Session Information
Title: Health Services Research, Quality Measures and Quality of Care - Innovations in Health Care Delivery
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: The HAQ [Arthritis Rheum 1980;23:137] has been used in almost all rheumatoid arthritis (RA) clinical trials conducted over the last two decades, and provides scores for the 3 patient self-report components of the RA Core Data Set: physical function, pain, and patient global estimate. However, RA patients now have significantly better clinical status than in previous decades [Arthritis Rheum 2005;52:1009], and some patients who experience functional disability score “0” on the HAQ, suggesting “normal” function. Furthermore, psychosocial issues remain important barriers to optimal outcomes. The MDHAQ includes 13 queries in the user-friendly HAQ format, 8 activities of daily living (ADL) from (and identical to) the HAQ, and 5 items not found on the HAQ: 2 complex activities, “walk 2 miles or 3 kilometers” and “participate in recreation and sports as you would like;” as well as 3 queries concerning poor sleep, anxiety and depression. Some of the unique MDHAQ items have been documented to recognize problems in patients with normal HAQ scores, but the traditional HAQ continues to be widely used in most clinical research. We analyzed mean scores for each of the 13 MDHAQ items in an Australian rheumatology setting.
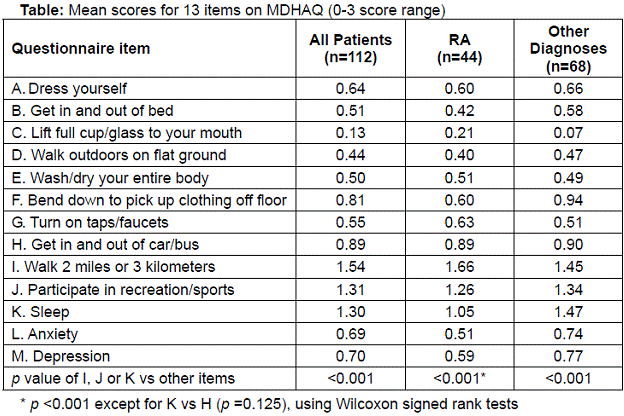
Methods: All patients are asked to complete an MDHAQ in the reception area while waiting to see the physician. The MDHAQ queries 13 items: ability to perform 8 ADL from the HAQ (see Table, A-H), 2 complex activities (“walk 2 miles or 3 kilometers” and “participate in recreation and sports as you would like”), and 3 psychological items: “get a good night’s sleep,” “deal with anxiety,” and “deal with depression.” The patient-friendly HAQ format provides 4 response options: without any difficulty=0, with some difficulty=1, with much difficulty=2, and unable to do=3. The first 112 completed MDHAQs from 118 patients (3 patients had language barriers and 3 refused) were analyzed for the mean scores of 13 MDHAQ items, all scored 0-3, in 3 groups: all patients (n=112), RA patients (n=44) and patients with other diagnoses (n=68). Median levels of the 13 items were compared in the 3 groups; statistical significance of differences was analyzed using 2X2 Wilcoxon signed rank tests.
Results: Highest scores, >1 on a 0-3 scale, were seen for 3 of the 13 items: “walk 3 kilometers,” “participate in recreation and sports as you would like,” and “poor sleep.” Similar patterns were seen in all patients, and subgroups of RA and other patients. Scores for 3 of the 5 MDHAQ items not found on the HAQ were significantly higher than scores for the other 10 items in all patients and “other” patients, and than 9 of 10 other items in RA patients (p <0.001).
 Conclusion: The MDHAQ recognizes patient problems that are not captured by the HAQ, which may be of value in clinical management and to document improvement over time. The MDHAQ might be considered for usual clinical care as well as for clinical trials.
Conclusion: The MDHAQ recognizes patient problems that are not captured by the HAQ, which may be of value in clinical management and to document improvement over time. The MDHAQ might be considered for usual clinical care as well as for clinical trials.
Disclosure:
K. Gibson,
None;
S. H. Park,
None;
T. Pincus,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/scores-on-the-multidimensional-health-assessment-questionnaire-mdhaq-for-walk-2-miles-or-3-kilometers-poor-sleep-and-participate-in-recreation/
