Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The Canadian government’s COVID Immunity Task Force funded SUCCEED to study COVID vaccination responses in immune-mediated inflammatory disease(IMID). We describe how drugs, clinical factors, and vaccine history influence serological response to vaccination, summarize safety, and describe breakthrough infections.
Methods: From Vancouver, Calgary, Winnipeg, Montreal, Quebec City, Sherbrooke, Toronto, and Hamilton, data and dried blood spots/sera post-COVID vaccination were collected from adults with rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, SLE, ankylosing spondylitis/spondyloarthritis and psoriasis/psoriatic arthritis, with the first sample at enrolment and then 3, 6, and 12 months after latest vaccine dose. We evaluated anti-spike(S) trimer and anti-receptor-binding domain(RBD) IgG (indicating successful serologic response to vaccine) and anti-nucleocapsid (N) IgG (indicating recent infection, cross-referenced with self-report). Multivariate generalized estimating equation regressions (accounting for repeated measures) were used to evaluate serologic response, based on log-transformed anti-RBD titres.
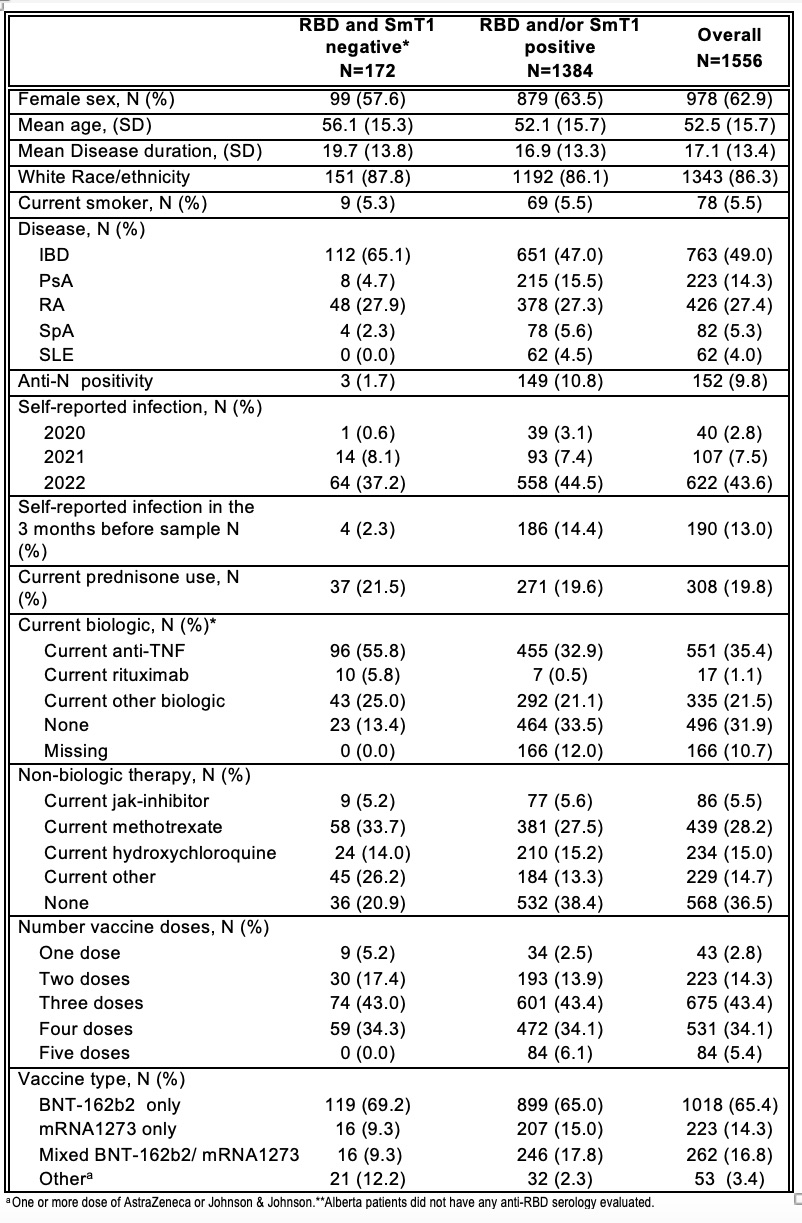
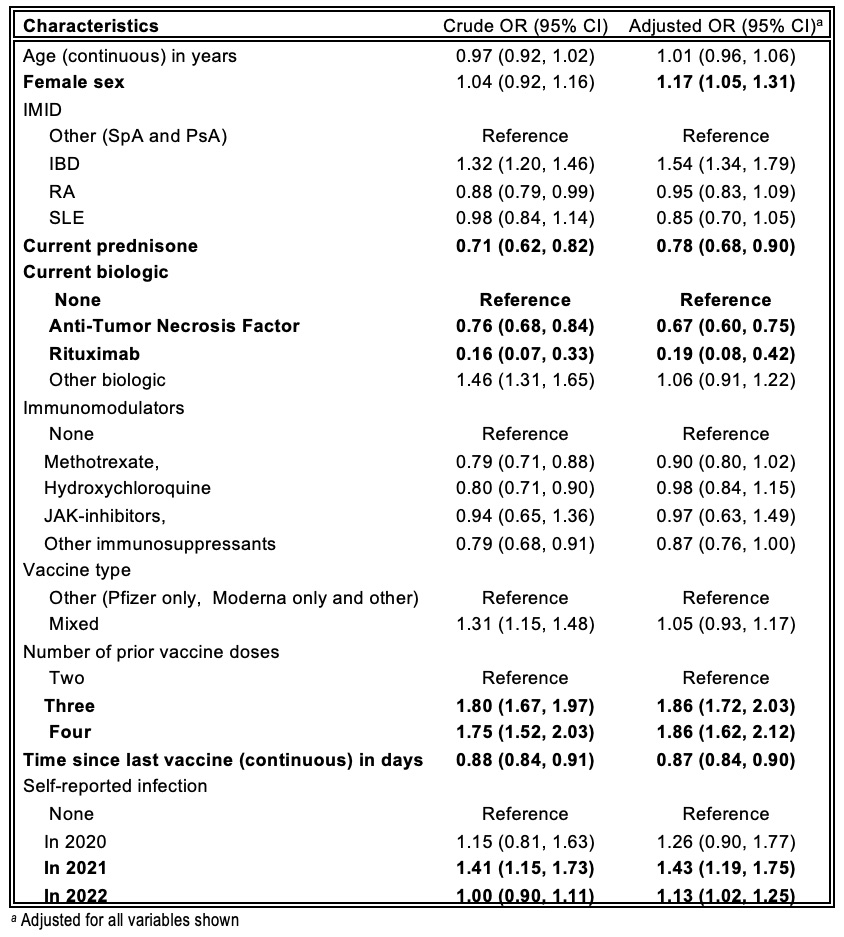
Results: Baseline characteristics of 1556 participants are shown in Table 1. Table 2 shows crude and adjusted odds ratios(OR). Positive associations for anti-RBD/anti-S serologic responses were seenwithfemale sex, number of vaccine doses and infections in 2021-2022. Negative associations were seen with prednisone, anti-TNF agents and rituximab. Diminution of response was clearly seen even for daily prednisone doses of 1-10 mg (adjusted OR 0.73 95%CI 0.58-0.91) and 11-20 mg (aOR 0.62 95%CI 0.43-0.90). Methotrexate and other immunosuppressants were associated with reduced response only in univariate analyses. Time since last vaccination was negatively associated with serologic response; rate of decrease was similar during the period 15-120 days since last vaccine (OR 0.75 95%CI 0.64,0.87) and 121-210 days post-last vaccine (OR 0.79 95%CI 0.67,0.92) but worse after >210 days (OR 0.53 95%CI 0.43,0.66).
