Session Information
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Secukinumab (SEC) has provided significant and sustained improvement in the signs and symptoms of active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and ankylosing spondylitis1. Evidence is limited on the efficacy of biologics in the treatment of patients (pts) with PsA having axial manifestations that affect between 30–70% of pts2, particularly as validated classification criteria for this subtype of PsA are not yet available; an effort to develop criteria is being undertaken by ASAS/GRAPPA. MAXIMISE is an ongoing study evaluating the efficacy and safety of secukinumab 300 mg or 150 mg in managing axial manifestations in pts with PsA. Here, we report the primary analysis results at Week (Wk) 12 from the MAXIMISE trial (NCT02721966).
Methods: This phase 3b, double blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled, multicenter 52-wk trial included 498 pts (aged ≥18 years) with PsA (CASPAR criteria), clinician-diagnosed axial involvements, spinal pain VAS > 40/100 and BASDAI > 4 despite trial of at least two NSAIDs. Pts were randomized to subcutaneous (SC) SEC (300/150 mg) or PBO weekly for 4 wks and every 4 wks thereafter. At Wk 12, PBO pts were re-randomized to SC SEC 300/150 mg. The primary endpoint was ASAS20 response with SEC 300 mg at Wk 12. The key secondary endpoint was ASAS20 response with SEC 150 mg at Wk 12 after superiority of 300 mg was established. Analyses used multiple imputation.
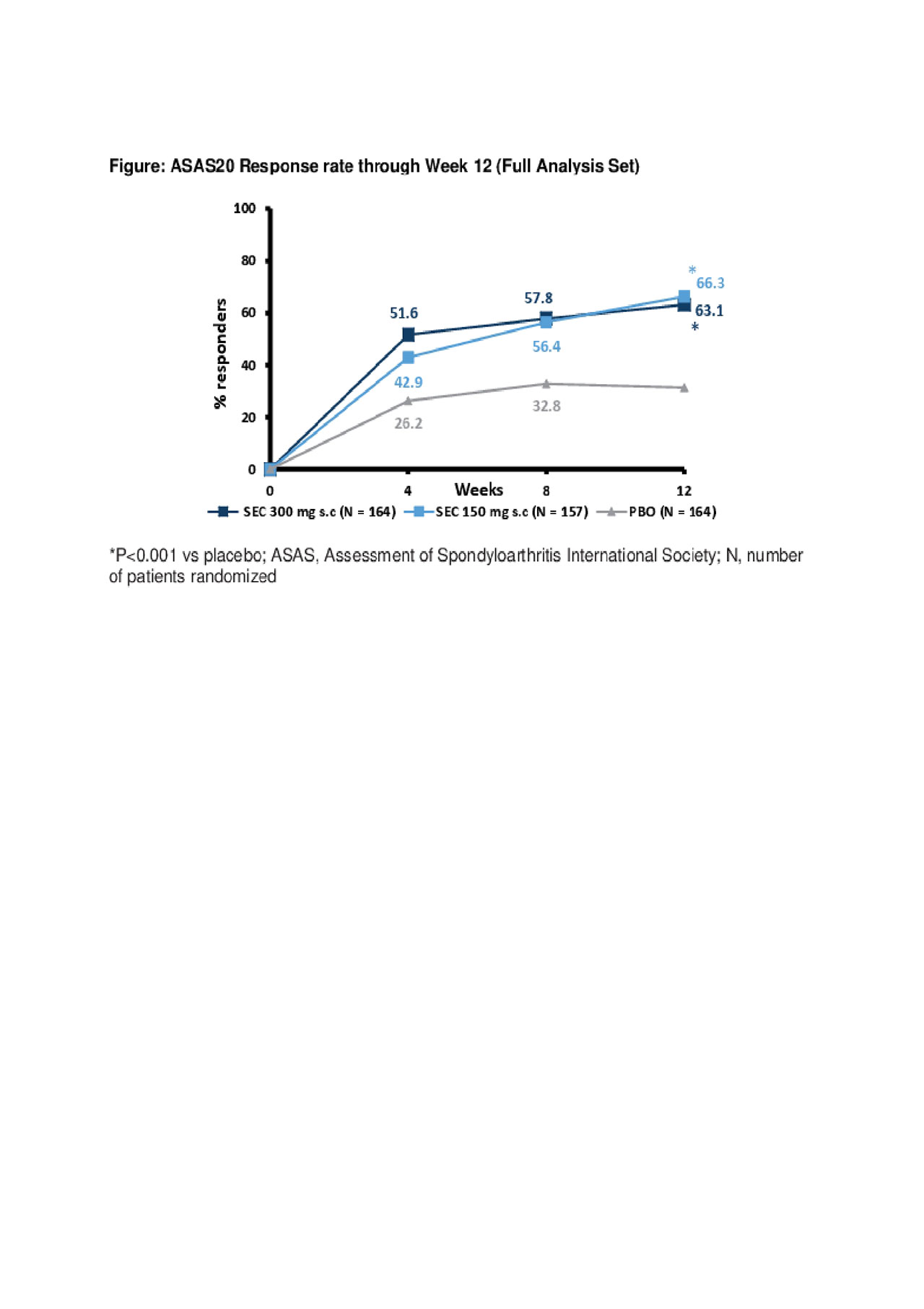
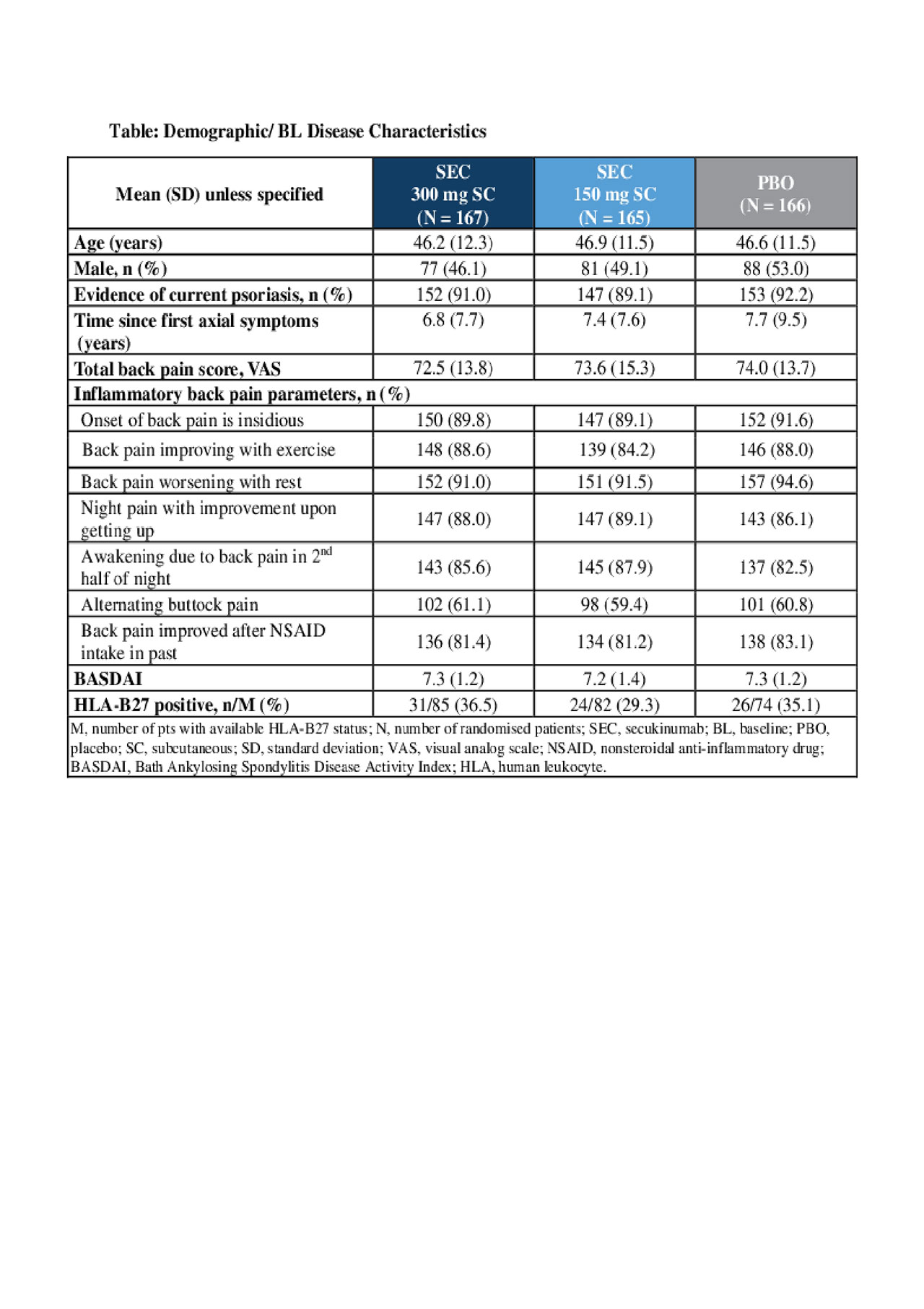
