Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Sarcopenia is a generalized skeletal muscle disorder characterized by the loss of muscle strength and muscle mass, leading to functional limitation, worse quality of life and increased mortality. Although frequently attributable to ageing, sarcopenia due to inflammatory processes has been recognized. However, data on sarcopenia in axial Spondylarthritis (axSpA) are scarce. Our purpose is to determine the prevalence of sarcopenia in young patients with axSpA; in addition, to assess the muscle strength and body composition of different body segments.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted on 54 participants aged 18 to 50 years, 27 patients with axSpA (according to ASAS classification criteria, with symptoms duration ≤ 10 years), and 27 healthy controls (HC), matched by gender and age (1:1).
Sarcopenia was defined as per the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People 2 (EWGSOP2).
Muscle strength of three different body segments (trunk, upper and lower limbs, on both sides) was measured by resisted hand-held dynamometer performed by a single reader and through five times sit-to-stand test. The criteria for low muscle strength was chair stand test >15 seconds for five rises.
Body composition was measured by octapolar multifrequency bioelectrical impedance analysis (InBody770). Low skeletal muscle mass was defined according to the equipment’s inbuilt and personalized reference values.
Physical activity was assessed by the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ). Appropriate statistical tests were used to compare differences between groups.
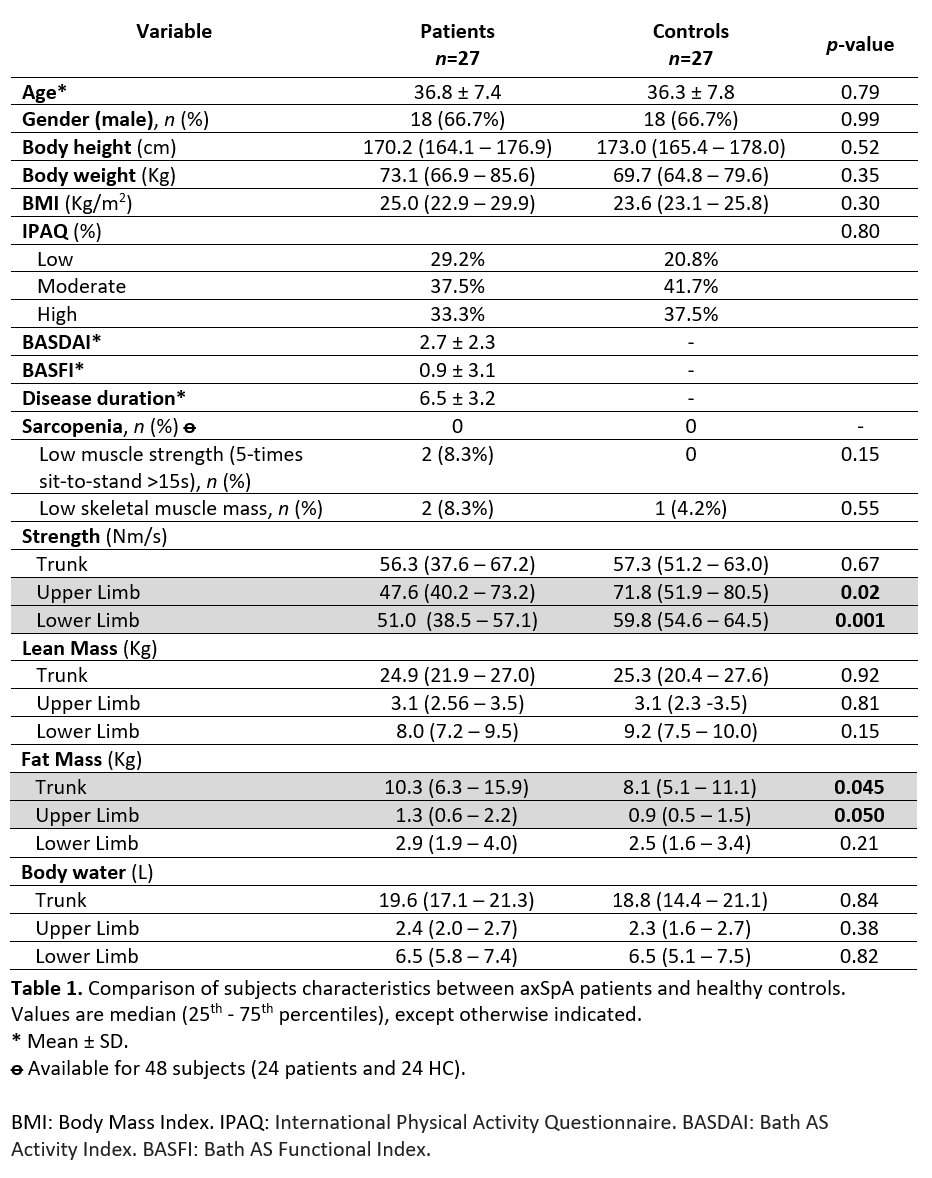
Results: A total of 27 axSpA patients and 27 HC were included. Mean age was 36.5 ± 7.5 years, 67% were males. There was no significant difference between both groups in terms of age, gender, body mass index and physical activity. AxSpA patients had a mean symptoms duration of 6.5 ± 3.2 years, BASDAI 2.7±2.3 and BASFI 0.9±3.1.
There were no participants (patients or controls) fulfilling the definition of sarcopenia. Low muscle strength, measured by the chair rise test, was found in 8.3% of patients vs 0% of HC (p=0.15). Skeletal muscle mass was reduced in 8.3% of patients vs 4.2% of HC (p=0.55).
Regarding the different body segments, axSpA patients had median lower muscle strength in the upper limbs (47.60 vs 71.75, p=0.023) and lower limbs (51.0 vs 59.83, p=0.001), compared to HC. Trunk muscle strength did not show any difference between groups (56.3 vs 57.30, p=0.67).
There were no significant differences in lean mass and body water, between both groups, for each segment (upper limbs, lower limbs and trunk). Fat mass was marginally higher in the trunk (10.3 vs 8.1, p=0.045) and upper limbs (1.3 vs 0.89, p=0.05) of axSpA patients, but not in the lower limbs (2.9 vs 2.5, p=0.21) – Table 1.
Conclusion: In our cohort, young patients with axSpA with short disease duration did not show higher prevalence of sarcopenia according to EWGSOP2 definition. However, a reduced appendicular muscle strength was found compared with HC, with no differences in lean mass, suggesting a possible muscle dysfunction. New criteria for sarcopenia in young populations are needed and further studies should be conducted to confirm these findings.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Neto A, Pinheiro Torres R, Domingues L, Teixeira D, Rodrigues-Manica S, Marona J, Lopes C, Lagoas Gomes J, Costa T, Gonçalves M, Silva I, Araújo P, Mateus M, Castelão W, Costa M, Falcão S, Mourão A, Sardoo A, Maia S, Sepriano A, Ramiro S, Calhau C, Branco J, Pimentel-Santos F. Sarcopenia, Segmental Muscle Strength and Body Composition in Young Axial Spondylarthritis Patients: Results from MyoSpA Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sarcopenia-segmental-muscle-strength-and-body-composition-in-young-axial-spondylarthritis-patients-results-from-myospa-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sarcopenia-segmental-muscle-strength-and-body-composition-in-young-axial-spondylarthritis-patients-results-from-myospa-study/