Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster III: Psoriatic Arthritis II (1801–1835)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Oligoarticular psoriatic arthritis (PsA), defined as involvement of ≤ 4 joints, affects approximately 50% of the PsA population.1,2 Disease burden is comparable for patients with oligoarticular or polyarticular disease, and most patients progress from oligoarticular to polyarticular PsA.1,2 Evidence for the efficacy of biologics in patients with oligoarticular PsA is limited, as inclusion criteria for randomized controlled trials in PsA typically require ≥ 3 swollen and tender joints. We evaluated the efficacy of the interleukin 17 inhibitor secukinumab (SEC) in patients with oligoarticular PsA pooled from 5 phase 3 studies.
Methods: This post hoc analysis included patients with oligoarticular PsA from the FUTURE 2-5 and MAXIMISE trials (NCT01649375, NCT01989468, NCT02294227, NCT02404350, and NCT02721966). Oligoarticular PsA was defined as the presence of 1-4 tender joints and 1-4 swollen joints at baseline as measured by the tender joint count of 78 joints (TJC78) and the swollen joint count of 76 joints (SJC76), respectively. For this analysis, patients were pooled by treatment received at Week 12 and Week 52 according to the following groups: Week 12 (SEC 300 mg, SEC 150 mg with or without loading dose [LD], or placebo [PBO]) and Week 52 (any SEC 300 mg or any SEC 150 mg). Efficacy was assessed by the proportion of patients achieving 50% improvement in Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis (DAPSA50), DAPSA75, DAPSA-based low disease activity (LDA) and remission (REM), resolution of TJC78, resolution of SJC76, and a ≥ 0.35-point improvement in the Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index score. Descriptive statistics are provided for each endpoint using an observed-case approach. Logistic regression analysis was used to identify potential predictors of DAPSA response at Weeks 12 and 52; multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed thereafter.
Results: In total, 84 patients were included in this analysis: 48 with active PsA from the FUTURE 2-5 trials and 36 with active PsA and axial manifestations from the MAXIMISE trial. Demographics and baseline disease characteristics are presented in the Table. At Week 12, notable improvements were observed for the SEC vs PBO groups across all the assessed outcome measures (Figures 1A, 2A). These improvements were sustained or increased further through Week 