Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment I: Psoriatic Arthritis (0504–0508)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-3:50PM
Background/Purpose: Axial disease may affect up to 25–70% of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) patients, depending on the definition used. Current evidence on efficacy of biologics in the treatment of axial manifestations is limited,1 particularly as validated classification criteria for this subtype of PsA are not yet available. MAXIMISE (NCT02721966); the first randomized controlled trial evaluating the efficacy of a biologic drug in the management of the axial manifestations of PsA, showed that secukinumab (SEC) 300 and 150 mg provided rapid and significant improvement in ASAS20 responses through Week (Wk) 12.2 Here, we report the effect of SEC on clinical and imaging outcomes through 52 wks from the MAXIMISE trial.
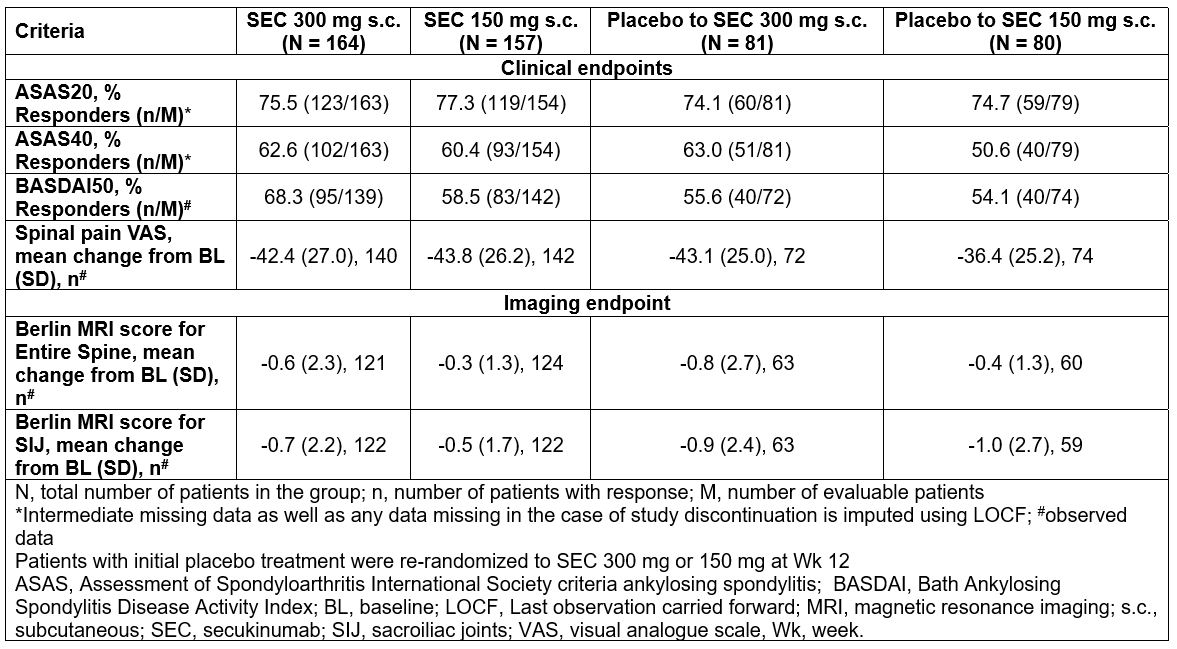
Methods: This phase-3, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial included 498 patients (≥18 years) diagnosed with PsA and fulfilling CASPAR criteria presenting with spinal-pain VAS-score ≥40/100 and BASDAI-score ≥4 and inadequate response to ≥2 NSAIDs. Patients were randomized to SEC 300 mg (N=167); 150 mg (N=165) or placebo (N=166) wkly for 4 wks and every 4 wks thereafter. At Wk 12, placebo patients were re-randomized to SEC 300/150 mg. The primary endpoint was ASAS20 response with SEC 300 mg at Wk 12. Assessments at Wk 52 were exploratory and included ASAS20/40, BASDAI50, spinal pain (VAS), and improvement in Berlin MRI score for the spine and the sacroiliac joints. Multiple imputation and last observation carried forward (LOCF) were used to account for missing data for analysis of ASAS20/40 at Wk 12 and Wk 52, respectively. All other data were reported as observed.
Results: The primary endpoint was met.2 ASAS20/40 responses at Wk 12 were 62.9%/43.6% (SEC 300 mg) and 66.3%/39.5% (SEC 150 mg) versus 31.2%/12.2% (placebo), respectively (P< 0.0001). ASAS20/40 responses improved further with SEC 300/150 mg treatment from baseline through 52 wks. 74.1%/75.0% and 63.0%/50.0% of placebo patients re-randomized at Wk 12 to SEC 300/150 mg, achieved ASAS20/40 response at Wk 52. At baseline, 59.5% (SEC 300 mg), 53.5% (SEC 150 mg) and 64.2% (placebo) of the pts had positive MRI scores for the sacroiliac joints and/or the spine. The reductions of Berlin MRI score for entire spine and sacroiliac joints were sustained with SEC 300/150 mg from baseline through 52 wks (Table). 64.6%, 69.1% and 33.6% of patients with inflammatory back pain at baseline as confirmed by the ASAS, Calin et al. and Berlin criteria in the secukinumab 300 mg, 150 mg and placebo groups, respectively, achieved an ASAS20 response at Wk 12.
Conclusion: Secukinumab provided further improvement in signs and symptoms of axial disease as assessed by ASAS20/40 through 52 wks and showed reduced inflammatory MRI lesions in the spine and sacroiliac joints in patients with PsA with axial manifestations. Efficacy responses at Wk 52 were comparable in patients who switched at Wk 12 from placebo to SEC 300/150 mg.
References:
- McInnes IB, et al. Lancet. 2015;386(9999):1137–46.
- Baraliakos X, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(suppl 10).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Baraliakos X, Gossec L, Pournara E, Jeka S, Blanco R, D'Angelo S, Schett G, Schulz B, Rissler M, Whyms D, Perella C, Coates L. Secukinumab Provides Sustained Improvements in Clinical and Imaging Outcomes in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis and Axial Manifestations: Results from the MAXIMISE Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secukinumab-provides-sustained-improvements-in-clinical-and-imaging-outcomes-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-and-axial-manifestations-results-from-the-maximise-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secukinumab-provides-sustained-improvements-in-clinical-and-imaging-outcomes-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-and-axial-manifestations-results-from-the-maximise-trial/