Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Guselkumab (GUS) is a fully human monoclonal antibody that selectively binds to the p19 subunit of interleukin-23, inhibiting its function. GUS has been shown to have a favorable safety profile across Phase 2 and 3 studies conducted in adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis (PsO) and with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA). In this integrated analysis, safety data from 11 Phase 2/3 studies of GUS, including 7 in PsO (X-PLORE, VOYAGE 1, VOYAGE 2, NAVIGATE, ORION, ECLIPSE, Japanese registration) and 4 in PsA (Phase 2, DISCOVER-1, DISCOVER-2, COSMOS), were pooled to comprehensively evaluate the safety experience with GUS in a large population of patients with psoriatic disease.
Methods: GUS was generally administered as 100 mg subcutaneous injections at Week (W) 0, W4, then every 8 weeks (Q8W) in PsO studies (additional doses included in X-PLORE; see Tables‡) and at W0, W4, then Q4W or Q8W in PsA studies. Patients randomized to placebo (PBO) crossed over to GUS Q8W at W16 in 5 PsO studies (X-PLORE, VOYAGE 1, VOYAGE 2, ORION, Japan registration) and to GUS Q4W or Q8W at W24 in PsA studies. Safety data were summarized for the PBO-controlled period (W0-W16 in PsO; W0-W24 in PsA) and through the end of the reporting period (up to 5 years in PsO; up to 2 years in PsA). Incidence rates of key safety events were integrated post hoc, adjusted for duration of follow-up, and reported per 100 patient-years (PY).
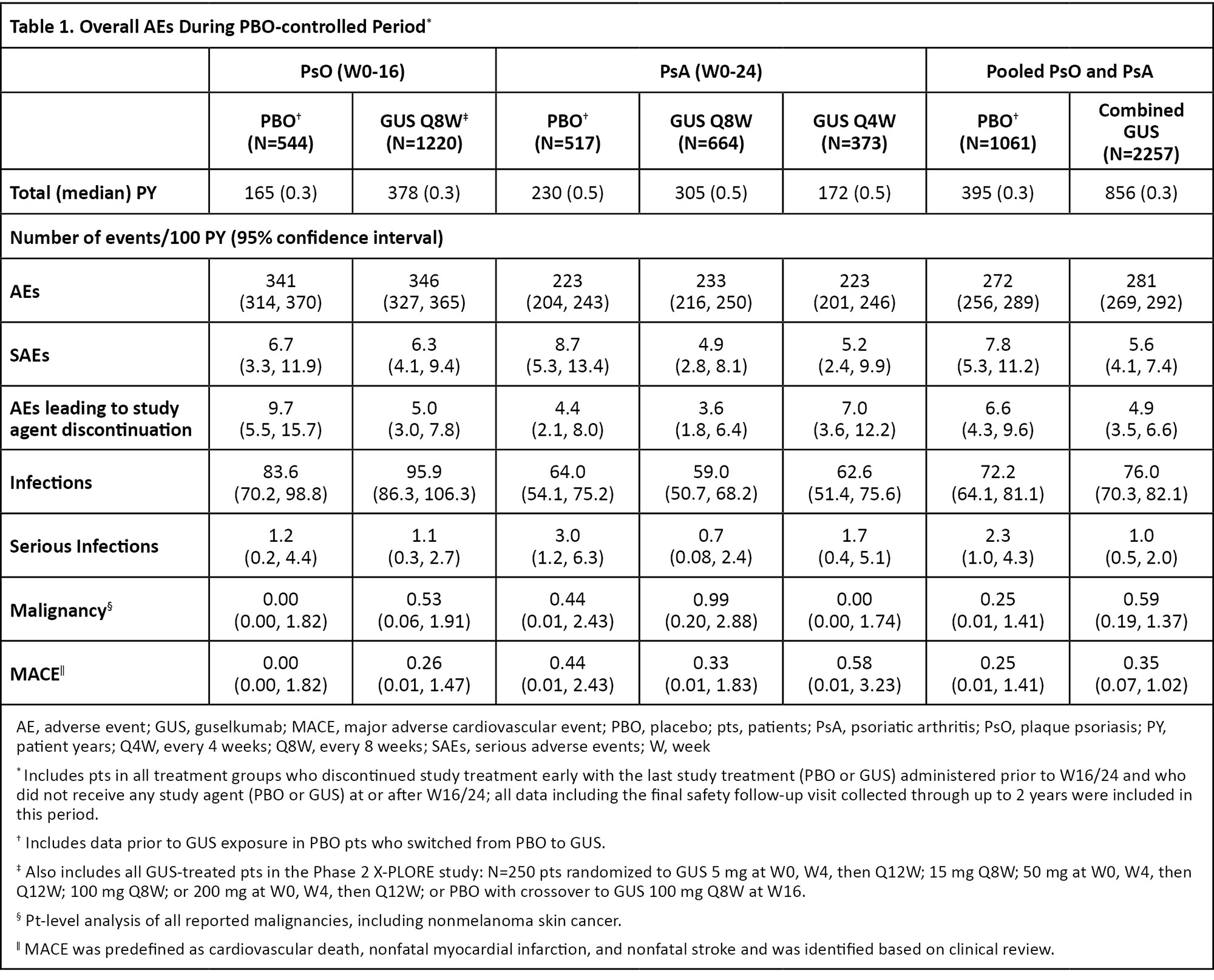
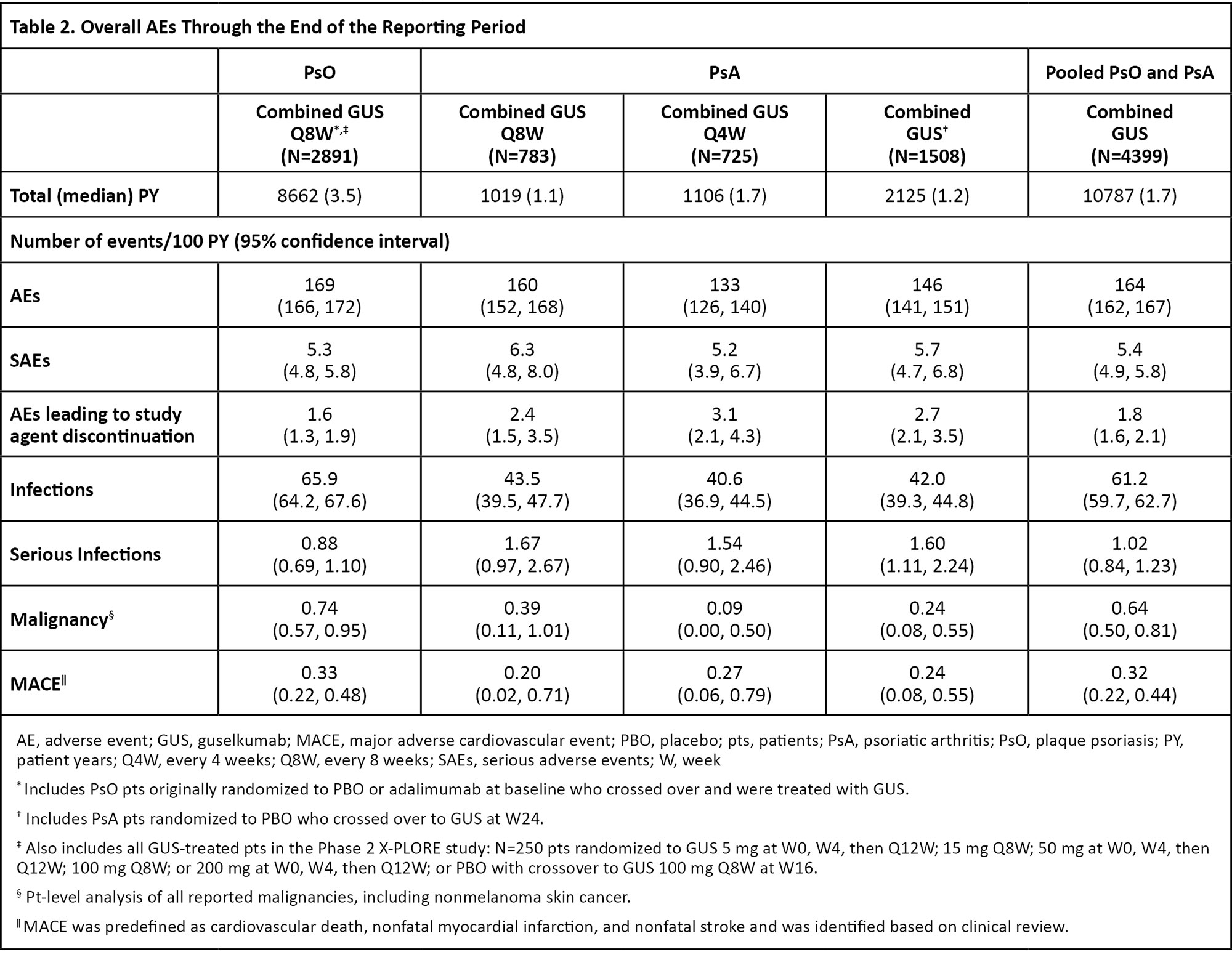
Results: During the PBO-controlled periods, 1061 patients received PBO (395 PY) and 2257 received GUS (856 PY). Through the end of the reporting periods, 4399 GUS-treated patients (PsO: 2891; PsA: 1508) contributed 10787 PY of follow-up (PsO: 8662 PY; PsA: 2125 PY). In PsO and PsA studies, pooled incidence rates of overall adverse events (AEs) were similar between