Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: RA activity during the year was assessed to investigate whether seasonal changes influenced parameters of RA activity.
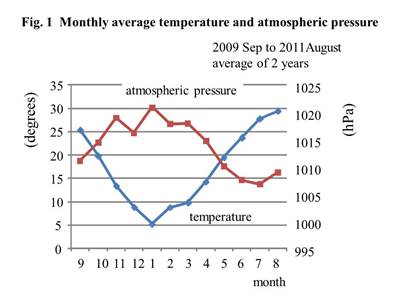
Methods: This study was performed in Fukuoka, a Japanese city with four distinct seasons. From September 1, 2009 to August 31, 2011, parameters of RA activity were assessed in a total of 3811 visits by 348 patients (mean age, 62.1 years; mean duration of RA, 10.8 years), including 2174 visits by 140 patients treated with biologics (mean age, 63.0 years; mean duration of RA, 11.9 years). The following parameters were assessed: C-reactive protein (CRP); erythrocyte sedimentation ratio (ESR); matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-3; rheumatoid factor; DAS28-CRP and DAS28-ESR. All parameters in each month in the first and second years were assessed and results were compared among months. Monthly mean temperature and mean atmospheric pressure in Fukuoka in the 2 years of the study are shown in Figure 1.
Results: For all cases, mean CRP level was 0.65 mg/dl from October to December, and 0.53 mg/dl from July to September. In cases treated using biologics, mean CRP level was 0.67 mg/dl from October to December and 0.50 mg/dl from January to March. These differences were significant (p<0.05). CRP level from April to June (mean, 0.70 mg/dl) was also significantly higher than that from January to March (p<0.01). CRP was significantly higher in autumn and spring than in summer and winter, even in patients treated with biologics. Seasonal changes thus clearly influenced CRP levels. No significant differences in other parameters were found, although MMP-3 levels were also higher from October to December and from April to May compared to other months (Fig. 2).
Conclusion: The results clearly show that seasonal changes significantly influence CRP levels. In the city, the temperature rapidly fell and atmospheric pressure rose in autumn to early winter, and the reverse occurred in spring. RA activity may correlate with changes in temperature and atmospheric pressure.
Disclosure:
R. Nagamine,
None;
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/seasonal-changes-may-influence-activity-of-rheumatoid-arthritis/