Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster III: Psoriatic Arthritis II (1801–1835)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Enthesitis is a key musculoskeletal manifestation of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). In the double-blind, head-to-head EXCEED study (NCT02745080), although the primary endpoint of superiority of ACR20 response for secukinumab (SEC) vs adalimumab (ADA) was not met, similar efficacy was observed across a range of musculoskeletal endpoints, including resolution of enthesitis at Week 52.1 However, a detailed, site-level analysis of enthesitis was not conducted. Here, we report the baseline anatomical distribution of enthesitis, site-level entheseal response to SEC and ADA treatment through 52 weeks, and the dynamics of response based on the number of entheseal sites at baseline.
Methods: In this post hoc, descriptive analysis of patients in the EXCEED study who received SEC 300 mg or ADA 40 mg, enthesitis was assessed using the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada Enthesitis Index (SPARCC). We reported the anatomical distribution of enthesitis at baseline based on the 16 sites targeted by SPARCC. Through descriptive efficacy analysis, we explored resolution of enthesitis at site level through Week 52 across the 2 treatment groups. Patients were further classified into subgroups of baseline enthesis severity as follows: mild (SPARCC < 3), moderate (SPARCC ≥ 3 to ≤ 6), or severe (SPARCC > 6 to ≤ 16). Resolution of enthesitis at Week 52 was assessed in patients stratified by baseline enthesitis severity. For enthesitis severity subgroups, resolution of enthesitis was assessed at Week 52, and time to resolution was estimated using Kaplan-Meier analysis with nonresponder imputation for missing data. Descriptive statistics are provided for each endpoint using an observed-case approach.
Results: Overall, 301 of 426 patients (70.7%) randomized to receive SEC and 331 of 427 patients (77.5%) randomized to ADA had enthesitis at baseline as determined by SPARCC. Baseline distribution of enthesitis sites was well balanced among patients across the 2 treatment groups (Figure 1). By Week 12, a high proportion of patients in both treatment groups achieved similar resolution of enthesitis at the level of individual entheses with sustained improvement through Week 52 (Table). Achievement of enthesitis resolution at Week 52 was similar between treatment groups irrespective of disease severity (Figure 2). Median (95% CI) number of days to resolution of enthesitis increased with increasing baseline enthesitis severity and was similar for SEC and ADA groups with mild (SEC: 29, 29-57; ADA: 31, 29-57), moderate (SEC: 100.5, 58-169; ADA: 113, 85-120), and severe (SEC: 372, 282-not estimable [NE]; ADA: 386, 281-NE) enthesitis.
