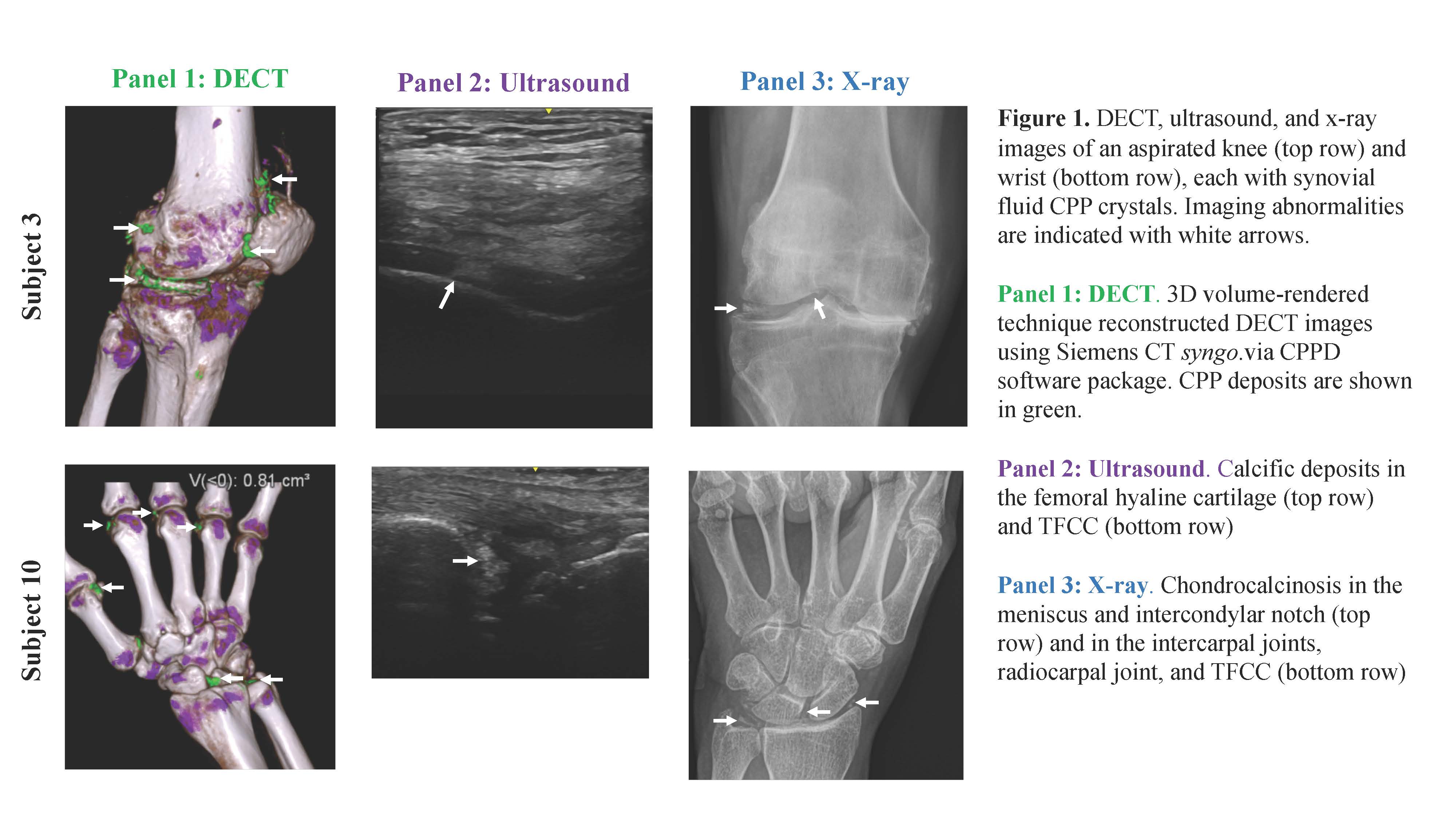
Background/Purpose: Advanced imaging modalities such as ultrasound (US) and dual-energy CT (DECT) can help diagnose crystalline arthritis. DECT is a highly sensitive and specific modality to detect gout and has not been well studied in pseudogout. We compared the sensitivity of DECT, US, and x-ray (XR) in pseudogout.
Methods: We prospectively enrolled patients with crystal-proven pseudogout in a pilot study at a tertiary care center, 3/2018-11/2018. Eligible patients were 18 years old with acute monoarthritis, joint aspiration, and synovial fluid calcium pyrophosphate (CPP) crystals identified via polarized microscopy. Patients with both monosodium urate and CPP crystals were excluded. Subjects underwent DECT, US, and XR of the aspirated joint and a standardized joint (right wrist). A musculoskeletal radiologist interpreted all images; a rheumatologist trained in US additionally interpreted US images and consensus was reached for each scan. DECT images were post-processed using Siemens syngo.via software, applying color-coded overlay indicating volume and location of CPP deposits. DECT was defined as positive if color-coded overlay consistent with CPP was present. We excluded artifacts in nail beds, skin, motion or beam hardening, and deposits < 1 mm. We considered two volume thresholds (cm3) for a positive DECT scan after inspecting the data: >0.40 cm3 and >0.01 cm3. Ultrasound was defined as positive if hyperechoic deposits in hyaline cartilage, fibrocartilage, or tendon were observed. X-ray was defined as positive if chondrocalcinosis was observed in hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage. We calculated the sensitivity of a positive scan in the aspirated joint (reference standard: synovial fluid CPP crystals) and prevalence in the standardized joint.
Results: Ten patients enrolled a mean (SD) of 17 (9) days after joint aspiration. Mean age was 73 (10) years and 40% were female. The knee was aspirated in 8/10 and the wrist was aspirated in 2/10. Six subjects received intra-articular steroids before enrollment. In the aspirated joint, sensitivity (95% confidence interval) was 90% (62-100%) for DECT volume >0.40 cm3, and 100% (74-100%) for DECT volume >0.01 cm3; 100% (74-100%) for US; and 70% (41-92%) for XR (Table 1). In the standardized joint, DECT was positive in 20% (4-49%) for volume >0.40 cm3, and 90% (62-100%) for volume >0.01 cm3. XR chondrocalcinosis was present in 30% (9-59%) and US was positive in 80% (51-96%) of wrists. Representative images from an aspirated knee and wrist are presented in Figure 1.
Conclusion: DECT and US had high sensitivity for pseudogout using synovial fluid CPP crystal analysis as the reference standard. Larger studies testing the sensitivity and specificity of DECT in pseudogout vs. other types of arthritis and establishing a volume threshold are needed.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tedeschi S, Solomon D, Vanni K, Suh D, Smith S. Sensitivity of Dual-Energy CT, Ultrasound, and X-Ray for Pseudogout: A Pilot Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sensitivity-of-dual-energy-ct-ultrasound-and-x-ray-for-pseudogout-a-pilot-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sensitivity-of-dual-energy-ct-ultrasound-and-x-ray-for-pseudogout-a-pilot-study/