Self-reported post-vaccine adverse events leading to emergency department(ED) visits or hospitalizations occurred in only 1.5% of participants. Bell’s Palsy represented one ED visit, with no confirmed Guillain-Barre or transverse myelitis in our preliminary analyses. Over 2021-2022, anti-N positivity (indicating recent infection) was present in 9.8% of samples; most (85%) were associated with a self-reported infection. Anti-N positivity was lowest in the summer of 2021 and highest post-Omicron (fall 2022).
Conclusion: Past infections and number of COVID-19 vaccine doses were positively associated with serologic response. Time since vaccination, particularly >210 days, was negatively associated with response. Anti-TNF agents, rituximab, and prednisone were associated with less immunogenicity. Few vaccine-related adverse events led to ED or hospitalization. Ours is the first assessment of drugs, vaccine history, and other factors on serologic COVID vaccine response in a large, pan-Canadian IMID sample. These findings may help patients, clinicians, and other stakeholders make personalized decisions about vaccination in 2023-2024 and beyond.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tsyruk O, Chandran V, Hitchon C, Avina-Zubieta J, Colmegna I, Fortin P, Larche M, Boire G, Lukusa L, Bowish D, Kaplan G, Pereira D, Dayam R, Lee J, Turnbull E, Valerio V, Proulx L, Gunderson J, Gingras A, Bernatsky S. Safety & ImmUnogenicity of COVID-19 VaCcines in SystEmic immunE Mediated Inflammatory Diseases (SUCCEED) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-immunogenicity-of-covid-19-vaccines-in-systemic-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases-succeed/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-immunogenicity-of-covid-19-vaccines-in-systemic-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases-succeed/