Results: Demographic and baseline (BL) disease characteristics were comparable across groups (Table). Primary and key secondary endpoints were met; ASAS20 response rates at Wk 12 were 63.1% (SEC 300 mg; P< 0.0001) and 66.3% (150 mg; P< 0.0001) versus 31.3% (PBO; Figure). ASAS20 responses in pts using concomitant methotrexate (MTX) were 65.1% [300 mg], 67.3% [150 mg] versus 33.9% [PBO]; corresponding values in pts without concomitant MTX use were 60.5%, 64.4% versus 27.1%. The safety profile was similar across groups through Wk 12.
Conclusion: MAXIMISE is the first randomized controlled trial evaluating the efficacy of a biologic in the management of the axial manifestations of psoriatic arthritis. Secukinumab 300 mg and 150 mg provided rapid and significant improvement in ASAS20 responses through Week 12 in patients with psoriatic arthritis with axial manifestations and inadequate responses to NSAIDs.
References:
- Lubrano E and Perrotta FM. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2016;12:1587-92
- Feld J, et al. Rheum Rev.2018;14:363
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Baraliakos X, Coates L, Gossec L, Jeka S, Mera A, Schulz B, Rissler M, Das Gupta A, Perella C, Pournara E. Secukinumab Improves Axial Manifestations in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis and Inadequate Response to NSAIDs: Primary Analysis of Phase 3 Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secukinumab-improves-axial-manifestations-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-and-inadequate-response-to-nsaids-primary-analysis-of-phase-3-trial/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secukinumab-improves-axial-manifestations-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-and-inadequate-response-to-nsaids-primary-analysis-of-phase-3-trial/