GUS- and PBO-treated patients (Table 1). Rates of serious AEs (SAEs), AEs leading to study agent discontinuation, serious infections, malignancy, and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) were low and generally similar between GUS- and PBO-treated patients (Table 1). The rates of safety events evaluated remained consistent through the end of the reporting period for GUS-treated patients (Table 2). No cases of Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis were reported in GUS-treated patients. No serum sickness-like or anaphylactic reactions related to GUS were reported. No opportunistic infections were reported in any GUS-treated PsO patients. Three cases of opportunistic infection were reported in pooled PsA studies (0.14/100 PY; all post-W52 in DISCOVER-2). No cases of active tuberculosis were reported across all studies.
Conclusion: In the most comprehensive analysis of GUS safety to date, evaluating ~4400 patients with psoriatic disease followed for up to 5 years of treatment (10787 PY of exposure), GUS demonstrated a favorable and consistent safety profile compared with previous reports. Safety event rates in GUS-treated patients were similar to those observed with PBO and remained stable throughout the long-term follow-up.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Strober B, Coates L, Yu J, Rowland K, Leibowitz E, Miller M, Kollmeier A, Li S, Wang Y, Chan D, Chakravarty S, Yang Y, Shawi M, Lebwohl M, Rahman P. Safety of Guselkumab in Patients with Psoriatic Disease: An Integrated Analysis of 11 Phase 2/3 Clinical Studies in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-of-guselkumab-in-patients-with-psoriatic-disease-an-integrated-analysis-of-11-phase-2-3-clinical-studies-in-psoriasis-and-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-of-guselkumab-in-patients-with-psoriatic-disease-an-integrated-analysis-of-11-phase-2-3-clinical-studies-in-psoriasis-and-psoriatic-arthritis/