Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2022
Title: Plenary III
Session Type: Plenary Session
Session Time: 11:30AM-1:00PM
Background/Purpose: IL-6 is elevated in patients with active PMR and is associated with disease activity, relapse and severity. Clinical trials with IL-6 receptor (IL-6R) inhibitors in PMR showed higher remission rates and reduced glucocorticoid (GC) use vs GC alone (Mori 2016; Akiyama 2020; Lally 2016, Devauchelle Pensec 2015).
The SAPHYR study (NCT03600818) assessed the efficacy and safety of sarilumab (SAR), a human anti IL-6Rα monoclonal antibody, with a 14 week (wk) GC taper in patients with steroid resistant active PMR who flared on ≥7.5 mg/day prednisone or equivalent.
Methods: Patients were randomized (1:1) to 52 wks of treatment with SAR 200 mg every 2 wks (Q2W) + 14 wk GC tapered regimen (SAR arm) OR placebo Q2W + 52 wk GC tapered regimen (comparator arm). The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving sustained remission at wk 52, defined as disease remission by wk 12, as well as absence of disease flare, CRP normalization and adherence to the per protocol GC taper from wks 12 to 52.
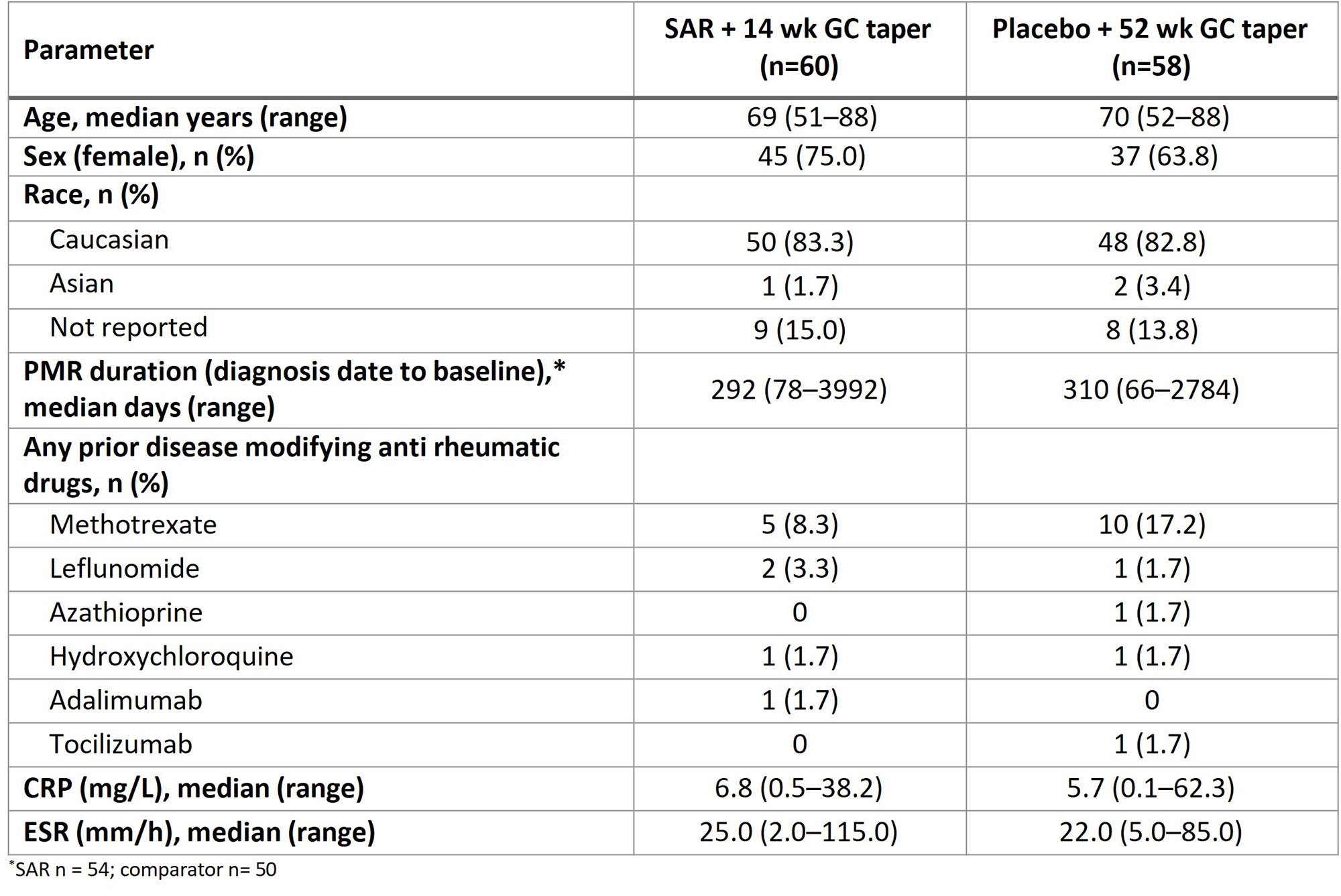
Results: The study was terminated early due to protracted recruitment timelines during the COVID-19 pandemic, resulting in 118 of the intended 280 patients recruited between Oct 2018 and Jul 2020, and 117 were treated (SAR n=59, comparator n=58). The demographics were balanced; patients were primarily female, Caucasian, and a median age of ~70 years (Table). Overall, 78 patients completed the treatment (SAR n=42; comparator n=36). Primary reasons for treatment discontinuation were adverse events (AEs; SAR n=7, comparator n=4) and lack of efficacy (SAR n=4, comparator n=9).
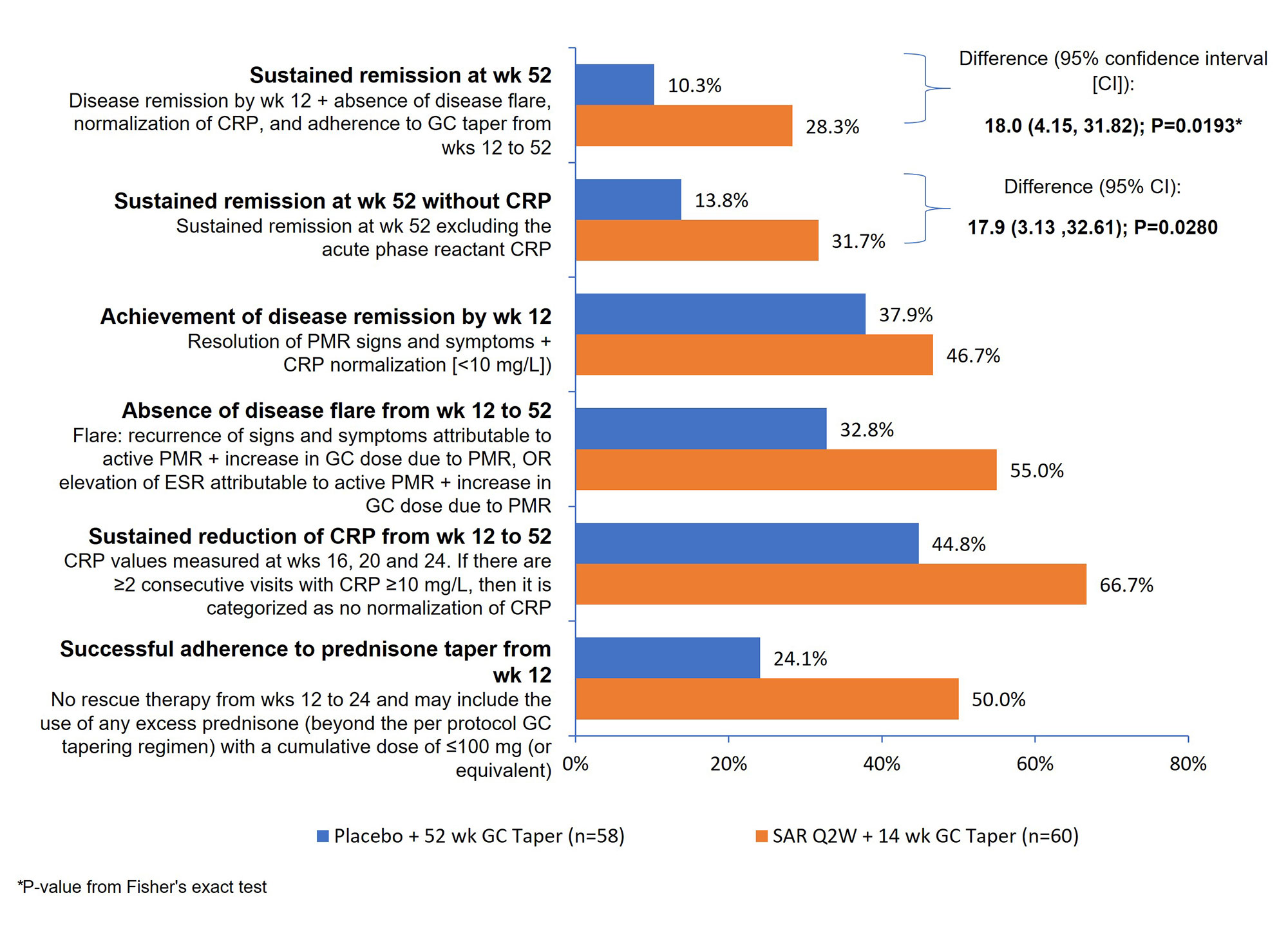
Sustained remission rate was significantly higher in the SAR arm vs the comparator arm (28.3% vs 10.3%; P=0.0193). Results of a sensitivity analysis excluding CRP from the sustained remission definition was consistent with the primary analysis (31.7% vs 13.8%; P=0.0280). All sustained remission components favored SAR (Figure).
Patients in the SAR arm were 44% less likely to have a flare after achieving clinical remission vs the comparator arm (16.7% vs 29.3%; HR 0.56; 95% CI 0.35–0.90; P=0.0153).
The comparator arm required more additional GCs vs the SAR arm, mainly due to PMR flare (median difference in actual and expected cumulative dose 199.5 mg vs 0.0 mg; P=0.0189). The cumulative GC toxicity index scores numerically favored SAR but the difference was not statistically significant. PMR activity scores improved in the SAR arm vs the comparator arm (least squares mean -15.57 vs -10.27, nominal P=0.0002). Patient reported outcomes (eg, physical and mental health component scores, disability index, etc) favored SAR.
