Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Anemia of chronic disease, a common extra-articular manifestation of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), which has a substantial impact on patient function, is driven in part by proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-6. Sarilumab, the first fully human monoclonal antibody directed against the alpha subunit of the IL-6 receptor (IL-6Rα), blocks receptor binding of IL-6. In the phase 2 MOBILITY Part A trial, sarilumab administered subcutaneously demonstrated significant and clinically relevant improvements in ACR20 at Week 12 relative to placebo in patients with active RA receiving methotrexate (MTX). The current analysis evaluated the effects of sarilumab on hemoglobin (Hb) levels.
Methods: MOBILITY Part A was a phase 2, 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of adults with active RA despite MTX. Patients continued MTX and were equally randomized to placebo or 1 of 5 sarilumab doses: 100 mg every other week (q2w); 150 mg q2w; 100 mg weekly (qw); 200 mg q2w; or 150 mg qw. Blood samples collected at baseline and every 2 weeks during treatment were analyzed for Hb levels (ANCOVA model comparing Hb change over 12 weeks for each sarilumab group vs. placebo) and high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), an inflammatory marker.
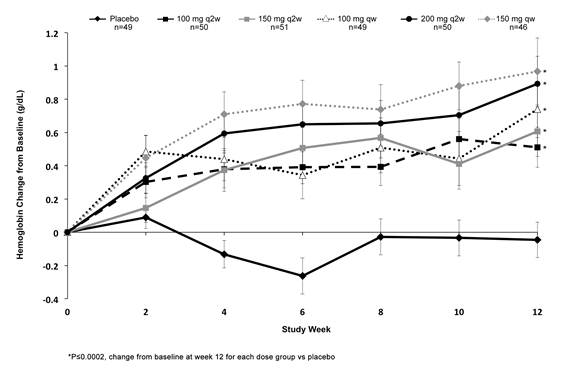
Results: 306 patients were randomized. Baseline characteristics were similar across all groups: mean age 52.2±12.3 years; 79% female; mean disease duration 7.8±8.1 years; RF+ 79.7%; mean hs-CRP 2.8±3.0 mg/dL. Week 0 Hb data were available for 295 patients: mean baseline Hb 12.6±1.6 mg/dL; 25.4% of patients had low Hb, defined as ≤12.5 mg/dL. Increase in Hb levels was observed as early as Week 2 in all sarilumab groups, with significant increases vs. placebo (P£0.0002) at Week 12 (Figure). The effect was greatest with the 150 mg qw dose, followed by 200 mg q2w. All placebo patients who had low baseline Hb (n=17) still had low Hb at Week 12; 65.5% of the sarilumab patients low at baseline (n=58) had normalized Hb (n=38) at Week 12. Mean hs-CRP levels were £0.8 mg/dL by Week 12 in all treatment groups except placebo (2.6 mg/dL) and sarilumab 100 mg q2w (1.8 mg/dL); reductions in hs-CRP at Week 12 were also significant relative to placebo (P<0.0001), except for 100 mg q2w (P=0.0661). The most common treatment emergent adverse events (AEs) reported in the sarilumab arms were infections (non-serious) 12-26%, neutropenia 0-20%, and ALT increase 0-6%. Eight patients (3 receiving sarilumab 100 mg q2w, 3 receiving 100 mg qw, and 2 receiving placebo) experienced at least 1 treatment emergent serious AE (SAE); of these, 6 led to permanent treatment discontinuation, including 1 death in the sarilumab 100 mg q2w group (acute respiratory distress syndrome, cerebrovascular accident). There were no infection-related SAEs in patients with grade 3 or 4 neutropenia.
Conclusion: Sarilumab treatment for RA over 12 weeks resulted in significant improvements in hemoglobin relative to placebo.
Disclosure:
M. C. Genovese,
Eli Lilly and Company,
2,
Eli Lilly and Company,
5,
Sanofi-Aventis Pharmaceutical,
2,
Sanofi-Aventis Pharmaceutical,
5;
R. Fleischmann,
Pfizer Inc., Roche, Abbott, Amgen, UCB, Genentech, BMS, Lilly, Sanofi, Lexicon, MSD, Novartis, BiogenIdec, Astellas, Astra-Zeneca, Jansen,
2,
Roche, Abbott, Amgen, UCB, Pfizer, BMS, Lilly, Sanofi, Lexicon, Novartis, Astellas, Astra-Zeneca, Jansen, HGS,
5;
M. Jasson,
Sanofi-Aventis Pharmaceutical,
1,
Sanofi-Aventis Pharmaceutical,
3;
A. R. Radin,
Regeneron,
1,
Regeneron,
3;
J. Hamilton,
Regeneron,
1,
Regeneron,
3;
T. W. J. Huizinga,
Merck, UCB, Bristol Myers Squibb, Biotest AG, Pfizer, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi, Abbott, Crescendo Bioscience, Nycomed, Axis-Shield,
5.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sarilumab-a-subcutaneously-administered-fully-human-monoclonal-antibody-inhibitor-of-the-il-6-receptor-effects-on-hemoglobin-levels-in-a-clinical-trial-for-the-treatment-of-moderate-to-severe-rheum/