52 (Figures 1B, 2B). More than 90% of patients who received any SEC 300 mg or SEC 150 mg achieved LDA or REM at Week 52 (Figure 1B). At Week 52, a higher proportion of patients who received any SEC 300 mg vs any SEC 150 mg achieved higher hurdle endpoints of DAPSA 75 and DAPSA REM (Figure 1B). At Week 12, younger age was a predictor for the achievement of DAPSA LDA or REM and the achievement of DAPSA50, while lower baseline SJC was a predictor of the achievement of DAPSA REM (P < .05). No predictors were identified at Week 52.
Conclusion: SEC provides greater improvements vs PBO across a number of disease activity and physical function outcome measures in patients with oligoarticular PsA at Week 12, with sustained responses through Week 52.
References:
- Huscher D, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(suppl 10). Abstract 679.
- Gladman D, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(suppl 10). Abstract 2495.
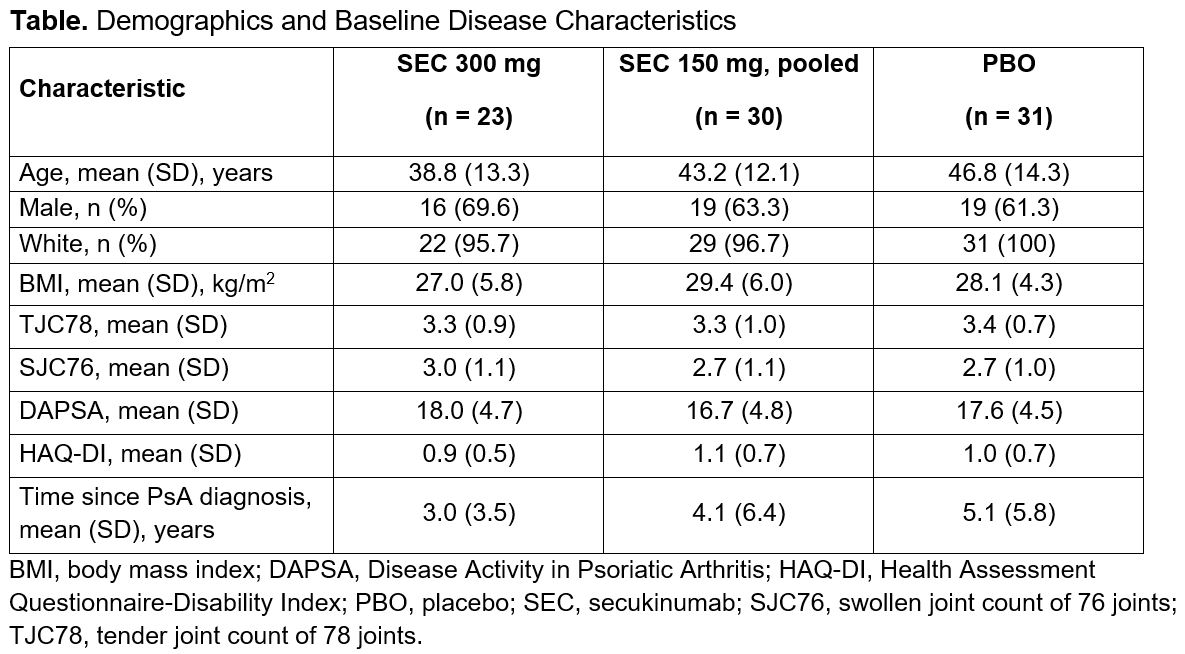 Table. Demographics and Baseline Disease Characteristics
Table. Demographics and Baseline Disease Characteristics
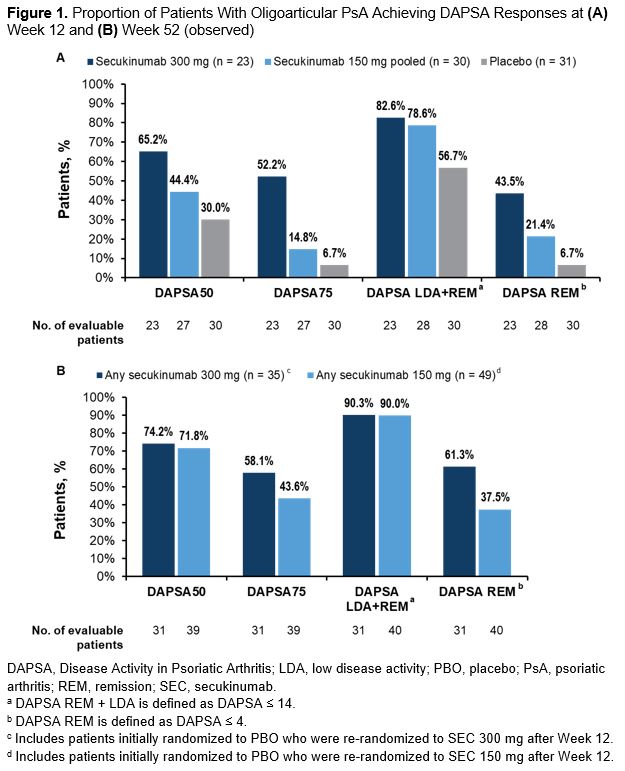 Figure 1. Proportion of Patients With Oligoarticular PsA Achieving DAPSA Responses at (A) Week 12 and (B) Week 52 (observed)
Figure 1. Proportion of Patients With Oligoarticular PsA Achieving DAPSA Responses at (A) Week 12 and (B) Week 52 (observed)
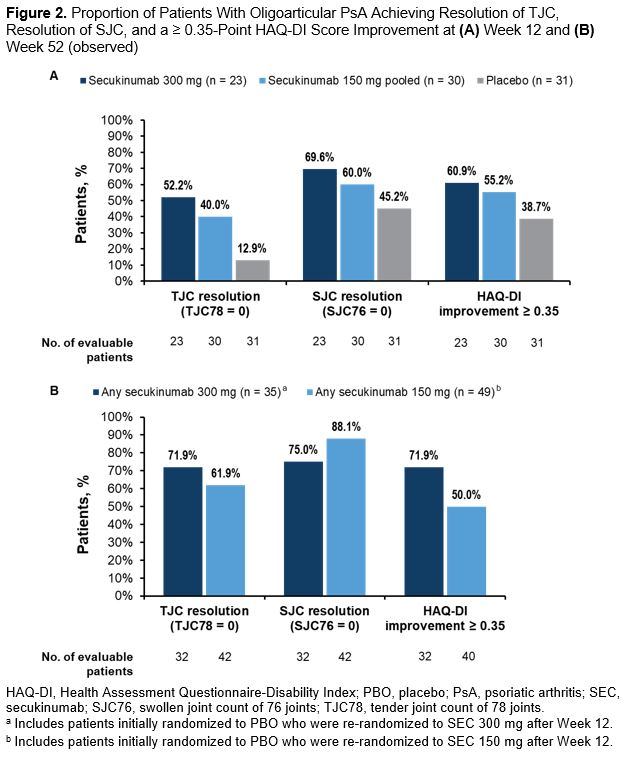 Figure 2. Proportion of Patients With Oligoarticular PsA Achieving Resolution of TJC, Resolution of SJC, and a ≥ 0.35-Point HAQ-DI Score Improvement at (A) Week 12 and (B) Week 52 (observed)
Figure 2. Proportion of Patients With Oligoarticular PsA Achieving Resolution of TJC, Resolution of SJC, and a ≥ 0.35-Point HAQ-DI Score Improvement at (A) Week 12 and (B) Week 52 (observed)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ogdie A, Gladman D, Coates L, Pournara E, Meng X, Parikh B, Mease P. Secukinumab Provides Clinical Improvements in Patients with Active Oligoarticular Psoriatic Arthritis: Results from a Pooled Analysis of 5 Phase 3 Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secukinumab-provides-clinical-improvements-in-patients-with-active-oligoarticular-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-a-pooled-analysis-of-5-phase-3-studies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secukinumab-provides-clinical-improvements-in-patients-with-active-oligoarticular-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-a-pooled-analysis-of-5-phase-3-studies/
