Background/Purpose:
Retrospective studies have demonstrated that patients of advanced age with systemic vasculitis experience a higher mortality and adverse events than their younger counterparts. However, no study has prospectively examined the safety of remission induction treatment of Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (GPA) or Microscopic Polyangiitis (MPA) in patients of advanced age. We analyzed the results of the Rituximab in ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) (RAVE) trial in order to evaluate adverse events (AEs) and mortality in patients ≥ 65 years old.
Methods:
Randomized controlled trial comparing rituximab (RTX, n=99) to cyclophosphamide (CYC) followed by azathioprine (AZA, n=98) for remission induction in patients with GPA or MPA. Glucocorticoids were tapered over 5 months. Subjects were followed for 18 months.
Results:
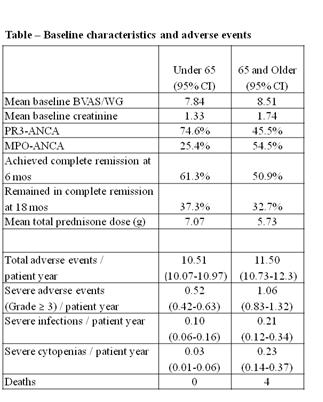
55 patients were ≥ 65 years old (36 RTX, 19 CYC/AZA) and 142 patients were < 65 years old (63 RTX, 79 CYC/AZA). Baseline characteristics of both groups are reported in the table. Treatment regimens achieved similar efficacy in both age groups.
While total adverse events were similar between both age groups, patients ≥ 65 had more severe AEs (Grade ≥ 3) than those < 65 (Table). Severe cytopenias occurred more frequently in older patients. All four deaths during the study period occurred in patients ≥ 65 (2 RTX, 2 CYC/AZA).
Comparing the two treatment arms among patients 65 and older, frequencies of total AEs or severe AEs were similar between the RTX and CYC/AZA groups (11.52/patient year RTX vs 11.44/patient year CYC/AZA; 1.15/patient year (95% CI 0.87-1.50) RTX vs 0.85/patient year (0.52-1.31) CYC/AZA, respectively). Similarly, the frequency of severe cytopenias and severe infections were comparable between the two groups (0.24 (95% CI 0.13-0.42)/patient year RTX vs 0.21 (95% CI 0.07-0.49)/patient year CYC/AZA; 0.22 (95% CI 0.11-0.40)/patient year RTX vs 0.17 (95% CI 0.05-0.43)/patient year CYC/AZA), respectively.
Conclusion:
Patients ≥ 65 undergoing remission induction treatment for GPA or MPA may experience more severe adverse events than their younger counterparts, including more frequent severe cytopenias. Both RTX and CYC/AZA-based regimens have a similar adverse event profile in patients ≥ 65 years old.
Disclosure:
E. Miloslavsky,
Genentech Inc,
9;
U. Specks,
None;
P. A. Merkel,
None;
P. Seo,
None;
R. F. Spiera,
Roche Pharmaceuticals, g,
2;
C. A. Langford,
Bristol-Myers Squibb,
9,
Genentech and Biogen IDEC Inc.,
9;
G. S. Hoffman,
None;
C. G. M. Kallenberg,
Roche,
8;
E. W. St. Clair,
Biogen Idec,
9,
Up-to-Date,
7;
N. Tchao,
None;
L. Ding,
None;
D. Ikle,
Rho,
3;
B. Jepson,
Rho,
3;
P. Brunetta,
Genentech Inc,
3;
J. H. Stone,
Genentech and Biogen IDEC Inc.,
2,
Genentech and Biogen IDEC Inc.,
5,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
2.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-of-remission-induction-with-rituximab-versus-cyclosphosphamide-in-patients-65-and-older-with-severe-anca-associated-vasculitis/