Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA) suffer from comparable disease burden to patients with ankylosing spondylitis/radiographic axSpA (AS/r-axSpA), including inflammatory back pain, morning stiffness, fatigue, and reduced spinal mobility.1 Secukinumab 150 mg has demonstrated sustained improvement in the signs and symptoms in patients with AS over 4 years.2 Here, we report a post hoc analysis evaluating the effect of secukinumab treatment on back pain, morning stiffness, fatigue, and physical function in tumor necrosis factor inhibitor naïve (TNFi-naïve) patients with nr-axSpA from the PREVENT study (NCT02696031).
Methods: This study included patients with nr-axSpA receiving either subcutaneous secukinumab 150 mg with loading (LD), without loading (NL), or placebo (PBO).3 Patients with inadequate response to treatment were permitted to switch to open-label secukinumab 150 mg or standard of care (TNFi) after Week 20 based on clinical judgement of disease activity by the investigator and the patient. This post-hoc analysis assessed nocturnal back pain scores (on visual analog scale [0–100]; ASAS outcome component), morning stiffness (overall level; on visual analog scale [0-10] ASAS outcome component), FACIT-Fatigue and SF-36 PCS scores in TNFi-naïve patients. Continuous values were imputed as mixed-effect model repeated measures (MMRM; valid under the missing at random assumption) for mean change from baseline through Week 16 and as observed at Week 52. Minimal clinically important difference (MCID) data were assessed using non-responder imputation through Week 16 and as observed at Week 52.
Results: Overall, 501 TNFi-naïve patients were included in this analysis (LD, N=164; NL, N=166; PBO, N=171). Up to 64% of placebo and approximately 50% secukinumab treated patients switched to open label secukinumab 150 mg between Week 20 – 52. Secukinumab-treated patients vs PBO (p< 0.05) demonstrated a higher mean reduction from baseline in nocturnal back pain and morning stiffness, both at Weeks 4 and 16 which was sustained at Week 52 (Table 1). Also, improvements in secukinumab-treated patients vs PBO (p< 0.05) were reported in FACIT-Fatigue and SF-36 PCS scores from baseline at Weeks 16 and 52 (Table 1). At Week 16, a higher proportion of secukinumab-treated patients met the MCID criteria vs PBO (p< 0.05) across pre-specified efficacy assessments, which was sustained at Week 52 (Table 2).
Conclusion: Secukinumab provided clinically meaningful improvement in back pain, morning stiffness, fatigue, and physical function in TNFi-naïve patients with nr-axSpA over 52 weeks.
References:
- Garrido-Cumbrera et al. Current Rheumatology Reports. 2019;21:19.
- Marzo-Ortega H, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71 (suppl 10):1504.
- Deodhar A et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71 (suppl 10):L21.
 Table 1: Mean change from baseline up to Week 52 in TNFi-naïve population
Table 1: Mean change from baseline up to Week 52 in TNFi-naïve population
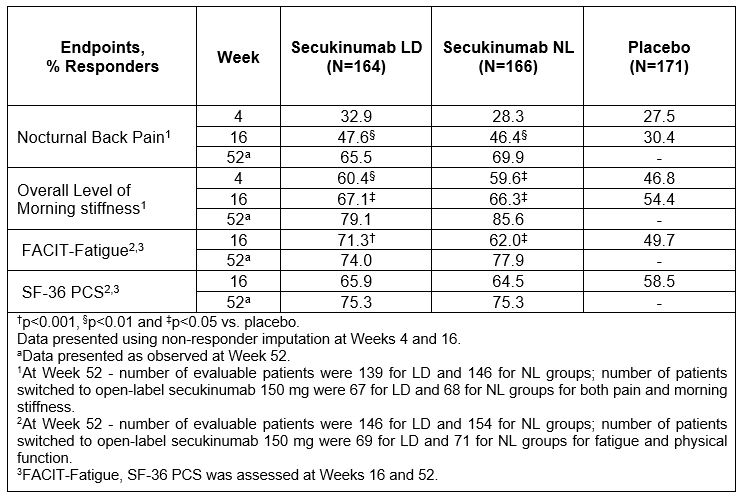 Table 2: Proportion of patients meeting MCID criteria up to Week 52 in TNFi-naïve population
Table 2: Proportion of patients meeting MCID criteria up to Week 52 in TNFi-naïve population
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Marzo-Ortega H, Deodhar A, Blanco R, Kameda H, Kivitz A, Poddubnyy D, Magrey M, Wang J, Haemmerle S, Shete A, Braun J. Secukinumab Improves Pain, Morning Stiffness, Fatigue and Physical Function in Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor-Naïve Patients with Non-Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis: Results from a Randomized Controlled Phase III Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secukinumab-improves-pain-morning-stiffness-fatigue-and-physical-function-in-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitor-naive-patients-with-non-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis-results-from-a-randomized-c/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secukinumab-improves-pain-morning-stiffness-fatigue-and-physical-function-in-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitor-naive-patients-with-non-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis-results-from-a-randomized-c/