Incidence of treatment-emergent AEs (TEAEs) was numerically higher in the SAR arm vs the comparator arm (94.9% vs 84.5%) and included neutropenia (15.3%) and arthralgia (15.3%) in the SAR arm, and insomnia (15.5%) in the comparator arm. Conversely, the frequency of serious AEs was higher in the comparator arm vs the SAR arm (20.7% vs 13.6%). No deaths were reported.
Conclusion: SAR + 14 wk GC taper demonstrated significant efficacy vs the comparator arm in steroid refractory PMR patients, including clinically meaningful improvement in quality of life. Safety was consistent with the known safety profile of SAR.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Spiera R, Unizony S, Warrington K, Sloane Lazar J, Giannelou A, Nivens M, Akinlade B, Wong W, Lin Y, Buttgereit F, Devauchelle V, Rubbert-Roth A, Dasgupta B. Sarilumab in Patients with Relapsing Polymyalgia Rheumatica: A Phase 3, Multicenter, Randomized, Double Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial (SAPHYR) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sarilumab-in-patients-with-relapsing-polymyalgia-rheumatica-a-phase-3-multicenter-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-trial-saphyr/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sarilumab-in-patients-with-relapsing-polymyalgia-rheumatica-a-phase-3-multicenter-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-trial-saphyr/