Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Baricitinib (bari), an oral, selective inhibitor of Janus kinase (JAK) 1 and JAK 2, is approved in the EU for the treatment of moderately to severely active RA in adults. We further describe the drug’s safety profile with updated data from an on-going long-term extension (LTE) study.
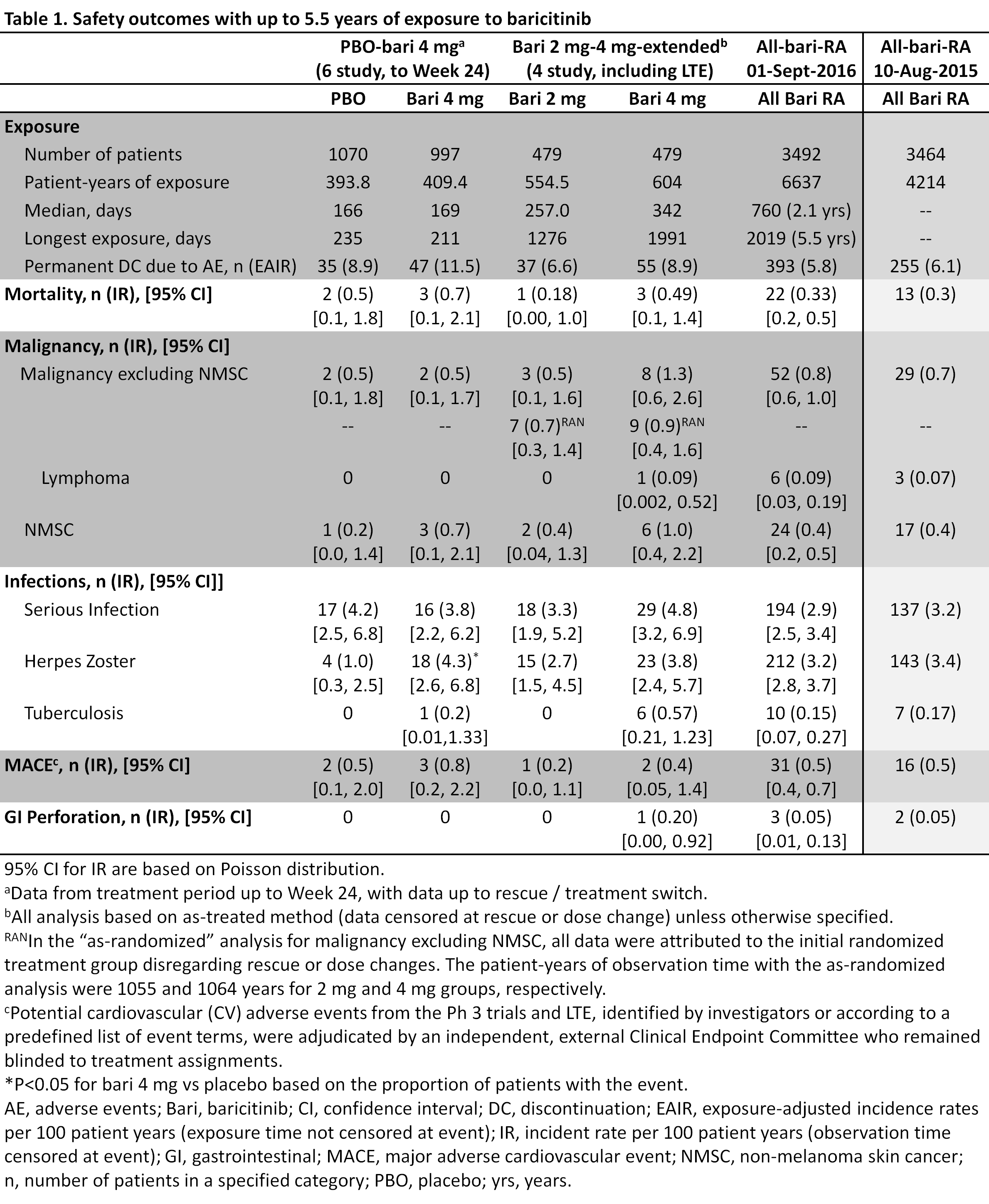
Methods: Long-term safety of once-daily bari was evaluated in the “all-bari-RA” dataset, which includes all patients (pts) with active RA exposed to any bari dose from 8 randomized trials (4 Ph3, 3 Ph2, 1 Ph1b) and 1 LTE study (data up to 01-Sept-2016). Previous all-bari-RA analyses1 are provided for comparison (data up to 10-Aug-2015). Placebo (PBO) comparisons were evaluated for up to Wk 24 in the “PBO-4mg” dataset from the 6 Ph2/3 trials in which pts were randomized to bari 4mg, with censoring at rescue or treatment switch. Dose responses were evaluated based on the 4 Ph2/3 trials in which pts were randomized to 2 or 4mg and includes data from the LTE (the “2mg-4mg-extended” dataset). Data were censored at rescue or dose change (as-treated analysis). Because of the latent period for malignancy, 2mg-4mg-extended was also analyzed without censoring for rescue or dose change (as-randomized analysis). Incidence rates (IR) per 100 patient-years (PY) were calculated.
Results: In the current analysis, 3492 pts received bari for 6637 total PY of exposure (an increase of over 2400 PY from previous analysis); maximum exposure was 5.5 yrs (Table 1). No differences were seen for bari 4mg vs PBO in adverse events (AEs) leading to permanent study drug discontinuation, death, malignancy, serious infection, or major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE) (Table 1). Herpes zoster IR was significantly higher for bari 4mg vs PBO (IR 1.0 vs 4.3; PBO, 4mg, respectively). In 2mg-4mg-extended, no significant differences were observed comparing bari 2mg vs 4mg for the above mentioned events. Malignancy (excluding non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC)) IR were 0.5 and 1.3 for 2mg and 4mg, respectively, with as-treated analysis and 0.7 and 0.9 with as-randomized analysis. For the above events, the current IRs in all-bari-RA are similar to those previously reported (Table 1). The following IRs were observed in the current all-bari-RA: lymphoma (0.09), gastrointestinal (GI) perforation (0.05), and tuberculosis (TB) (0.15, all in endemic areas). The IRs for these events are also similar to those previously reported (Table 1). Fewer than 1% of pts discontinued due to abnormal lab results.
Conclusion: In this updated integrated analysis of patients with moderately to severely active RA, including patients exposed for up to 5.5 years, baricitinib maintained a safety profile that was similar to that previously reported1 and acceptable in the context of demonstrated efficacy.2,3
References:
1Smolen JS et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2016:75(Suppl 2):243-4.
2Taylor PC et al. NEJM 2017:376:652-62.
3Genovese Mc et al. NEJM 2016:374:1243-52.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Genovese MC, Smolen JS, Takeuchi T, Hyslop D, Macias WL, Rooney TP, Chen L, Dickson CL, Riddle Camp J, Cardillo T, Ishii T, Winthrop K. Safety Profile of Baricitinib for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis up to 5.5 Years: An Updated Integrated Safety Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-profile-of-baricitinib-for-the-treatment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-up-to-5-5-years-an-updated-integrated-safety-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-profile-of-baricitinib-for-the-treatment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-up-to-5-5-years-an-updated-integrated-safety-analysis/