Conclusion: The anatomical distribution of enthesitis at baseline was mostly balanced between the upper and lower extremities in both SEC and ADA groups in a pattern consistent with previous reports.2 These analyses also highlight the early and sustained resolution of enthesitis through 52 weeks at site level with both drugs. SEC and ADA displayed similar dynamics of response on enthesitis irrespective of enthesitis severity at baseline.
References:
1. McInnes IB, et al. Lancet. 2020;395:1496-1505.
2. Mease PJ, et al. J Rheumatol. 2021;48:367-375.
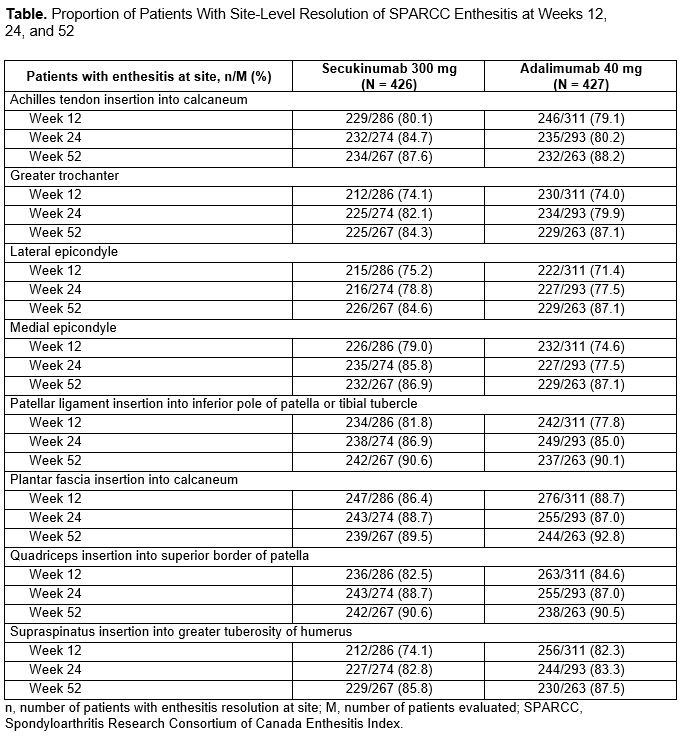 Table. Proportion of Patients With Site-Level Resolution of SPARCC Enthesitis at Weeks 12, 24, and 52
Table. Proportion of Patients With Site-Level Resolution of SPARCC Enthesitis at Weeks 12, 24, and 52
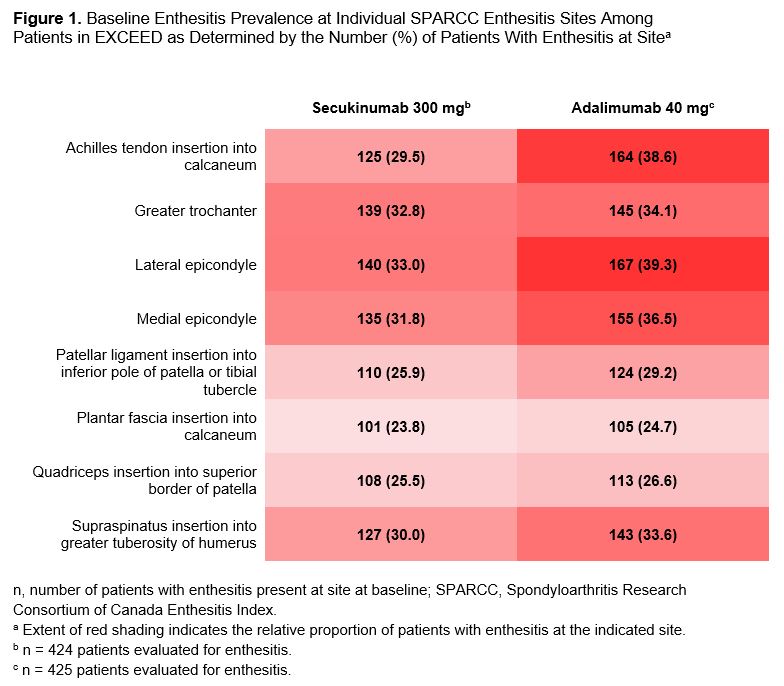 Figure 1. Baseline Enthesitis Prevalence at Individual SPARCC Enthesitis Sites Among Patients in EXCEED as Determined by the Number (%) of Patients With Enthesitis at Site
Figure 1. Baseline Enthesitis Prevalence at Individual SPARCC Enthesitis Sites Among Patients in EXCEED as Determined by the Number (%) of Patients With Enthesitis at Site
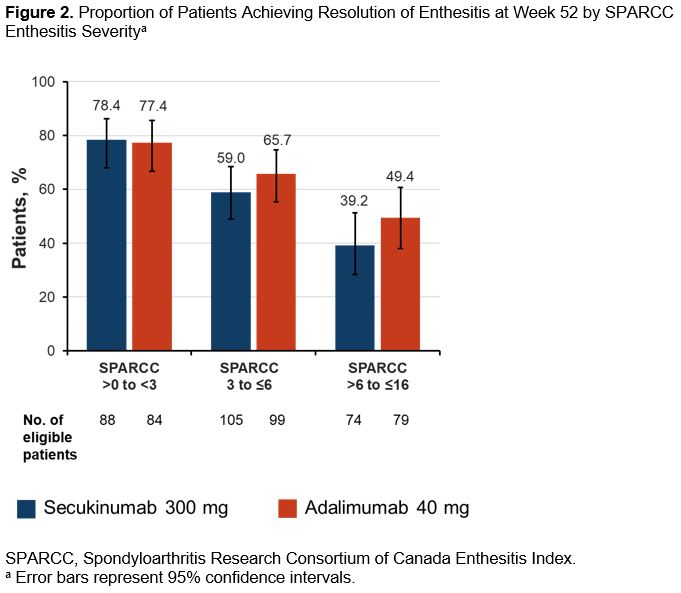 Figure 2. Proportion of Patients Achieving Resolution of Enthesitis at Week 52 by SPARCC Enthesitis Severity
Figure 2. Proportion of Patients Achieving Resolution of Enthesitis at Week 52 by SPARCC Enthesitis Severity
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kaeley G, Schett G, Conaghan P, McGonagle D, Behrens F, Goupille P, Gaillez C, Parikh B, Meng X, Bakewell C. Secukinumab Treatment Provides Sustained Resolution of Enthesitis at Individual Joints Through 52 Weeks in a Phase 3b, Double-Blind, Randomized, Active-Controlled Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secukinumab-treatment-provides-sustained-resolution-of-enthesitis-at-individual-joints-through-52-weeks-in-a-phase-3b-double-blind-randomized-active-controlled-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secukinumab-treatment-provides-sustained-resolution-of-enthesitis-at-individual-joints-through-52-weeks-in-a-phase-3b-double-blind-randomized-active-controlled-study/
